
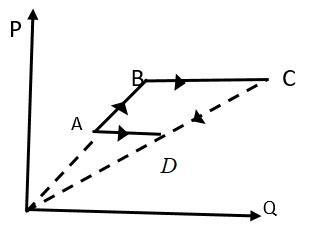
Six moles of an ideal gas performs a cycle shown in figure. The temperatures are \[{T_A} = 600K,{T_B} = 800K,{T_C} = 2200K\]and${T_D} = 1200K$. The work done by the cycle $ABCDA$ is
A $20KJ$ B$30KJ$ C$40KJ$ D$60KJ$
Answer
240k+ views
Hint: As we know that we have to find out total work done by the cycle$ABCDA$ , to calculate this we need to find work done by $AB,BC,CD$and$DA$. Then add all of them, and we will get work done by cycle.
Formula used: $\Delta {W_{BC}} = nR\Delta T$
Given: Moles of gas, $n = 6$and Temperatures as below:
\[{T_A} = 600K\]
\[{T_B} = 800K\]
\[{T_C} = 2200K\]
${T_D} = 1200K$
Complete step by step solution:
When volume of a gas remains constant this is known as an isochoric process which is shown by AB and CD given in figure.
$AB$is isochoric process,
So, work done in $AB$will be zero
$\Delta {W_{BC}} = 0......(1)$
When pressure of a gas remains constant then the process will be an isobaric process as shown by BC and DA in the given figure.
$BC$ is isobaric process,
So, work done for ideal gas in $BC$will be
$\Delta {W_{BC}} = nR\Delta T$ (Here R is universal gas constant)
$ = nR({T_C} - {T_B})$
Putting values of${T_c}$ , ${T_B}$ and $n$
$ = 6 \times R(2200 - 800)$
$ = 8400R$
Here we will put value of universal gas constant, $R = 8.3J/K - mol$
$ = 8400 \times 8.3 = 69720J......\left( 2 \right)$
$CD$is isochoric process,
So, work done in $CD$will be zero
$\Delta {W_{CD}} = 0......(3)$
$DA$ is isobaric process,
So, work done for ideal gas in $DC$will be
$\Delta {W_{DA}} = nR\Delta T$
$ = nR({T_A} - {T_D})$
Putting values of ${T_c}$ , ${T_B}$ and $n$
$ = 6 \times R(600 - 1200)$
$ = 6 \times R \times \left( { - 600} \right)$
$ = - 3600R$
Here we will put value of universal gas constant, $R = 8.3J/K - mol$
$ = - 3600 \times 8.3$
$ = - 29880J......(4)$
Now, we will add all four work done to find total work done by the cycle$ABCDA$
\[\Delta {W_{Total}} = \Delta {W_{AB}} + \Delta {W_{BC}} + \Delta {W_{CD}} + \Delta {W_{DA}}......(5)\]
$ = 0 + 69720 + 0 - 29880$(Putting values of equation 1, 2, 3 and 4 in equation 5)
$ = 39840J$
Here, the total work done by cycle$ABCDA$.
Note: We should note that, to find out work done by a cycle, we must break that cycle in individual parts. And calculate their individual work done with the help of the formula of work done, then add all of them.
Formula used: $\Delta {W_{BC}} = nR\Delta T$
Given: Moles of gas, $n = 6$and Temperatures as below:
\[{T_A} = 600K\]
\[{T_B} = 800K\]
\[{T_C} = 2200K\]
${T_D} = 1200K$
Complete step by step solution:
When volume of a gas remains constant this is known as an isochoric process which is shown by AB and CD given in figure.
$AB$is isochoric process,
So, work done in $AB$will be zero
$\Delta {W_{BC}} = 0......(1)$
When pressure of a gas remains constant then the process will be an isobaric process as shown by BC and DA in the given figure.
$BC$ is isobaric process,
So, work done for ideal gas in $BC$will be
$\Delta {W_{BC}} = nR\Delta T$ (Here R is universal gas constant)
$ = nR({T_C} - {T_B})$
Putting values of${T_c}$ , ${T_B}$ and $n$
$ = 6 \times R(2200 - 800)$
$ = 8400R$
Here we will put value of universal gas constant, $R = 8.3J/K - mol$
$ = 8400 \times 8.3 = 69720J......\left( 2 \right)$
$CD$is isochoric process,
So, work done in $CD$will be zero
$\Delta {W_{CD}} = 0......(3)$
$DA$ is isobaric process,
So, work done for ideal gas in $DC$will be
$\Delta {W_{DA}} = nR\Delta T$
$ = nR({T_A} - {T_D})$
Putting values of ${T_c}$ , ${T_B}$ and $n$
$ = 6 \times R(600 - 1200)$
$ = 6 \times R \times \left( { - 600} \right)$
$ = - 3600R$
Here we will put value of universal gas constant, $R = 8.3J/K - mol$
$ = - 3600 \times 8.3$
$ = - 29880J......(4)$
Now, we will add all four work done to find total work done by the cycle$ABCDA$
\[\Delta {W_{Total}} = \Delta {W_{AB}} + \Delta {W_{BC}} + \Delta {W_{CD}} + \Delta {W_{DA}}......(5)\]
$ = 0 + 69720 + 0 - 29880$(Putting values of equation 1, 2, 3 and 4 in equation 5)
$ = 39840J$
Here, the total work done by cycle$ABCDA$.
Note: We should note that, to find out work done by a cycle, we must break that cycle in individual parts. And calculate their individual work done with the help of the formula of work done, then add all of them.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 1 (55/1/1) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Marking Scheme




