
When succinic acid is heated, product formed is:
A. Succinic anhydride
B. Acetic acid
C. CO2 and methane
D. Propionic acid
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Succinic acid is a carboxylic acid comprising two carboxylic acids. It is depicted by the chemical formula of \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\] . Its production is done from liquefied petroleum gas. Also, the production of succinic is done from different microbes as petroleum gas is very expensive.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of succinic acid is,
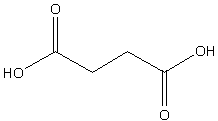
Image: Succinic acid
The above structure clearly shows that the structure is of cis form and there is the existence of a dipole moment.
Let's understand the product gives on heating of succinic acid. The heating of succinic anhydride gives the product of succinic anhydride. And in this process, the loss of a water molecule takes place. The chemical reaction is as follows:
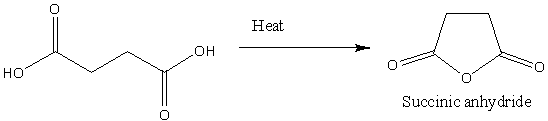
Image: Heating of succinic anhydride
Additional Information:
Succinic acid belongs to the group of carboxylic acids. It is one of the common organic acids. It is useful in industries such as chemical, food, and pharmaceutical for the production of many substances such as perfumes, plasticizers, solvents, and photographic chemicals. It is also helpful in the form of antibiotics. It possesses the property of softening skin and bacteria-inhibiting properties.
Note: To prepare succinic acid, the method that is most commonly used is the catalytic hydrogenation of maleic acid or its anhydride. There are some other methods which are also used for the same. Succinic acid occurs in nature in the form of crystalline solids of no colour. It is soluble in water.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of succinic acid is,

Image: Succinic acid
The above structure clearly shows that the structure is of cis form and there is the existence of a dipole moment.
Let's understand the product gives on heating of succinic acid. The heating of succinic anhydride gives the product of succinic anhydride. And in this process, the loss of a water molecule takes place. The chemical reaction is as follows:

Image: Heating of succinic anhydride
Additional Information:
Succinic acid belongs to the group of carboxylic acids. It is one of the common organic acids. It is useful in industries such as chemical, food, and pharmaceutical for the production of many substances such as perfumes, plasticizers, solvents, and photographic chemicals. It is also helpful in the form of antibiotics. It possesses the property of softening skin and bacteria-inhibiting properties.
Note: To prepare succinic acid, the method that is most commonly used is the catalytic hydrogenation of maleic acid or its anhydride. There are some other methods which are also used for the same. Succinic acid occurs in nature in the form of crystalline solids of no colour. It is soluble in water.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




