
Starting from rest a car moves with uniform acceleration and attains a velocity of $90{\text{km/h}}$ in \[25\;{\text{s}}\]. It then moves with uniform speed for $30\;{\text{s}}$ and is then brought to rest in \[20\;{\text{s}}\] under uniform retardation. Find total distance travelled using velocity - time graph.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, the concept of the velocity time graph will be used, that is the area under the curve of the graph represents the total distance travelled. Plot the velocity-time graph according to the question given. Find the area of the graph which will give the result for total distance travelled using velocity - time graph.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly, to solve this question, we have to convert the velocity given for the car in ${\text{m/s}}$format.
So,
$ \Rightarrow 90{\text{km/h}} = 90 \times \dfrac{{1000}}{{360}}{\text{m/s}} = 25{\text{m/s}}$
Now, we plot the velocity-time graph (or the v-t graph) for the question, as shown below: -
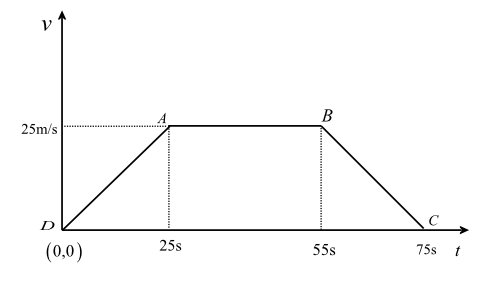
The above diagram represents the velocity time graph (v-t graph) for the question.
As we have given in the question, velocity of the car is plotted in the $y$-axis and time is plotted in the $x$ -axis.
In case of $x$ -axis (that is for plotting time): The car moves with uniform acceleration and attains a velocity of $25{\text{m/s}}$ in\[25{\text{ }}s\], so the first point is given as \[25{\text{ }}s\]. It then moves with uniform speed for$30s$, so the next point is given as $55\;{\text{s}}$ $(25 + 30 = 55s)$. Then the car is brought to rest in $20\;{\text{s}}$, so the last point is given as $75\;{\text{s}}$ $\left( {25 + 30 + 20 = 75\;{\text{s}}} \right)$.
Now, according to the formula for displacement, we have to calculate the Area under the velocity-time graph. (As Displacement= Area under velocity-time graph)
So we can clearly see in the figure that the figure forming in the velocity-time graph is a Trapezoid.
So,
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of Trapezoid}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {{\text{Sum of Parallel Sides}}} \right) \times \left( {{\text{Distance between them}}} \right)\]
Here, Parallel sides (according to the v-t graph) are \[AB\]and \[CD\]. And the distance between them is $25{\text{m/s}}$.
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of Trapezoid}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {AB + CD} \right) \times 25\]
Now, we substitute the given values as,
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of Trapezoid}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times (30 + 75) \times 25\]
After simplification we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of Trapezoid}} = 1312.5\;{\text{m}}\]
Hence, the total distance travelled using velocity-time graph is $1312.5\;{\text{m}}$.
Note: Mistakes occur while plotting the velocity-time graph. In $x$-axis, time plotted should be taken cautiously as the timestamps are summed up continuously and plotted. Conversion of units is done for the ease of calculation.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly, to solve this question, we have to convert the velocity given for the car in ${\text{m/s}}$format.
So,
$ \Rightarrow 90{\text{km/h}} = 90 \times \dfrac{{1000}}{{360}}{\text{m/s}} = 25{\text{m/s}}$
Now, we plot the velocity-time graph (or the v-t graph) for the question, as shown below: -

The above diagram represents the velocity time graph (v-t graph) for the question.
As we have given in the question, velocity of the car is plotted in the $y$-axis and time is plotted in the $x$ -axis.
In case of $x$ -axis (that is for plotting time): The car moves with uniform acceleration and attains a velocity of $25{\text{m/s}}$ in\[25{\text{ }}s\], so the first point is given as \[25{\text{ }}s\]. It then moves with uniform speed for$30s$, so the next point is given as $55\;{\text{s}}$ $(25 + 30 = 55s)$. Then the car is brought to rest in $20\;{\text{s}}$, so the last point is given as $75\;{\text{s}}$ $\left( {25 + 30 + 20 = 75\;{\text{s}}} \right)$.
Now, according to the formula for displacement, we have to calculate the Area under the velocity-time graph. (As Displacement= Area under velocity-time graph)
So we can clearly see in the figure that the figure forming in the velocity-time graph is a Trapezoid.
So,
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of Trapezoid}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {{\text{Sum of Parallel Sides}}} \right) \times \left( {{\text{Distance between them}}} \right)\]
Here, Parallel sides (according to the v-t graph) are \[AB\]and \[CD\]. And the distance between them is $25{\text{m/s}}$.
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of Trapezoid}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {AB + CD} \right) \times 25\]
Now, we substitute the given values as,
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of Trapezoid}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times (30 + 75) \times 25\]
After simplification we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of Trapezoid}} = 1312.5\;{\text{m}}\]
Hence, the total distance travelled using velocity-time graph is $1312.5\;{\text{m}}$.
Note: Mistakes occur while plotting the velocity-time graph. In $x$-axis, time plotted should be taken cautiously as the timestamps are summed up continuously and plotted. Conversion of units is done for the ease of calculation.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




