
The black graph pictured below represents the position-time graph for a spring-mass system oscillating with simple harmonic motion.
The coloured, dashed graphs represent shapes of possible velocity time graphs for the same motion. The vertical axis stands for position or velocity, but the scaling does not matter. The time axis is the same for all the graphs.
Which coloured graph best represents the position velocity for the mass in this spring.
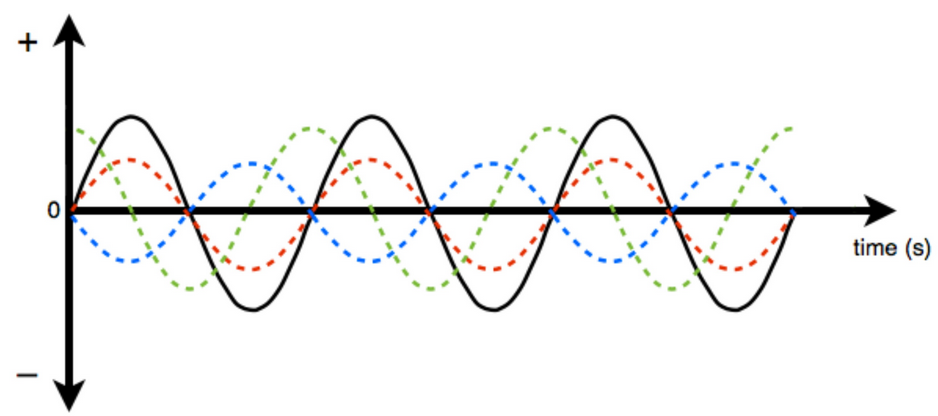
(A) Red
(B) Blue
(C) Green
(D) The velocity graph is the same as the position graph
(E) All three coloured graphs are equally possible
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: We should know that velocity is defined as the rate change of displacement per unit time. Speed in a specific direction is also known as velocity. Velocity is equal to displacement divided by time. Speed, being a scalar quantity, is the rate at which an object covers distance. The average speed is the distance which is a scalar quantity per time ratio. On the other hand, velocity is a vector quantity; it is direction-aware. An object which moves in the negative direction has a negative velocity. If the object is slowing down then its acceleration vector is directed in the opposite direction as its motion in this case. Based on this we have to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer
We can say that in mechanics and physics, simple harmonic motion is a special type of periodic motion where the restoring force on the moving object is directly proportional to the object's displacement magnitude and acts towards the object's equilibrium position. Simple harmonic motion, in physics, repetitive movement back and forth through an equilibrium, or central, position, so that the maximum displacement on one side of this position is equal to the maximum displacement on the other side. The time interval of each complete vibration is the same.
It can be said that the motion of a particle moving along a straight line with an acceleration whose direction is always towards a fixed point on the line and whose magnitude is proportional to the distance from the fixed point is called simple harmonic motion. Simple Harmonic motion is periodic in nature, that is it repeats its position again and again, and in harmonic motion Hooke's Law is applicable which states that Force is always proportional to displacement but due to air resistance and other factors the amplitude goes on decreasing which restricts the motion.
It is known that for the spring mass system, an SHM, the position of mass is given by $x=A\sin (\omega t+\phi )$.
Now the velocity of the mass would be $v=\dfrac{dx}{dt}=A\omega \cos (\omega t+\phi )$.
Hence the function representing them must be ${{90}^{o}}$out of phase. Only the green curve can represent the velocity-time graph.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: We should know that if an object's speed or velocity is increasing at a constant rate then we say it has uniform acceleration. The rate of acceleration is constant. If a car speeds up then slows down then speeds up it doesn't have uniform acceleration. The instantaneous acceleration, or simply acceleration, is defined as the limit of the average acceleration when the interval of time considered approaches 0. It is also defined in a similar manner as the derivative of velocity with respect to time. If an object begins acceleration from rest or a standstill, its initial time is 0. If we get a negative value for acceleration, it means the object is slowing down. The acceleration of an object is its change in velocity over an increment of time. This can mean a change in the object's speed or direction. Average acceleration is the change of velocity over a period of time. Constant or uniform acceleration is when the velocity changes the same amount in every equal time period.
Complete step by step answer
We can say that in mechanics and physics, simple harmonic motion is a special type of periodic motion where the restoring force on the moving object is directly proportional to the object's displacement magnitude and acts towards the object's equilibrium position. Simple harmonic motion, in physics, repetitive movement back and forth through an equilibrium, or central, position, so that the maximum displacement on one side of this position is equal to the maximum displacement on the other side. The time interval of each complete vibration is the same.
It can be said that the motion of a particle moving along a straight line with an acceleration whose direction is always towards a fixed point on the line and whose magnitude is proportional to the distance from the fixed point is called simple harmonic motion. Simple Harmonic motion is periodic in nature, that is it repeats its position again and again, and in harmonic motion Hooke's Law is applicable which states that Force is always proportional to displacement but due to air resistance and other factors the amplitude goes on decreasing which restricts the motion.
It is known that for the spring mass system, an SHM, the position of mass is given by $x=A\sin (\omega t+\phi )$.
Now the velocity of the mass would be $v=\dfrac{dx}{dt}=A\omega \cos (\omega t+\phi )$.
Hence the function representing them must be ${{90}^{o}}$out of phase. Only the green curve can represent the velocity-time graph.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: We should know that if an object's speed or velocity is increasing at a constant rate then we say it has uniform acceleration. The rate of acceleration is constant. If a car speeds up then slows down then speeds up it doesn't have uniform acceleration. The instantaneous acceleration, or simply acceleration, is defined as the limit of the average acceleration when the interval of time considered approaches 0. It is also defined in a similar manner as the derivative of velocity with respect to time. If an object begins acceleration from rest or a standstill, its initial time is 0. If we get a negative value for acceleration, it means the object is slowing down. The acceleration of an object is its change in velocity over an increment of time. This can mean a change in the object's speed or direction. Average acceleration is the change of velocity over a period of time. Constant or uniform acceleration is when the velocity changes the same amount in every equal time period.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




