
The compounds A and B are mixed in equimolar proportion to form the products.
$A+B\rightleftharpoons C+D$
At equilibrium, one-third of A and B are consumed. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is:
(A) 0.5
(B) 4.0
(C) 2.5
(D) 0.25
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The term "chemical equilibrium state" refers to reactant and product concentrations in a reaction occurring in a closed system that are no longer changing over time. Chemical equilibrium is reached when a reversible reaction proceeds both backwards and forwards by the same amount at the same time. In the presence of a catalyst, this equilibrium can be reached more quickly. Chemical equilibrium cannot be changed by a catalyst since it only changes the rate of both forward and backward reactions to the same degree. Its nature is dynamic.
Formula Used: For the reaction,
$A+B\rightleftharpoons C+D$
The equilibrium state is calculated as: $K=\frac{\left[ C \right]\left[ D \right]}{\left[ A \right]\left[ B \right]}$; where A and B are the reactants, C and D are the products.
Complete step by step solution:
The compounds A and B are mixed in equal proportions to form the products C and D.
The initial concentrations of the reactants A and B are taken as 1M. It is given that at equilibrium, one-third of A and B are consumed.
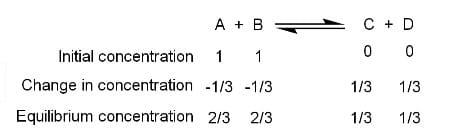
The equilibrium constant is given by:
$K=\frac{\left[ C \right]\left[ D \right]}{\left[ A \right]\left[ B \right]}$
$K=\frac{\frac{1}{3}\times \frac{1}{3}}{\frac{2}{3}\times \frac{2}{3}}$
$K=\frac{1}{4}$
$K=0.25$
Thus, the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.25.
Correct Option: (D) 0.25.
Note: The factors which affect the equilibrium constant are change in pressure, change in temperature, change in concentration, addition of catalyst, etc. The value of the equilibrium constant is definite for each chemical reaction.
Formula Used: For the reaction,
$A+B\rightleftharpoons C+D$
The equilibrium state is calculated as: $K=\frac{\left[ C \right]\left[ D \right]}{\left[ A \right]\left[ B \right]}$; where A and B are the reactants, C and D are the products.
Complete step by step solution:
The compounds A and B are mixed in equal proportions to form the products C and D.
The initial concentrations of the reactants A and B are taken as 1M. It is given that at equilibrium, one-third of A and B are consumed.

The equilibrium constant is given by:
$K=\frac{\left[ C \right]\left[ D \right]}{\left[ A \right]\left[ B \right]}$
$K=\frac{\frac{1}{3}\times \frac{1}{3}}{\frac{2}{3}\times \frac{2}{3}}$
$K=\frac{1}{4}$
$K=0.25$
Thus, the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.25.
Correct Option: (D) 0.25.
Note: The factors which affect the equilibrium constant are change in pressure, change in temperature, change in concentration, addition of catalyst, etc. The value of the equilibrium constant is definite for each chemical reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




