
The angle of deviation $(\delta )$ vs angle of incidence $(i)$ is plotted for a prism. Pick up the correct statements.
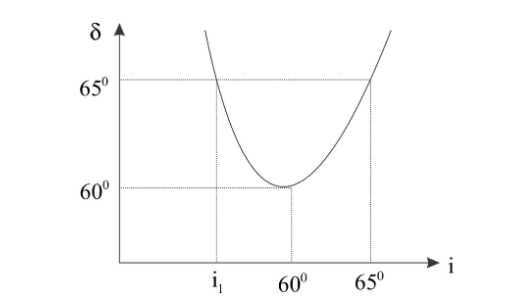
(A) The angle of the prism is ${60^0}$.
(B) The refractive index of prism is $n = \sqrt 3 $.
(C) The curve of $\delta {\text{ vs }}i$ is parabolic.
(D) For the deviation to be ${65^0}$ the angle of incidence to be ${i_1} = {55^0}$.
Answer
242.7k+ views
Hint We know that deviation of prism is given by $\delta = i + e - A$, where $\delta $ is deviation, $i$ is angle of incidence, $e$ is angle of emergence and $A$ is angle of prism. For minimum deviation, $i = e$. Using these equations, we find the angle of the prism. Using minimum deviation, we find a refractive index of prism. After this, find ${i_1}$ using the given information.
Complete step by step solution
We know that deviation of prism is given by $\delta = i + e - A$, where $\delta $ is deviation, $i$ is angle of incidence, $e$ is angle of emergence and $A$ is angle of prism. For minimum deviation, $i = e$.
From the figure, for minimum deviation, $\delta = {60^0}$ and also ${i_1} = {60^0}$.
For minimum deviation, $\delta = 2i - A$ or $A = 2i - \delta $.
After putting value in above equation, we get
$A = 2 \times 60 - 60 = {60^0}$.
Now refractive of given is given by
$n = \dfrac{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{{A + \delta }}{2}} \right)}}{{\sin \dfrac{A}{2}}}$
Then, $n = \dfrac{{\sin 60}}{{\sin 30}} = \sqrt 3 $.
Here for angle of deviation ${65^0}$, angle of emergence is given in figure that is $e = {70^0}$,
Then, ${\delta _1} = {i_1} + e - A$ or ${i_1} = {\delta _1} - e + A$
${i_1} = 65 - 70 + 60 = {55^0}$.
From the graph we can see that the curve of $\delta {\text{ vs }}i$ is parabolic.
Hence all options are correct.
Note We know that of each angle of deviation there are two points on the graph, these two are angle of incidence and angle of emergence and always exist in pairs. These angles are such that if we take angle of emergence as angle of incidence the angle of emergence for that case is angle of incident of given case.
Complete step by step solution
We know that deviation of prism is given by $\delta = i + e - A$, where $\delta $ is deviation, $i$ is angle of incidence, $e$ is angle of emergence and $A$ is angle of prism. For minimum deviation, $i = e$.
From the figure, for minimum deviation, $\delta = {60^0}$ and also ${i_1} = {60^0}$.
For minimum deviation, $\delta = 2i - A$ or $A = 2i - \delta $.
After putting value in above equation, we get
$A = 2 \times 60 - 60 = {60^0}$.
Now refractive of given is given by
$n = \dfrac{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{{A + \delta }}{2}} \right)}}{{\sin \dfrac{A}{2}}}$
Then, $n = \dfrac{{\sin 60}}{{\sin 30}} = \sqrt 3 $.
Here for angle of deviation ${65^0}$, angle of emergence is given in figure that is $e = {70^0}$,
Then, ${\delta _1} = {i_1} + e - A$ or ${i_1} = {\delta _1} - e + A$
${i_1} = 65 - 70 + 60 = {55^0}$.
From the graph we can see that the curve of $\delta {\text{ vs }}i$ is parabolic.
Hence all options are correct.
Note We know that of each angle of deviation there are two points on the graph, these two are angle of incidence and angle of emergence and always exist in pairs. These angles are such that if we take angle of emergence as angle of incidence the angle of emergence for that case is angle of incident of given case.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

Trending doubts
JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Step-by-Step Guide to Young’s Double Slit Experiment Derivation

Other Pages
CBSE Class 10 Sanskrit Set 4 52 Question Paper 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

Essential Derivations for CBSE Class 12 Physics: Stepwise & PDF Solutions

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Diffraction of Light - Young’s Single Slit Experiment

Assertion The energy E and momentum p of a photon are class 12 physics JEE_Main

Electric field due to uniformly charged sphere class 12 physics JEE_Main




