
The number of moles of KI required to produce 0.1 moles of \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\]is?
A. 1.6
B. 0.8
C. 3.2
D. 0.4
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: -To produce \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\]from KI we need a chemical. The required chemical is \[HgC{{l}_{2}}\] (mercuric chloride).
-The name of the KI is potassium Iodide.
-The name of the\[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\]is potassium mercuric iodide.
-The colour of the potassium mercuric iodide is yellow.
Complete step by step solution:
-The formation of \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\] from KI is a two-step process.
Step-1: Potassium iodide reacts with \[HgC{{l}_{2}}\] (Mercuric chloride) and forms \[Hg{{I}_{2}}\] (Mercuric Iodide).
\[2KI+HgC{{l}_{2}}\to Hg{{I}_{2}}+2KCl\]
Step-2: The formed \[Hg{{I}_{2}}\] (Mercuric Iodide) reacts with excess amount of KI and forms potassium mercuric iodide (\[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\]).
\[Hg{{I}_{2}}+2KI\to \underset{\text{potassium mercuric iodide}}{\mathop{{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]}}\,\]
-The overall reaction can be written as follows.
\[4KI+HgC{{l}_{2}}\to {{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]+2KCl\]
-From the above equation we can say that four moles of potassium iodide reacts with Mercuric iodide and forms one mole of\[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\](potassium mercuric iodide).
1 moles of \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\] requires 4 moles of KI
0.1 moles of \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\] requires = 0.1 (4) = 0.4 moles of KI.
-Therefore to produce 0.1 moles of \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\], there is a requirement of 0.4 moles of KI.
So, the correct option is D.
Additional information:
- Potassium mercuric iodide is a yellow colour solid and it is odourless.
-Potassium mercuric iodide is a salt and it is used as Nessler's reagent.
- Potassium mercuric iodide is soluble in water.
-The colour of the alkaline Potassium mercuric iodide is pale orange.
Note: Potassium mercuric iodide is used widely to determine the number of ammonium compounds. The structure of Potassium mercuric iodide is as follows.
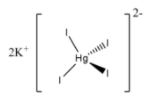
0.09mol/L Potassium mercuric iodide in 0.25mol/L potassium hydroxide is called Nessler’s reagent.
-The name of the KI is potassium Iodide.
-The name of the\[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\]is potassium mercuric iodide.
-The colour of the potassium mercuric iodide is yellow.
Complete step by step solution:
-The formation of \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\] from KI is a two-step process.
Step-1: Potassium iodide reacts with \[HgC{{l}_{2}}\] (Mercuric chloride) and forms \[Hg{{I}_{2}}\] (Mercuric Iodide).
\[2KI+HgC{{l}_{2}}\to Hg{{I}_{2}}+2KCl\]
Step-2: The formed \[Hg{{I}_{2}}\] (Mercuric Iodide) reacts with excess amount of KI and forms potassium mercuric iodide (\[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\]).
\[Hg{{I}_{2}}+2KI\to \underset{\text{potassium mercuric iodide}}{\mathop{{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]}}\,\]
-The overall reaction can be written as follows.
\[4KI+HgC{{l}_{2}}\to {{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]+2KCl\]
-From the above equation we can say that four moles of potassium iodide reacts with Mercuric iodide and forms one mole of\[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\](potassium mercuric iodide).
1 moles of \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\] requires 4 moles of KI
0.1 moles of \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\] requires = 0.1 (4) = 0.4 moles of KI.
-Therefore to produce 0.1 moles of \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\], there is a requirement of 0.4 moles of KI.
So, the correct option is D.
Additional information:
- Potassium mercuric iodide is a yellow colour solid and it is odourless.
-Potassium mercuric iodide is a salt and it is used as Nessler's reagent.
- Potassium mercuric iodide is soluble in water.
-The colour of the alkaline Potassium mercuric iodide is pale orange.
Note: Potassium mercuric iodide is used widely to determine the number of ammonium compounds. The structure of Potassium mercuric iodide is as follows.

0.09mol/L Potassium mercuric iodide in 0.25mol/L potassium hydroxide is called Nessler’s reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




