
The circular boundary of the concave mirror subtends a cone of half angle \[\theta \] at its center of curvature. The minimum value of \[\theta \] for which ray incident on this mirror parallel to the principal axis suffers reflection more than one is:
A) \[{30^\circ}\]
B) \[{45^\circ}\]
C) \[{60^\circ}\]
D) \[{75^\circ}\]
Answer
242.7k+ views
Hint: Multiple reflection of light is the reflection of light that happens between reflecting surfaces many a times. If a light that is reflected from a surface is made to incident on another surface, this process is called multiple reflection of light.
Complete step by step solution:
When two mirrors are placed in front of each other, then multiple images are formed. This is because the image formed by one mirror will act as an object to the second mirror. This pattern continues and further images of image are formed. If the mirrors are placed at some angle to each other then the reflections produced will be curved. The number of reflections can be increased by increasing the number of mirrors. These days multiple reflection of sound waves principle is used to make a stethoscope used by doctors to check heartbeat or pulse rate.
An incident ray will suffer many reflections if it is incident on only one part of the mirror. It reflects in a perpendicular direction and intersects the other side of the mirror. This is obtained if the angle of incidence is \[{45^ \circ }\]. Let the angle between them be \[\theta \]. Since the reflected ray will act as incident ray to other surfaces so \[\angle i = \angle r\].
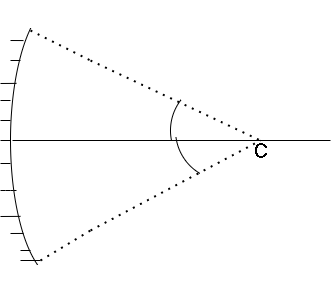
\[\Rightarrow \angle i + \angle r = {90^ \circ }\]
\[\Rightarrow \theta + \theta = {90^ \circ }\]
\[\Rightarrow 2\theta = {90^ \circ }\]
\[\Rightarrow \theta = {45^ \circ }\]
The minimum value for which the incident ray will suffer many reflections is \[{45^ \circ }\].
Option B is the correct answer.
Note: If the plane mirrors are used for multiple reflections and if the angle between the plane mirrors is \[\theta \], then the number of images formed can be calculated by using \[n = 360\theta - 1\].
Complete step by step solution:
When two mirrors are placed in front of each other, then multiple images are formed. This is because the image formed by one mirror will act as an object to the second mirror. This pattern continues and further images of image are formed. If the mirrors are placed at some angle to each other then the reflections produced will be curved. The number of reflections can be increased by increasing the number of mirrors. These days multiple reflection of sound waves principle is used to make a stethoscope used by doctors to check heartbeat or pulse rate.
An incident ray will suffer many reflections if it is incident on only one part of the mirror. It reflects in a perpendicular direction and intersects the other side of the mirror. This is obtained if the angle of incidence is \[{45^ \circ }\]. Let the angle between them be \[\theta \]. Since the reflected ray will act as incident ray to other surfaces so \[\angle i = \angle r\].

\[\Rightarrow \angle i + \angle r = {90^ \circ }\]
\[\Rightarrow \theta + \theta = {90^ \circ }\]
\[\Rightarrow 2\theta = {90^ \circ }\]
\[\Rightarrow \theta = {45^ \circ }\]
The minimum value for which the incident ray will suffer many reflections is \[{45^ \circ }\].
Option B is the correct answer.
Note: If the plane mirrors are used for multiple reflections and if the angle between the plane mirrors is \[\theta \], then the number of images formed can be calculated by using \[n = 360\theta - 1\].
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

Trending doubts
JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Step-by-Step Guide to Young’s Double Slit Experiment Derivation

Other Pages
CBSE Class 10 Sanskrit Set 4 52 Question Paper 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

Essential Derivations for CBSE Class 12 Physics: Stepwise & PDF Solutions

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Diffraction of Light - Young’s Single Slit Experiment

Assertion The energy E and momentum p of a photon are class 12 physics JEE_Main

Electric field due to uniformly charged sphere class 12 physics JEE_Main




