
The number of stereoisomers obtained by bromination of trans$ - 2 - $butene is:
(A) $1$
(B) $2$
(C) $3$
(D) $4$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and also the same sequence of bonded atoms but a different three-dimensional orientation of their atoms in space is usually known as stereoisomerism. There are basically two types of stereoisomers i.e. geometrical isomers and optical isomers.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The addition of a halogen on alkenes is mainly anti-addition. The anti-addition of bromine on trans alkene gives us a meso compound as given below:
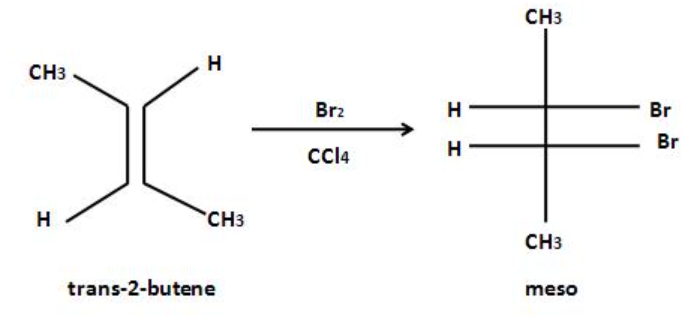
To calculate the number of stereoisomers of any compound, we have to first find the number of chiral carbon atoms in the given chemical compound. Then we can calculate the number of stereoisomers that the given chemical compound can show. Stereoisomers are those chemical compounds that have at least one chiral carbon atom, and also have a different arrangement of atoms having the same chemical formula.
The chiral carbon atoms can be defined as those carbon atoms in which all the substituents are not the same. These carbon atoms are usually represented with the star at the top. Only the carbon atoms consisting of a single bond can be a chiral carbon atom. One stereoisomer is obtained by the bromination of trans$ - 2 - $butane.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer.
Note: ${2^n}$ is generally used to find the number of stereoisomers where $n$ is the number of chiral carbon atoms in the given chemical compound. Let’s say that a given chemical compound has one chiral carbon atom. Then we will have the value of $n$ as $1$. By putting this value in ${2^n}$. we get $2$. So, the compound will have $2$stereoisomers.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The addition of a halogen on alkenes is mainly anti-addition. The anti-addition of bromine on trans alkene gives us a meso compound as given below:

To calculate the number of stereoisomers of any compound, we have to first find the number of chiral carbon atoms in the given chemical compound. Then we can calculate the number of stereoisomers that the given chemical compound can show. Stereoisomers are those chemical compounds that have at least one chiral carbon atom, and also have a different arrangement of atoms having the same chemical formula.
The chiral carbon atoms can be defined as those carbon atoms in which all the substituents are not the same. These carbon atoms are usually represented with the star at the top. Only the carbon atoms consisting of a single bond can be a chiral carbon atom. One stereoisomer is obtained by the bromination of trans$ - 2 - $butane.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer.
Note: ${2^n}$ is generally used to find the number of stereoisomers where $n$ is the number of chiral carbon atoms in the given chemical compound. Let’s say that a given chemical compound has one chiral carbon atom. Then we will have the value of $n$ as $1$. By putting this value in ${2^n}$. we get $2$. So, the compound will have $2$stereoisomers.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




