
The $cis,2-butene$ on reaction with $B{{r}_{2}}$ in $CC{{l}_{4}}$produces mainly
(A) $\text{1-bromo-2-butene}$
(B) $2,3-\text{dibromobutane}$
(C) $\text{meso-2,3-dibromobutane}$
(D) $(\pm )2,3-\text{dibromobutane}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The electrophilic addition reaction of bromine molecules takes place with the alkene, known as the bromination process. It involves the breaking of the C-C double bond in the alkene given.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given reaction, between an alkene and bromine molecule in presence of carbon tetrachloride, it leads to an additional reaction.
-As in the bromine molecule, the bromine atoms have the same electronegativity and are nonpolar in nature. So, the $CC{{l}_{4}}$ having a polar C-Cl bond interacts with it and induces a partial positive charge on the closest bromine atom through the dipole-induced dipole interaction. Thus, making the bromine molecule partially charged.
-Then, the nucleophilic $C=C$ bond of the butene attacks the electrophilic centre, that is the $B{{r}^{+}}$ in the Br-Br molecule bond. This is the electrophilic addition step where the $B{{r}^{+}}$gets added to the $C=C$ bond. It forms a three-membered ring and hence, a bridged intermediate is formed known as the bromonium.
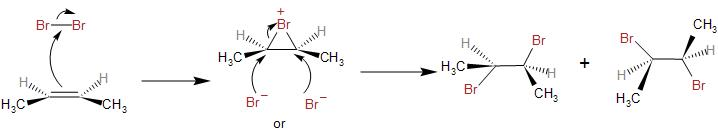
-The $B{{r}^{-}}$ left behind, now being highly nucleophilic, attacks the bromonium intermediate through nucleophilic addition. It attacks from the opposite side of the bridged ring as it may hinder its attack on the partially positive carbon atom. Therefore, the addition of the bromine molecule in the given reaction is anti-addiction, that is, both the bromine atoms are on opposite faces of the C-C bond.
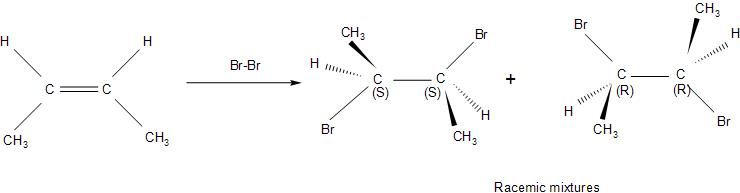
-This leads to the formation of a racemic mixture of $2,3-\text{dibromobutane}$, that is, the two forms being $(2R,3R)-2,3-\text{dibromobutane}$and $(2S,3S)-2,3-\text{dibromobutane}$.They are enantiomers.
Therefore, the $cis,\,2-Butene$ on reaction with $B{{r}_{2}}$ in $CC{{l}_{4}}$produces mainly option (D)- $(\pm )2,3-\text{dibromobutane}$.
Note: It can be seen that the reaction is an anti-addition reaction and also stereospecific in nature. The carbon tetrachloride solvent only provides the opportunity for the reactant to get polarized and has no other effect on the reaction process.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given reaction, between an alkene and bromine molecule in presence of carbon tetrachloride, it leads to an additional reaction.
-As in the bromine molecule, the bromine atoms have the same electronegativity and are nonpolar in nature. So, the $CC{{l}_{4}}$ having a polar C-Cl bond interacts with it and induces a partial positive charge on the closest bromine atom through the dipole-induced dipole interaction. Thus, making the bromine molecule partially charged.
-Then, the nucleophilic $C=C$ bond of the butene attacks the electrophilic centre, that is the $B{{r}^{+}}$ in the Br-Br molecule bond. This is the electrophilic addition step where the $B{{r}^{+}}$gets added to the $C=C$ bond. It forms a three-membered ring and hence, a bridged intermediate is formed known as the bromonium.

-The $B{{r}^{-}}$ left behind, now being highly nucleophilic, attacks the bromonium intermediate through nucleophilic addition. It attacks from the opposite side of the bridged ring as it may hinder its attack on the partially positive carbon atom. Therefore, the addition of the bromine molecule in the given reaction is anti-addiction, that is, both the bromine atoms are on opposite faces of the C-C bond.

-This leads to the formation of a racemic mixture of $2,3-\text{dibromobutane}$, that is, the two forms being $(2R,3R)-2,3-\text{dibromobutane}$and $(2S,3S)-2,3-\text{dibromobutane}$.They are enantiomers.
Therefore, the $cis,\,2-Butene$ on reaction with $B{{r}_{2}}$ in $CC{{l}_{4}}$produces mainly option (D)- $(\pm )2,3-\text{dibromobutane}$.
Note: It can be seen that the reaction is an anti-addition reaction and also stereospecific in nature. The carbon tetrachloride solvent only provides the opportunity for the reactant to get polarized and has no other effect on the reaction process.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




