
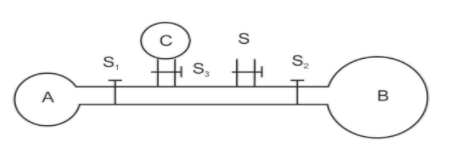
The adjoining diagram shows three soap bubbles$A,B$ and $C$ prepared by blowing the capillary tube fitted with stop cocks $S,{S_1},{S_2}$ and ${S_3}$ with stop cock $S$ closed and stop cocks $S,{\text{ }}{S_1}{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}{S_2}$opened :-
A) ${\text{B will start collapsing with volumes of A and C increasing }}$
B) ${\text{C will start collapsing with volumes of A and B increasing }}$
C) ${\text{C and A will both start collapsing with volumes of B increasing }}$
D) ${\text{Volumes of A,B,C will becomes equal at equilibrium}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To answer such a question, one has to be very much aware of the relation between the pressure and radius of the bubble. We know that the pressure under the soap bubble is always greater than the pressure that exists outside the soap bubble.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we have been given three soap bubbles whose all the valves are being open then how the pressure inside the bubble changes.
From the figure given above we can conclude that the relation between the radius of $ \Rightarrow {r_C} < {r_A} < {r_B}$.
As we know that the pressure inside the soap bubble is always greater as compared to the pressure outside the bubble and the relation between the two is given as $\Delta P$.
The relation between the pressure and the radius is given as follows:
$ \Rightarrow \Delta P = \dfrac{{4s}}{r}$
Where, the symbols have their usual meaning as the $s$ stands for surface tension and the $r$ stands for radius of the bubble.
From the above equation one can find out that the pressure is inversely proportional to that of the radius of the bubble.
Therefore, the largest pressure is inside the $C$ as the pressure is lower as the radius is largest. Similarly, the radius of the bubble $A$ is also smaller as compared to that of the $B$ . Therefore, one can understand that the molecules from both the bubbles of smaller radius will move on the bubble of the larger radius and therefore that bubble will expand, and rest will collapse.
Looking at the options one can easily make out that the volume of both $A{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}C$ will collapse and volume of $B$ should increase.
Therefore, the correct option is option (C).
Note: The knowledge of pressure and volume should be clear to the person while handling such kinds of questions. One should also take care of the pressure inside and outside the system which is being considered. Also here we have assumed the surface tension of all bubbles to be equal
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we have been given three soap bubbles whose all the valves are being open then how the pressure inside the bubble changes.
From the figure given above we can conclude that the relation between the radius of $ \Rightarrow {r_C} < {r_A} < {r_B}$.
As we know that the pressure inside the soap bubble is always greater as compared to the pressure outside the bubble and the relation between the two is given as $\Delta P$.
The relation between the pressure and the radius is given as follows:
$ \Rightarrow \Delta P = \dfrac{{4s}}{r}$
Where, the symbols have their usual meaning as the $s$ stands for surface tension and the $r$ stands for radius of the bubble.
From the above equation one can find out that the pressure is inversely proportional to that of the radius of the bubble.
Therefore, the largest pressure is inside the $C$ as the pressure is lower as the radius is largest. Similarly, the radius of the bubble $A$ is also smaller as compared to that of the $B$ . Therefore, one can understand that the molecules from both the bubbles of smaller radius will move on the bubble of the larger radius and therefore that bubble will expand, and rest will collapse.
Looking at the options one can easily make out that the volume of both $A{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}C$ will collapse and volume of $B$ should increase.
Therefore, the correct option is option (C).
Note: The knowledge of pressure and volume should be clear to the person while handling such kinds of questions. One should also take care of the pressure inside and outside the system which is being considered. Also here we have assumed the surface tension of all bubbles to be equal
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




