
When sulphur monochloride is saturated with chlorine, the compound formed is
A) $SC{{l}_{6}}$
B) $SC{{l}_{4}}$
C) $SC{{l}_{2}}$
D) ${{S}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Sulphur has 2 free electrons in the outermost subshell to get covalent bonding in ground state and in an excited state it has 6 electrons free in its last shell. So, in less or saturated amount of chlorine sulphur be in ground state.
Complete step by step solution:
Now formula of sulphur monochloride is ${{S}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$
And electronic configuration of $S$in ground state be like that shown in diagram
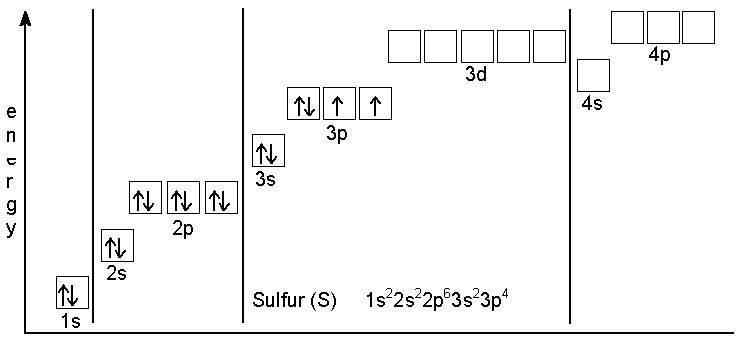
There are two atoms in last $3p$ subshell when sulphur is in ground state so sulphur breaks from its $S-S$ Bond in ${{S}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$ and make a coordinate bond with $Cl$ in which there is a last vacant shell in outer subshell.
Electronic configuration of chlorine is \[\left[ Ne \right]\text{ }3s{}^\text{2}\text{ }3{{p}^{5}}\]
So, the reaction be like-
\[{{S}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to SC{{l}_{2}}\]
Then in the excess or in saturated quantity of chlorine gas it gives sulphur dioxide as a product.
Hence Option (C) is correct.
Additional Information:
Disulfur dichloride is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the formula ${{S}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$ Some alternative names for this compound are sulfur monochloride, disulphur dichloride and sulphur monochloride.Its structure be like:
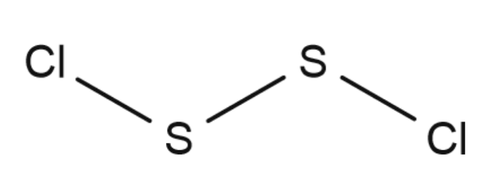
There is a covalent bond between sulphur and sulphur to complete inertness of its outer shell.
It is produced by partial chlorination of elemental sulfur. The reaction proceeds at usable rates at room temperature. In the laboratory, chlorine gas is led into a flask containing elemental sulfur. As disulfur dichloride is formed, the contents become a golden yellow liquid:
\[{{S}_{8}}~+\text{ }4\text{ }C{{l}_{2}}~\to \text{ }4\text{ }{{S}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}},~\Delta H~=\text{ }-58.2~kJ/mol\]
Note: It gives different reactions when chlorine is not present in sufficient amounts. So the saturated word in question decides many factors in which direction the reaction goes. It also depends on the stability of the final product. Also, temperature during reaction also plays a major factor on the final product.
Complete step by step solution:
Now formula of sulphur monochloride is ${{S}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$
And electronic configuration of $S$in ground state be like that shown in diagram

There are two atoms in last $3p$ subshell when sulphur is in ground state so sulphur breaks from its $S-S$ Bond in ${{S}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$ and make a coordinate bond with $Cl$ in which there is a last vacant shell in outer subshell.
Electronic configuration of chlorine is \[\left[ Ne \right]\text{ }3s{}^\text{2}\text{ }3{{p}^{5}}\]
So, the reaction be like-
\[{{S}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to SC{{l}_{2}}\]
Then in the excess or in saturated quantity of chlorine gas it gives sulphur dioxide as a product.
Hence Option (C) is correct.
Additional Information:
Disulfur dichloride is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the formula ${{S}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$ Some alternative names for this compound are sulfur monochloride, disulphur dichloride and sulphur monochloride.Its structure be like:

There is a covalent bond between sulphur and sulphur to complete inertness of its outer shell.
It is produced by partial chlorination of elemental sulfur. The reaction proceeds at usable rates at room temperature. In the laboratory, chlorine gas is led into a flask containing elemental sulfur. As disulfur dichloride is formed, the contents become a golden yellow liquid:
\[{{S}_{8}}~+\text{ }4\text{ }C{{l}_{2}}~\to \text{ }4\text{ }{{S}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}},~\Delta H~=\text{ }-58.2~kJ/mol\]
Note: It gives different reactions when chlorine is not present in sufficient amounts. So the saturated word in question decides many factors in which direction the reaction goes. It also depends on the stability of the final product. Also, temperature during reaction also plays a major factor on the final product.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




