
How do you tell if an image is upright or inverted?
Answer
239.4k+ views
Hint: The images formed by spherical surfaces can be of two types, that is real and inverted or virtual and erect. The images formed by the converging of light rays from an object form real and inverted images. Similarly, the image which is formed by the diverging light rays from the object will be virtual and erect.
Complete answer:
* If the image is real in the case of mirrors, it will always be inverted. Also in case of mirrors if the image distance is negative hence the image is inverted. These images will form on the same side of the mirror.
* If the image is real in the case of lenses, it will always be inverted. Also in case of lenses if the image distance is positive hence the image is inverted. These images will form on the opposite side of the lens.
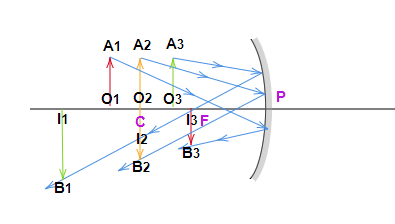
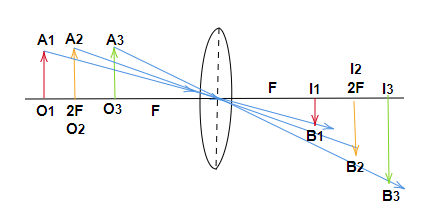
* If the image is virtual in the case of mirrors, it will always be upright. Also in case of mirrors if the image distance is positive hence the image is upright. These images will form on the opposite side of the mirror.
* If the image is virtual in the case of lenses, it will always be upright. Also in case of lenses if the image distance is negative hence the image is upright. These images will form on the same side of the lens.
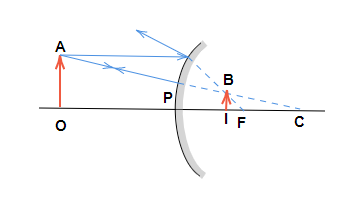
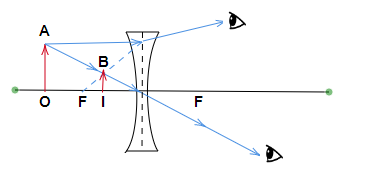
Note: The image formed by the convex mirror and concave lens will always be virtual and erect wherever the object is placed between \[\infty\] and P. The concave mirror and convex lens will form real and inverted images with varying sizes according to the object distance (u) and they can also form virtual images
Complete answer:
* If the image is real in the case of mirrors, it will always be inverted. Also in case of mirrors if the image distance is negative hence the image is inverted. These images will form on the same side of the mirror.
* If the image is real in the case of lenses, it will always be inverted. Also in case of lenses if the image distance is positive hence the image is inverted. These images will form on the opposite side of the lens.


* If the image is virtual in the case of mirrors, it will always be upright. Also in case of mirrors if the image distance is positive hence the image is upright. These images will form on the opposite side of the mirror.
* If the image is virtual in the case of lenses, it will always be upright. Also in case of lenses if the image distance is negative hence the image is upright. These images will form on the same side of the lens.


Note: The image formed by the convex mirror and concave lens will always be virtual and erect wherever the object is placed between \[\infty\] and P. The concave mirror and convex lens will form real and inverted images with varying sizes according to the object distance (u) and they can also form virtual images
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Step-by-Step Guide to Young’s Double Slit Experiment Derivation

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Essential Derivations for CBSE Class 12 Physics: Stepwise & PDF Solutions

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis




