
The peroxide effect involves:
(A) Ionic mechanism
(B) Free radical mechanism
(C) Heterocyclic fission of double bond
(D) Homolytic fission of double bond
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Peroxide effect is also called as Anti-Markovnikov’s rule.
Markovnikov’s rule: In this reaction, there is an involvement of Hydro halides to unsaturated compounds. The hydrogen from hydro halides is going to attach to carbon where high numbers of hydrogens are present. In Anti- Markovnikov's rule: The hydrogen from hydro halides is going to attach to carbon where fewer numbers of hydrogens are present.
Complete step by step solution:
-In Markovnikov’s rule the addition of hydro halide is through an ionic mechanism. Means there is an involvement of cations and anions in the reaction.
-Coming to Anti-Markovnikov's rule or peroxide effect the addition of hydro halides is not through the ionic mechanism. It is through a mechanism where free radicals are going to involve.
-The representation of the peroxide effect or Anti-Markovnikov’s rule is as follows.
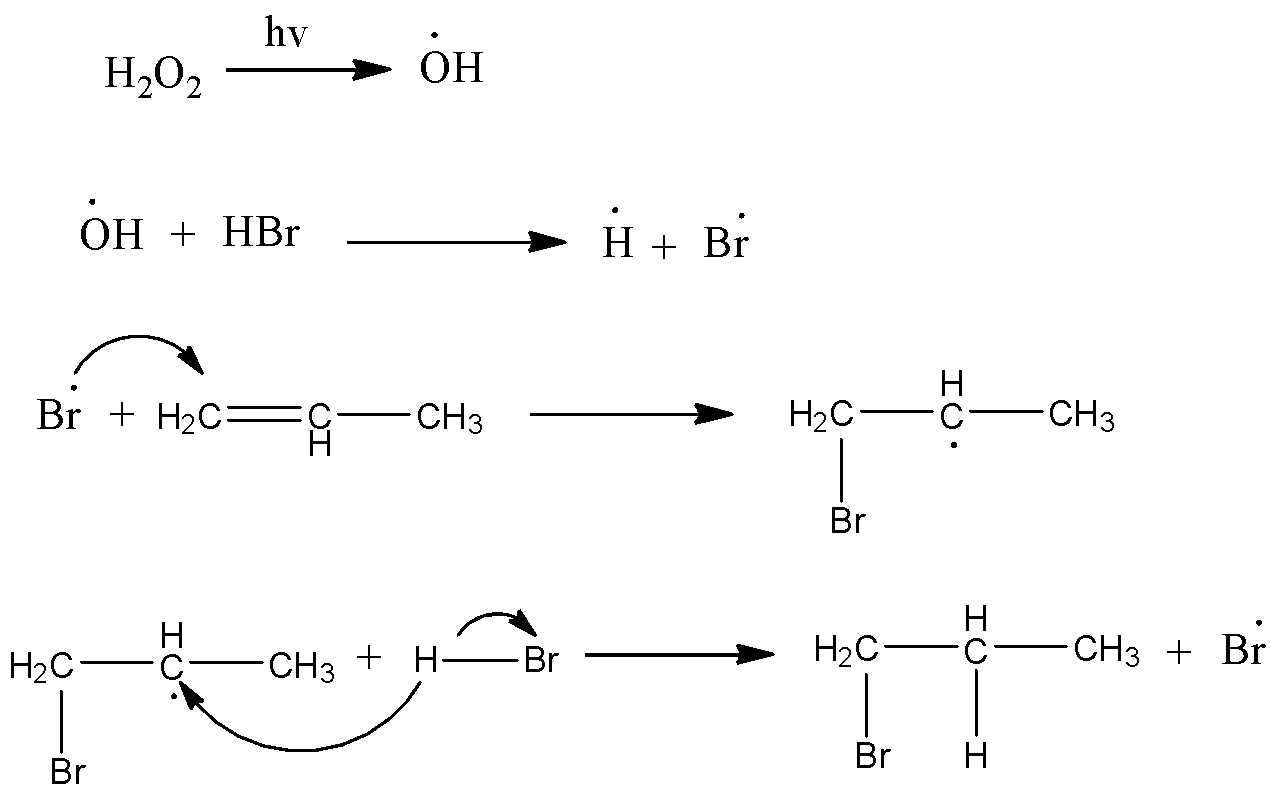
-Because of the initiation of the reaction through free radicals the addition of hydro halides to the position is going to change in alkenes.
- That is why the above reaction is called Anti-Markovnikov's rule or peroxide effect.
-Therefore a free radical mechanism is involved in the peroxide effect.
So, the correct option is B.
Note: The original mechanism of the Markovniov’s rule is going to change because of the presence of the peroxide chemical at the initial stage of the reaction of hydro halides with alkenes. That is why the reaction is called peroxide effect.
Markovnikov’s rule: In this reaction, there is an involvement of Hydro halides to unsaturated compounds. The hydrogen from hydro halides is going to attach to carbon where high numbers of hydrogens are present. In Anti- Markovnikov's rule: The hydrogen from hydro halides is going to attach to carbon where fewer numbers of hydrogens are present.
Complete step by step solution:
-In Markovnikov’s rule the addition of hydro halide is through an ionic mechanism. Means there is an involvement of cations and anions in the reaction.
-Coming to Anti-Markovnikov's rule or peroxide effect the addition of hydro halides is not through the ionic mechanism. It is through a mechanism where free radicals are going to involve.
-The representation of the peroxide effect or Anti-Markovnikov’s rule is as follows.

-Because of the initiation of the reaction through free radicals the addition of hydro halides to the position is going to change in alkenes.
- That is why the above reaction is called Anti-Markovnikov's rule or peroxide effect.
-Therefore a free radical mechanism is involved in the peroxide effect.
So, the correct option is B.
Note: The original mechanism of the Markovniov’s rule is going to change because of the presence of the peroxide chemical at the initial stage of the reaction of hydro halides with alkenes. That is why the reaction is called peroxide effect.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




