
The electronic configuration of four elements are given in brackets $L\left( 1{{s}^{2}},2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}} \right)$; $M\left( 1{{s}^{2}},2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{5}} \right)$; $Q\left( 1{{s}^{2}},2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}},3{{s}^{1}} \right)$; $R\left( 1{{s}^{2}},2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{2}} \right)$. The element that would most readily form a diatomic molecule is:
A) $Q$
B) $M$
C) $R$
D) $L$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The elements with seven electrons in their valence shell (Group 17 elements) readily combine with the other element of the same group through a nonpolar covalent bond resulting in the formation of a diatomic molecule.
Complete step by step solution:As per the given electronic configuration in the question, the element which require only one electron to complete its octet is $M\left( 1{{s}^{2}},2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{5}} \right)$ which belongs to group 17 group i.e., it is a part of halogen family in which all the elements shows a tendency to readily share their electrons to form a nonpolar covalent bond and results in formation of diatomic molecule as shown in the figure below:
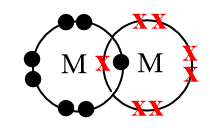
Also, diatomic molecules of alkali metals with electronic configuration $L\left( 1{{s}^{2}},2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}} \right)$ are detected in their gas phase but the bond between the elements is very weak because the outer orbitals of the alkali metals are very diffuse and thus, the possibility to exist as a diatomic molecule is very less. Due to this reason, the alkali metals mostly form ionic bonds with the elements.
Hence, the element that would most readily form a diatomic molecule is $M$.
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note: It is important to note that the only element in group 17 which does not exist as a diatomic molecule is Astatine because it is a short lived radioactive element which does not occur in nature. Thus, only fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine elements in group 17 exist as diatomic molecule.
Complete step by step solution:As per the given electronic configuration in the question, the element which require only one electron to complete its octet is $M\left( 1{{s}^{2}},2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{5}} \right)$ which belongs to group 17 group i.e., it is a part of halogen family in which all the elements shows a tendency to readily share their electrons to form a nonpolar covalent bond and results in formation of diatomic molecule as shown in the figure below:

Also, diatomic molecules of alkali metals with electronic configuration $L\left( 1{{s}^{2}},2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}} \right)$ are detected in their gas phase but the bond between the elements is very weak because the outer orbitals of the alkali metals are very diffuse and thus, the possibility to exist as a diatomic molecule is very less. Due to this reason, the alkali metals mostly form ionic bonds with the elements.
Hence, the element that would most readily form a diatomic molecule is $M$.
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note: It is important to note that the only element in group 17 which does not exist as a diatomic molecule is Astatine because it is a short lived radioactive element which does not occur in nature. Thus, only fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine elements in group 17 exist as diatomic molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




