
The magnification for a mirror is -3. How are u and v related?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Before we understand the concept of magnification in a mirror, it is important to understand the magnification is only possible in curved mirrors. In plane mirrors, the magnification is always 1 which means that the image is not enlarged or diminished in a plane mirror and always has the same size of the object. Hence, we have to consider curved mirrors only.
Complete step by step answer:
Magnification of the image is defined as the ratio of height of the image produced by the curved mirror to the ratio of height of the object.
Let us consider an object AB of height ${h_0}$ and distance -u from the pole P placed between centre of curvature C and focus F in front of a concave mirror as shown:
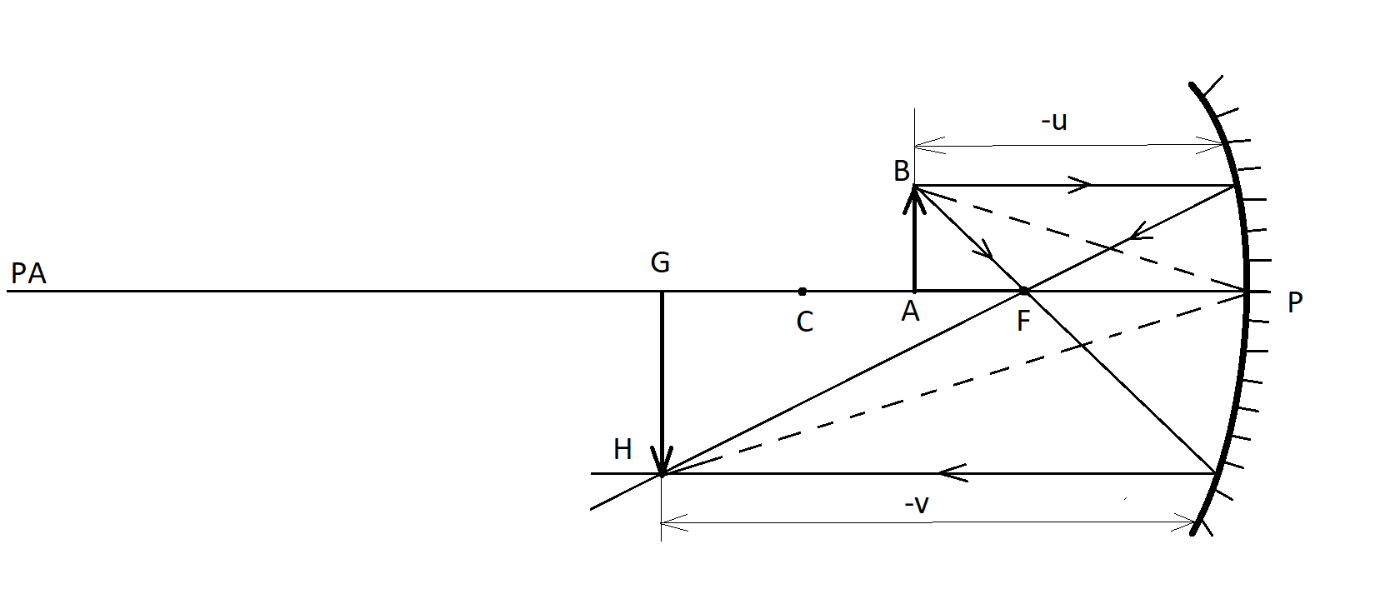
There are two rays emerging from the object.
i) First ray, parallel to the principal axis PA, after reflection, passes through focus.
ii) Second ray, passing through focus, after reflection, passes parallel to the principal axis.
These two rays meet beyond the centre of curvature C, to form the image GH of height ${h_i}$ at distance of -v from the pole.
Consider the triangles ABP and GHP.
$\Rightarrow \angle PAB = \angle PGH = {90^ \circ }$
By the law of reflection that incident angle equal to reflected angle, we have –
$\Rightarrow \angle APB = \angle GPH$
Hence, we can prove that the triangles ABP and GHP are similar.
By rule of similarity, we can say that –
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{GH}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{\left( { - v} \right)}}{{\left( { - u} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{GH}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{v}{u}$
Given that $AB = {h_0}$ and $GH = - {h_i}$ (the negative sign is because the height of image is measured downwards direction)
Magnification is equal to the ratio of height of image of height of object.
$\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{ - {h_i}}}{{{h_0}}}$
Substituting,
$\Rightarrow m = - \dfrac{v}{u}$
Therefore, magnification is defined as the ratio of v to u with a minus sign.
Note: The formula for the magnification in a lens is the same as that of a mirror, but only in the magnitude. The magnification formula for lenses has a positive sign while the magnification formula for a mirror has a negative sign.
Magnification for lens –
$m = \dfrac{v}{u}$
The students must understand the clear distinction between the two so that there is no confusion between the two formulae.
Complete step by step answer:
Magnification of the image is defined as the ratio of height of the image produced by the curved mirror to the ratio of height of the object.
Let us consider an object AB of height ${h_0}$ and distance -u from the pole P placed between centre of curvature C and focus F in front of a concave mirror as shown:

There are two rays emerging from the object.
i) First ray, parallel to the principal axis PA, after reflection, passes through focus.
ii) Second ray, passing through focus, after reflection, passes parallel to the principal axis.
These two rays meet beyond the centre of curvature C, to form the image GH of height ${h_i}$ at distance of -v from the pole.
Consider the triangles ABP and GHP.
$\Rightarrow \angle PAB = \angle PGH = {90^ \circ }$
By the law of reflection that incident angle equal to reflected angle, we have –
$\Rightarrow \angle APB = \angle GPH$
Hence, we can prove that the triangles ABP and GHP are similar.
By rule of similarity, we can say that –
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{GH}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{\left( { - v} \right)}}{{\left( { - u} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{GH}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{v}{u}$
Given that $AB = {h_0}$ and $GH = - {h_i}$ (the negative sign is because the height of image is measured downwards direction)
Magnification is equal to the ratio of height of image of height of object.
$\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{ - {h_i}}}{{{h_0}}}$
Substituting,
$\Rightarrow m = - \dfrac{v}{u}$
Therefore, magnification is defined as the ratio of v to u with a minus sign.
Note: The formula for the magnification in a lens is the same as that of a mirror, but only in the magnitude. The magnification formula for lenses has a positive sign while the magnification formula for a mirror has a negative sign.
Magnification for lens –
$m = \dfrac{v}{u}$
The students must understand the clear distinction between the two so that there is no confusion between the two formulae.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




