
The graph of the hyperbolic tangent function for all real values is:
A. Strictly increasing
B. Strictly decreasing
C. Strictly increasing in the interval [0,∞) and Strictly decreasing in the interval (-∞,0]
D. Strictly increasing in the interval (-∞,0] and Strictly decreasing in the interval [0,∞)
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: The hyperbolic tangent function,that is, \[{\text{tanh}}\] function is the ratio of \[\sinh \] function to the \[\cosh \] function. We can find the trend of the graph by giving different values of x and observing the corresponding trend in y value.
Complete step by step answer:
The tanh function or hyperbolic tangent function is the ratio between hyperbolic sine and hyperbolic cosine.
We know that,
$
{\text{sinhx = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{e}}^{\text{x}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{ - x}}}}}}{{\text{2}}} \\
{\text{coshx = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{e}}^{\text{x}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{ - x}}}}}}{{\text{2}}} \\
$
Then tanh is given by,
${\text{tanhx = }}\dfrac{{{\text{sinhx}}}}{{{\text{coshx}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{e}}^{\text{x}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{ - x}}}}}}{{{{\text{e}}^{\text{x}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{ - x}}}}}}$
For \[{\text{x = 0,tanhx = 0}}\].
As x increases, value of \[{\text{tanhx}}\] also increases,
Also, as x decreases, the value of \[{\text{tanhx}}\] decreases.
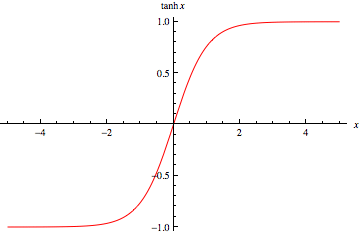
So, we can say that the graph of the hyperbolic tangent function is strictly increasing.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Note: It is important to know the graph of the basic functions and how the value varies as x varies. Even though the graph is strictly increasing, the value of the function tends to 1 as x tends to infinity and -1 as x tends to negative infinity. This can be proved by taking the limits,
$
\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \tanh x = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}} \\
= \dfrac{{\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \left( {1 - {e^{ - 2x}}} \right)}}{{\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \left( {1 + {e^{ - 2x}}} \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{{1 - \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } {e^{ - 2x}}}}{{1 + \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } {e^{ - 2x}}}} \\
= \dfrac{1}{1} \\
= 1 \\
$
Similarly, tanh tends to -1 when x tends to negative infinity. So the becomes almost straight at higher and lower values of x.
Complete step by step answer:
The tanh function or hyperbolic tangent function is the ratio between hyperbolic sine and hyperbolic cosine.
We know that,
$
{\text{sinhx = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{e}}^{\text{x}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{ - x}}}}}}{{\text{2}}} \\
{\text{coshx = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{e}}^{\text{x}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{ - x}}}}}}{{\text{2}}} \\
$
Then tanh is given by,
${\text{tanhx = }}\dfrac{{{\text{sinhx}}}}{{{\text{coshx}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{e}}^{\text{x}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{ - x}}}}}}{{{{\text{e}}^{\text{x}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{ - x}}}}}}$
For \[{\text{x = 0,tanhx = 0}}\].
As x increases, value of \[{\text{tanhx}}\] also increases,
Also, as x decreases, the value of \[{\text{tanhx}}\] decreases.

So, we can say that the graph of the hyperbolic tangent function is strictly increasing.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Note: It is important to know the graph of the basic functions and how the value varies as x varies. Even though the graph is strictly increasing, the value of the function tends to 1 as x tends to infinity and -1 as x tends to negative infinity. This can be proved by taking the limits,
$
\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \tanh x = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \dfrac{{{e^x} - {e^{ - x}}}}{{{e^x} + {e^{ - x}}}} \\
= \dfrac{{\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \left( {1 - {e^{ - 2x}}} \right)}}{{\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } \left( {1 + {e^{ - 2x}}} \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{{1 - \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } {e^{ - 2x}}}}{{1 + \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } {e^{ - 2x}}}} \\
= \dfrac{1}{1} \\
= 1 \\
$
Similarly, tanh tends to -1 when x tends to negative infinity. So the becomes almost straight at higher and lower values of x.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole




