
Silver benzoate reacts with bromine to form
A.

B.
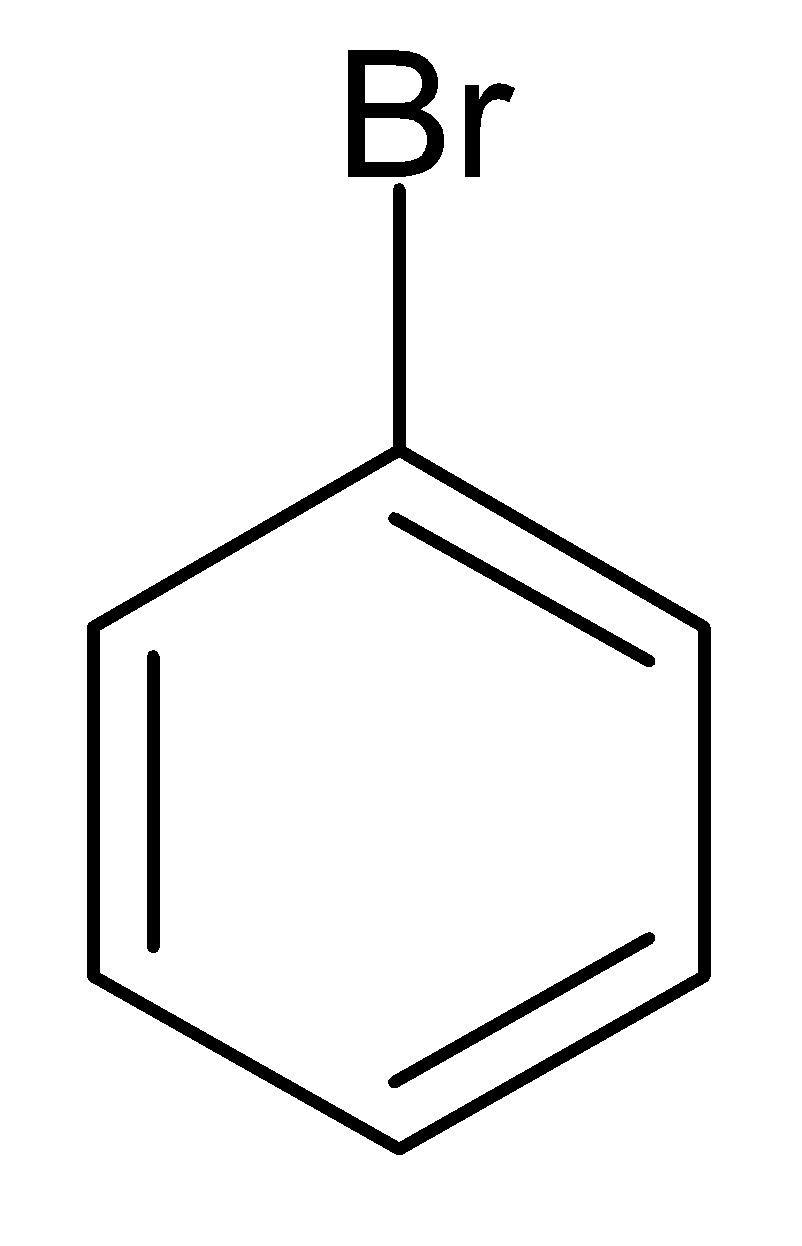
C.

D.
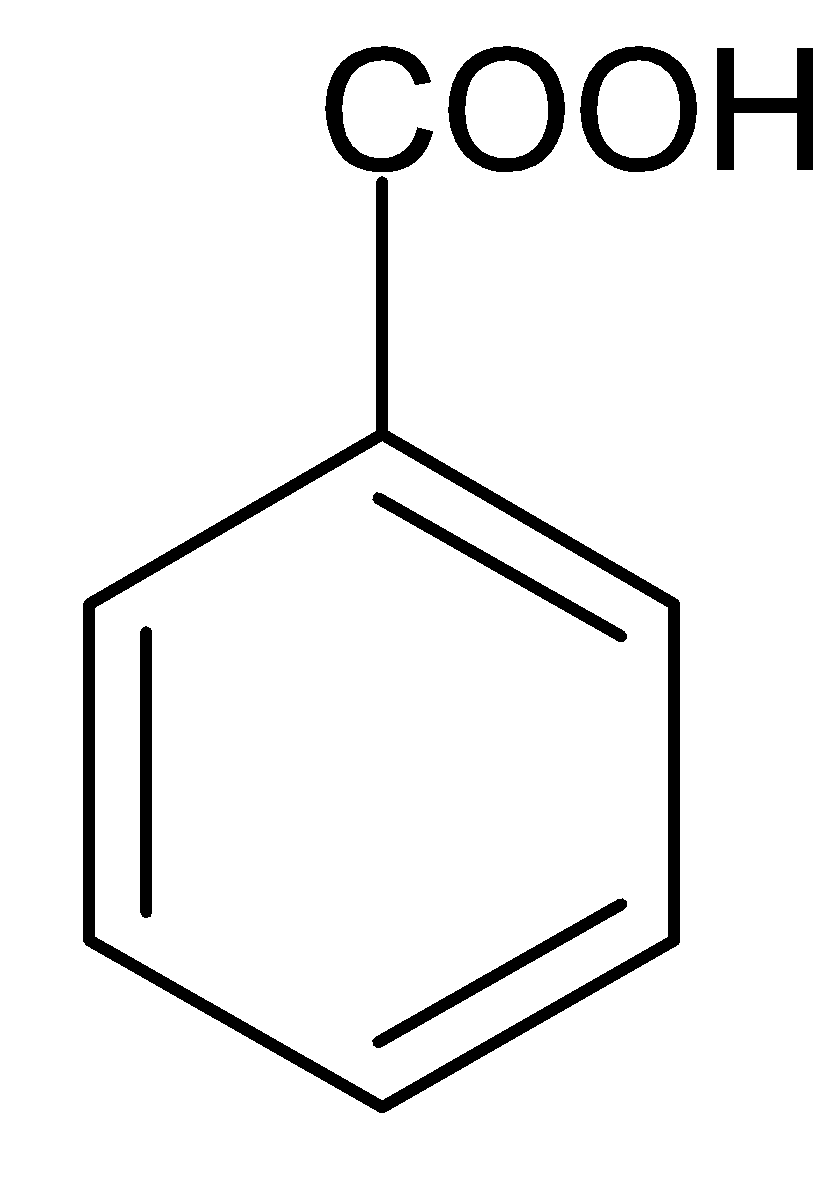
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Silver benzoate reacts with bromine in the presence of carbon tetrachloride under reflux conditions. An alkyl halide is formed as the final product. Whereas silver halide and carbon dioxide are the side products. The overall process can be explained by the Hunsdiecker reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
Alkyl carboxylic salt here is silver benzoate, reacts with bromine and first produces a very unstable intermediate. Under the refluxing condition, unstable reaction intermediates further decarboxylate to desired alkyl halides. According to the given question, silver benzoate reacts with bromine to give bromobenzene.
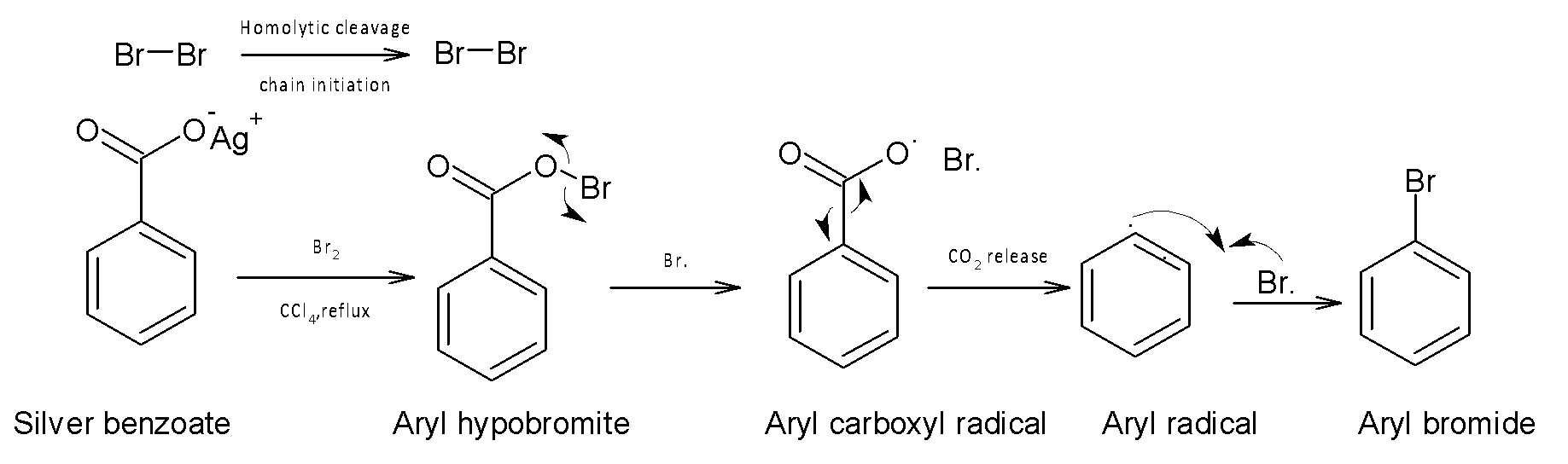
Here the overall reaction proceeds via a radical mechanism. It is one of the important pathways to get a product with one carbon less. The chain initiation consists of homolytic cleavage of carbon-bromine bond forming aryl carbonyl radical. The overall driving force of this reaction is the participation of silver bromide which is less soluble and stable. Silver benzoyate is transformed into Aryl hypobromite in the presence of Br atom. Then by radical mechanism, a carboxyl radical and a bromine atom is formed. Aryl carboxyl radical decomposes into carbon dioxide by decarboxylation to produce Aryl radical, which further reacts with Br radical to form aryl bromide or bromobenzene.
Mechanism:
Thus, Option (B) is correct.
Note: Hunsdiecker reaction is a very important reaction to synthesise higher bromoalkane compounds in case of long chain fatty acids. The overall yield of alkyl halide of this reaction follows the order: ${{1}^{{\mathrm O}}}>{{2}^{{\mathrm O}}}>{{3}^{{\mathrm O}}}$. If this reaction starts with ${{3}^{{\mathrm O}}}$ alkyl carboxylate, it gives alkene as a major product instead of alkyl halide.
Complete step by step solution:
Alkyl carboxylic salt here is silver benzoate, reacts with bromine and first produces a very unstable intermediate. Under the refluxing condition, unstable reaction intermediates further decarboxylate to desired alkyl halides. According to the given question, silver benzoate reacts with bromine to give bromobenzene.
Here the overall reaction proceeds via a radical mechanism. It is one of the important pathways to get a product with one carbon less. The chain initiation consists of homolytic cleavage of carbon-bromine bond forming aryl carbonyl radical. The overall driving force of this reaction is the participation of silver bromide which is less soluble and stable. Silver benzoyate is transformed into Aryl hypobromite in the presence of Br atom. Then by radical mechanism, a carboxyl radical and a bromine atom is formed. Aryl carboxyl radical decomposes into carbon dioxide by decarboxylation to produce Aryl radical, which further reacts with Br radical to form aryl bromide or bromobenzene.
Mechanism:

Thus, Option (B) is correct.
Note: Hunsdiecker reaction is a very important reaction to synthesise higher bromoalkane compounds in case of long chain fatty acids. The overall yield of alkyl halide of this reaction follows the order: ${{1}^{{\mathrm O}}}>{{2}^{{\mathrm O}}}>{{3}^{{\mathrm O}}}$. If this reaction starts with ${{3}^{{\mathrm O}}}$ alkyl carboxylate, it gives alkene as a major product instead of alkyl halide.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




