
The equivalent circuit is:
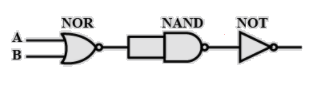
(A) NAND gate
(B) OR gates
(C) AND gates
(D) NOR gates
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: From the question we know that the circuit has a NOR gate, NAND gate, and a NOT gate. The input is sent to the NOR gate and the output of that becomes the input for NAND and the output of the NAND gate becomes the input for NOT gate. What exactly happens in each of these gates,
(1) In a NOR gate, the output is the inverse of the sum of A and B. (NOR, $OUTPUT = \overline {A + B} $).
(2) In a NAND gate, the output is the inverse of the multiplication of A and B. (NAND, $OUTPUT = \overline {A.B} $).
(3) in a NOT gate the output is the inverse of the input, the input of a NOT gate is always a single digit. ( NOT,$OUTPUT = \overline A $).
Complete step by step solution:
Taking outputs of all the gates as ${y_1},{y_2},{y_3}$,
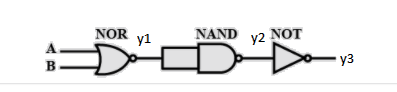
We know that a NOR gate inverses the sum of its inputs , so output at NOR is ${y_1} = \overline {A + B} $
${y_1}$ becomes the input for NAND gate , so $\overline {{y_1}.{y_1}} = {y_2} = \overline {\overline {A + B} .\overline {A + B} } = \overline {\overline {A + B} } + \overline {\overline {A + B} } = A + B$
${y_2}$ become the input for NOT gate , so, ${y_3} = \overline {{y_2}} = \overline {A + B} $
The output for the NOT gate is ${y_3}$ which is the final output and we get the output as the inverse of the sum of A and B which is nothing but the output of NOR gate.
Here, ${y_1},{y_2},{y_3}$ are the outputs of NOR, NAND and NOT gates respectively . The final output is ${y_3}$.
Hence option (D), NOR gate is the correct answer.
Note: Do not get confused with the diagram as OR and AND and NOT the small circle beside each of the gates makes them NOR and NAND gates. It represents the negation of OR and AND. The N represents “negation of” which means the inverse.
(1) In a NOR gate, the output is the inverse of the sum of A and B. (NOR, $OUTPUT = \overline {A + B} $).
(2) In a NAND gate, the output is the inverse of the multiplication of A and B. (NAND, $OUTPUT = \overline {A.B} $).
(3) in a NOT gate the output is the inverse of the input, the input of a NOT gate is always a single digit. ( NOT,$OUTPUT = \overline A $).
Complete step by step solution:
Taking outputs of all the gates as ${y_1},{y_2},{y_3}$,

We know that a NOR gate inverses the sum of its inputs , so output at NOR is ${y_1} = \overline {A + B} $
${y_1}$ becomes the input for NAND gate , so $\overline {{y_1}.{y_1}} = {y_2} = \overline {\overline {A + B} .\overline {A + B} } = \overline {\overline {A + B} } + \overline {\overline {A + B} } = A + B$
${y_2}$ become the input for NOT gate , so, ${y_3} = \overline {{y_2}} = \overline {A + B} $
The output for the NOT gate is ${y_3}$ which is the final output and we get the output as the inverse of the sum of A and B which is nothing but the output of NOR gate.
Here, ${y_1},{y_2},{y_3}$ are the outputs of NOR, NAND and NOT gates respectively . The final output is ${y_3}$.
Hence option (D), NOR gate is the correct answer.
Note: Do not get confused with the diagram as OR and AND and NOT the small circle beside each of the gates makes them NOR and NAND gates. It represents the negation of OR and AND. The N represents “negation of” which means the inverse.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions




