
The average kinetic energy of a simple harmonic oscillator is \[2J\] and its total energy is\[5J\]. Its minimum potential energy is:
A. \[1J\]
B. \[1.5J\]
C.\[2J\]
D. \[3J\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Before we proceed with the problem, it is necessary to know the simple harmonic oscillator. A simple harmonic oscillator is a system that is composed of a mass\[m\]. When a force \[F\] is applied to the mass, it starts to oscillate between mean positions and extreme positions.
Complete step by step solution:
In an oscillator, there are two extreme positions at \[{E_1}\]and\[{E_2}\]. The mass oscillates between these two positions. Therefore, an oscillator has,
A. Maximum K.E. and minimum P.E. at the mean position.
B. Minimum K.E. and maximum P.E. at the extreme position.
We know that total energy is equivalent to the sum of K.E. and P.E.
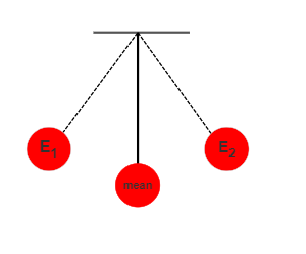
Image: Simple pendulum
Here it given that total energy \[ = 5J\]
Average kinetic energy \[\langle KE\rangle = 2J\]
We know that average kinetic energy is calculated by the formula,
\[\langle KE\rangle = \dfrac{{K{E_{\max }} + K{E_{\min }}}}{2}\]
\[\begin{array}{l}2 = \dfrac{{K{E_{\max }} + 0}}{2}\\ \Rightarrow K{E_{\max }} = 4\end{array}\]
When the potential energy is minimum then kinetic energy is maximum. Therefore total energy can be written as
\[TE = K{E_{\max }} + P{E_{\min }}\]
\[\Rightarrow 5 = 4 + P{E_{\min }}\]
\[\Rightarrow P{E_{\min }} = 5 - 4 = 1J\]
\[\therefore P{E_{\min }} = 1J\]
Hence, option \[A\] is correct.
Note: In the concept of the simple harmonic oscillator, students are often confused between the energies at the mean position and at the extreme position. At the mean position, the mass \[m\] is at rest i.e., \[x = 0\], so P.E. is zero and K.E. is maximum. At the extreme position, the mass \[m\] is at maximum distance from the mean position. So their P.E. is maximum while K.E. is zero.
Complete step by step solution:
In an oscillator, there are two extreme positions at \[{E_1}\]and\[{E_2}\]. The mass oscillates between these two positions. Therefore, an oscillator has,
A. Maximum K.E. and minimum P.E. at the mean position.
B. Minimum K.E. and maximum P.E. at the extreme position.
We know that total energy is equivalent to the sum of K.E. and P.E.

Image: Simple pendulum
Here it given that total energy \[ = 5J\]
Average kinetic energy \[\langle KE\rangle = 2J\]
We know that average kinetic energy is calculated by the formula,
\[\langle KE\rangle = \dfrac{{K{E_{\max }} + K{E_{\min }}}}{2}\]
\[\begin{array}{l}2 = \dfrac{{K{E_{\max }} + 0}}{2}\\ \Rightarrow K{E_{\max }} = 4\end{array}\]
When the potential energy is minimum then kinetic energy is maximum. Therefore total energy can be written as
\[TE = K{E_{\max }} + P{E_{\min }}\]
\[\Rightarrow 5 = 4 + P{E_{\min }}\]
\[\Rightarrow P{E_{\min }} = 5 - 4 = 1J\]
\[\therefore P{E_{\min }} = 1J\]
Hence, option \[A\] is correct.
Note: In the concept of the simple harmonic oscillator, students are often confused between the energies at the mean position and at the extreme position. At the mean position, the mass \[m\] is at rest i.e., \[x = 0\], so P.E. is zero and K.E. is maximum. At the extreme position, the mass \[m\] is at maximum distance from the mean position. So their P.E. is maximum while K.E. is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




