
The group having triangular planar structures is:
A.${ NCl }_{ 3 },{ BCl }_{ 3 }{ ,SO }_{ 3 }$
B.${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }{ ,NO }_{ 3 }^{ - }{ ,SO }_{ 3 }$
C.${ BF }_{ 3 }{ ,NF }_{ 3 }{ ,CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$
D.${ NH }_{ 3 } {, SO }_{ 3 }{ ,CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In the trigonal planar arrangement, there is a central atom, bonded to three other atoms. These three other atoms are arranged like a triangle around the central atom, with a bond angle measuring ${ 120 }^{ \circ }{ C }$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
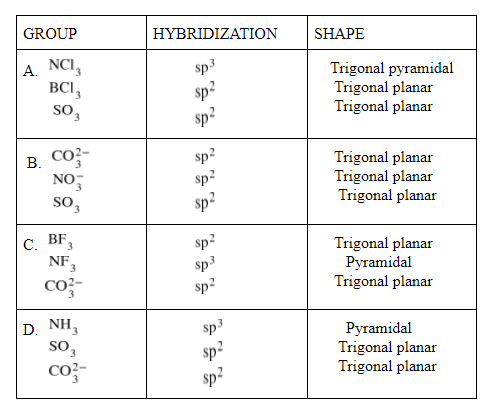
As we can see here that ${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }{ ,NO }_{ 3 }^{ - }{ ,SO }_{ 3 }$
has ${ sp }^{ 2 }$ and trigonal planar structure, so the correct option is B.
Additional Information:
-Hybridization is a process of mixing two or more atomic orbitals of an atom having comparable energy to form orbitals of equal energy known as hybrid orbitals.
-One s and three p orbitals of carbon mix/hybridize to give four ${ sp }^{ 3 }$ hybrid orbitals. The ${ sp }^{ 3 }$ hybrid orbitals are used by 4 hydrogen atoms for sigma bond formation.
-Trigonal planar is a subatomic geometry model with one molecule at the middle and three particles at the sides of a symmetrical triangle, called peripheral atoms, all in one plane.
- In an ideal trigonal planar species, every one of the three ligands are indistinguishable and all bond angles are ${ 120 }^{ \circ }{ C }$.
-When ${ sp }^{ 3 }$ orbitals are formed, they arrange themselves with the goal that they are as far separated as could be expected under the circumstances. That is a tetrahedral arrangement, with a point of ${ 109.5 }^{ \circ }{ C }$.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option A. But in that ${ NCl }_{ 3 }$ is trigonal pyramidal, not trigonal planar due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons on nitrogen atoms.
Complete step-by-step answer:

As we can see here that ${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }{ ,NO }_{ 3 }^{ - }{ ,SO }_{ 3 }$
has ${ sp }^{ 2 }$ and trigonal planar structure, so the correct option is B.
Additional Information:
-Hybridization is a process of mixing two or more atomic orbitals of an atom having comparable energy to form orbitals of equal energy known as hybrid orbitals.
-One s and three p orbitals of carbon mix/hybridize to give four ${ sp }^{ 3 }$ hybrid orbitals. The ${ sp }^{ 3 }$ hybrid orbitals are used by 4 hydrogen atoms for sigma bond formation.
-Trigonal planar is a subatomic geometry model with one molecule at the middle and three particles at the sides of a symmetrical triangle, called peripheral atoms, all in one plane.
- In an ideal trigonal planar species, every one of the three ligands are indistinguishable and all bond angles are ${ 120 }^{ \circ }{ C }$.
-When ${ sp }^{ 3 }$ orbitals are formed, they arrange themselves with the goal that they are as far separated as could be expected under the circumstances. That is a tetrahedral arrangement, with a point of ${ 109.5 }^{ \circ }{ C }$.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option A. But in that ${ NCl }_{ 3 }$ is trigonal pyramidal, not trigonal planar due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons on nitrogen atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




