
State Kirchoff’s current law and also give the sign convention for current.
Answer
243k+ views
Hint: We will start with discussing and understanding Kirchoff's law. Kirchoofs’s law is considered as fundamental laws that have a variety of applications in electrical engineering and electrical sciences. Kirchoff’s law is categorized and given by two laws, Kirchoff’s current law and Kirchoff's voltage laws.
Complete step by step solution:
Kirchoff's current law is also known as junction rule and it is also known as Kirchoff’s first law. The principle of this law is to preserve or conserve the electric charges. Kirchhoff's first or junction rule states that the amount of electric current flowing through any node in the electric circuits is equal to the sum of all the currents flowing out of it. Hence the nodal analysis can be done by using ohms’ law.
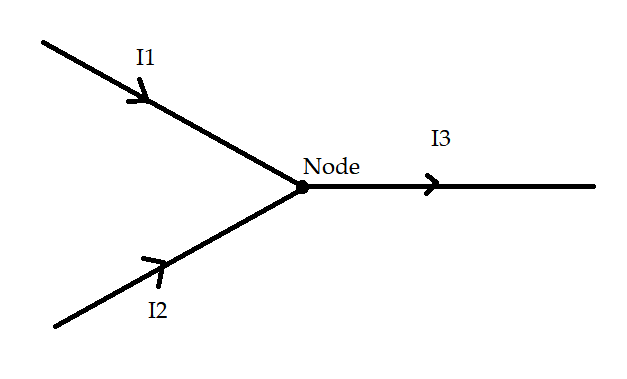
From the above diagram, it can be seen that the currents in the three wires can be given by ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$, and ${I_3}$. Hence the currents related to each other given as
${I_1} + {I_2} = {I_3}$.
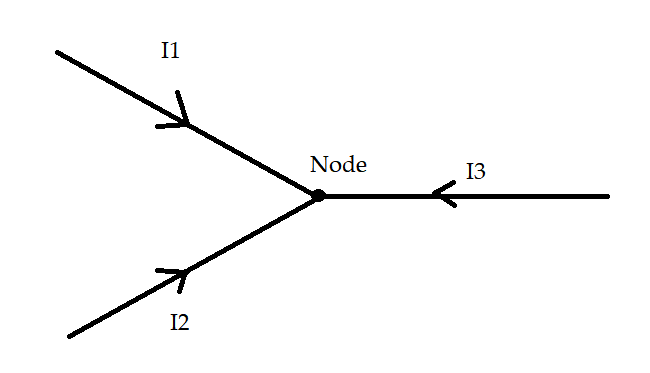
From the above diagram, it can be seen that the currents in the three wires can be given by ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$, and ${I_3}$. Hence the currents related to each other given as
${I_1} + {I_2} = - {I_3}$.
Hence from the above examples, the sign conventions of Kirchhoff's first law can be given.
The sign convention for Kirchoff's first law can be given that the current entering in the circuit is considered as positive as a result in the first diagram the currents ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$,${I_3}$ is positive while the current ${I_3}$ is considered as negative as it is leaving the circuit.
In the second figure the currents ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$, and ${I_3}$ are entering the circuits hence according to sign convection ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$, and ${I_3}$ is considered as positive.
Note: The second Kirchoff's law is Kirchoff's law of voltage states that the voltage at any node which is made up of two or more junctions of wire in an electrically closed circuit is equal to zero. Hence in a circuit, the total amount of energy that is gained is equal to the energy lost per unit charge.
Complete step by step solution:
Kirchoff's current law is also known as junction rule and it is also known as Kirchoff’s first law. The principle of this law is to preserve or conserve the electric charges. Kirchhoff's first or junction rule states that the amount of electric current flowing through any node in the electric circuits is equal to the sum of all the currents flowing out of it. Hence the nodal analysis can be done by using ohms’ law.

From the above diagram, it can be seen that the currents in the three wires can be given by ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$, and ${I_3}$. Hence the currents related to each other given as
${I_1} + {I_2} = {I_3}$.

From the above diagram, it can be seen that the currents in the three wires can be given by ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$, and ${I_3}$. Hence the currents related to each other given as
${I_1} + {I_2} = - {I_3}$.
Hence from the above examples, the sign conventions of Kirchhoff's first law can be given.
The sign convention for Kirchoff's first law can be given that the current entering in the circuit is considered as positive as a result in the first diagram the currents ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$,${I_3}$ is positive while the current ${I_3}$ is considered as negative as it is leaving the circuit.
In the second figure the currents ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$, and ${I_3}$ are entering the circuits hence according to sign convection ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$, and ${I_3}$ is considered as positive.
Note: The second Kirchoff's law is Kirchoff's law of voltage states that the voltage at any node which is made up of two or more junctions of wire in an electrically closed circuit is equal to zero. Hence in a circuit, the total amount of energy that is gained is equal to the energy lost per unit charge.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring




