
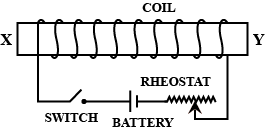
The diagram shows a coil wound around a soft iron bar XY. State the polarity at the ends X and Y as the switch is pressed:
(A) X- north pole, Y-south pole
(B) X- north pole, Y-north pole
(C) X- south pole, Y-south pole
(D) X- south pole, Y-north pole
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Magnetic fields curl around a wire carrying electric current. Right hand thumb rule can be used accordingly. According to the right thumb rule the magnetic lines move away from us which is similar in case of a magnet do the side from which the magnetic field lines are out it is considered as North Pole and the opposite side as South Pole.
Complete Step-by-Step solution When the current flows in a wire, magnetic loops are formed around it. The direction of the magnetic field lines can be measured with the help of your right hand. If your thumb is in the direction of the electric current in a straight wire, then your fingers will curl in the direction of magnetic field lines. In this case, when we see the solenoid from the top view, where X is above Y, the current will look like moving in an anti-clockwise direction. Therefore, applying the right-hand thumb rule, the magnetic field lines appear to be moving towards us (i.e. from Y to X). Similarly, when we see the solenoid from the bottom view, where Y is above X, the current will look like moving in a clockwise direction, therefore applying the thumb rule, the magnetic field lines appear to be moving away from us. This is similar to a magnet, so the side giving out magnetic field lines is said to be North Pole and the side taking in magnetic field lines is said to be South Pole. This will also form a closed loop. Thus, the polarity of the solenoid XY at X is North Pole and at Y is South Pole.
Hence the correct answer is A
Note Magnetic monopoles do not exist and magnetic field lines will always form a closed loop. Every magnet has dipole nature; it consists of both north and South poles. Even when the magnet is broken or cut into many pieces every part cut behaves as an individual magnet consisting of north and south poles.
Complete Step-by-Step solution When the current flows in a wire, magnetic loops are formed around it. The direction of the magnetic field lines can be measured with the help of your right hand. If your thumb is in the direction of the electric current in a straight wire, then your fingers will curl in the direction of magnetic field lines. In this case, when we see the solenoid from the top view, where X is above Y, the current will look like moving in an anti-clockwise direction. Therefore, applying the right-hand thumb rule, the magnetic field lines appear to be moving towards us (i.e. from Y to X). Similarly, when we see the solenoid from the bottom view, where Y is above X, the current will look like moving in a clockwise direction, therefore applying the thumb rule, the magnetic field lines appear to be moving away from us. This is similar to a magnet, so the side giving out magnetic field lines is said to be North Pole and the side taking in magnetic field lines is said to be South Pole. This will also form a closed loop. Thus, the polarity of the solenoid XY at X is North Pole and at Y is South Pole.
Hence the correct answer is A
Note Magnetic monopoles do not exist and magnetic field lines will always form a closed loop. Every magnet has dipole nature; it consists of both north and South poles. Even when the magnet is broken or cut into many pieces every part cut behaves as an individual magnet consisting of north and south poles.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




