
The formation of molecular complex \[B{F_3} - N{H_3}\] results in a change in hybridization of boron:
(A) From \[s{p^2}\] to \[ds{p^2}\]
(B) From \[s{p^2}\] to \[s{p^3}\]
(C) From \[s{p^3}\] to \[s{p^2}\]
(D) From \[s{p^3}\] to \[s{p^3}d\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: \[N{H_3}\] is electron rich as it has a lone pair and \[B{F_3}\] is electron deficient, due to this, ammonia donates its electron pair to \[B{F_3}\] , which has vacant orbital that takes up electrons and completes its octet by forming a coordinate bond and changing its hybridisation.
Complete step-by-step solution:
\[N{H_3}\] is an electron-rich species with a lone pair on a Nitrogen atom and so it is always ready to either share or donate this lone pair to other species. Therefore, it is known as a Lewis base. Lewis bases can donate a pair of non-bonding electrons.
While, \[B{F_3}\] is an electron-deficient species having vacant orbitals with an incomplete octet of Boron. So \[B{F_3}\] always looks for species which can donate electrons to it and complete its octet. Therefore, it is known as Lewis acid. These are electron acceptors.
So, when they come close to each other to form a bond, an ammonia molecule coordinates its lone pair to the empty p-shell or vacant p-orbitals of Boron forming a co-ordinate bond to give rise to an adduct which looks like this.
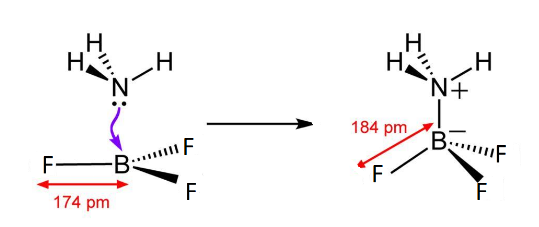
\[B{F_3}\] has a hybridisation of \[s{p^2}\] because of filling of 2s and 2 orbitals of 2p. But as it forms coordinate bond with ammonia, the lone pair accepted from ammonia leads to bond pair and lone pair repulsion, changing its shape from trigonal planar to tetrahedral and hybridisation from \[s{p^2}\] to \[s{p^3}\] due to filling of one more 2p orbital. This makes the system highly stable by removing the electron deficiency of boron.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: As per molecular orbital theory, one can also understand this concept as the HOMO on the Lewis base (\[N{H_3}\]) interacts with the electron pair in the LUMO of the Lewis acid (\[B{F_3}\]). This forms an adduct of these molecular orbitals and lowers the energy by stabilizing it.
Complete step-by-step solution:
\[N{H_3}\] is an electron-rich species with a lone pair on a Nitrogen atom and so it is always ready to either share or donate this lone pair to other species. Therefore, it is known as a Lewis base. Lewis bases can donate a pair of non-bonding electrons.
While, \[B{F_3}\] is an electron-deficient species having vacant orbitals with an incomplete octet of Boron. So \[B{F_3}\] always looks for species which can donate electrons to it and complete its octet. Therefore, it is known as Lewis acid. These are electron acceptors.
So, when they come close to each other to form a bond, an ammonia molecule coordinates its lone pair to the empty p-shell or vacant p-orbitals of Boron forming a co-ordinate bond to give rise to an adduct which looks like this.

\[B{F_3}\] has a hybridisation of \[s{p^2}\] because of filling of 2s and 2 orbitals of 2p. But as it forms coordinate bond with ammonia, the lone pair accepted from ammonia leads to bond pair and lone pair repulsion, changing its shape from trigonal planar to tetrahedral and hybridisation from \[s{p^2}\] to \[s{p^3}\] due to filling of one more 2p orbital. This makes the system highly stable by removing the electron deficiency of boron.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: As per molecular orbital theory, one can also understand this concept as the HOMO on the Lewis base (\[N{H_3}\]) interacts with the electron pair in the LUMO of the Lewis acid (\[B{F_3}\]). This forms an adduct of these molecular orbitals and lowers the energy by stabilizing it.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




