
Same spring is attached with 2kg, 3kg and 1 kg blocks in three different cases as shown in figure. If x1, x2, x3 be the extension in the three cases then,
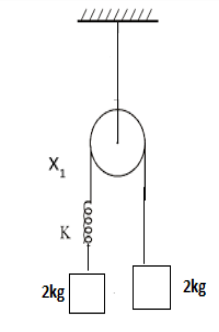
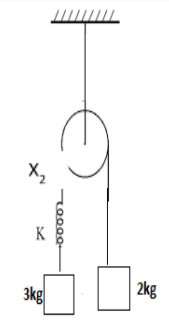
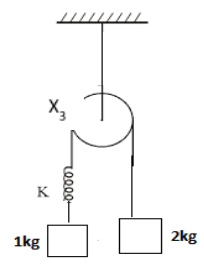
A) x1=0, x3 >x2
B) x1>x2>x3
C) x3>x2>x1
D) x2>x1>x3
Answer
243k+ views
Hint: Above problem is based on connected motion concept with the presence of second law of motion (Newton’s law of motion). In the connected system tension (force applied upwards due to the presence of pulley) is given as:
$T = \dfrac{{2{m_1}{m_2}g}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}$
Forces acting on a body balance each other, the force which is greater in magnitude exists in the system.
Like in the question pulley will move down if the downward force (mg) will be greater than tension.
Using the similar concept we will solve the problem.
Complete step by step solution:
We have ${x_1},{x_2},{x_3}$ proportional to tension T of the pulley:
So, we will find the tension T of the springs in each three cases by using the formula for tension of the connected system of motion.
$
\Rightarrow {T_1} = \dfrac{{2{m_1}{m_2}g}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {T_1} = \dfrac{{2 \times 2 \times 2g}}{{2 + 2}} \\
\Rightarrow {T_1} = 2g \\
$
We have substituted the value of masses in the formula given and calculated T1.
Now, we will calculate tension for second diagram
$
\Rightarrow {T_2} = \dfrac{{2 \times 3 \times 2g}}{{3 + 2}} \\
\Rightarrow {T_2} = \dfrac{{12g}}{5} = 2.4g \\
$ (Tension calculated for second diagram)
Now, we will move on to the third figure:
$
\Rightarrow {T_3} = \frac{{2 \times 1 \times 2g}}{{2 + 1}} \\
\Rightarrow {T_3} = \frac{{4g}}{3} = 1.66g \\
$(Tension in figure 3 is calculated)
By observation we got;
${T_2} > {T_1} > {T_3}$
As $T \propto x$
Therefore, we can write as:
${x_2} > {x_1} > {x_3}$
Option: (D) is correct.
Note: We have a number of daily life examples where we are observing Newton’s second law of motion such as, hitting the golf ball, cricket ball, football with a force the more we exert force the more we will observe the reaction. As in our question above force having higher magnitude was existing in the system.
$T = \dfrac{{2{m_1}{m_2}g}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}$
Forces acting on a body balance each other, the force which is greater in magnitude exists in the system.
Like in the question pulley will move down if the downward force (mg) will be greater than tension.
Using the similar concept we will solve the problem.
Complete step by step solution:
We have ${x_1},{x_2},{x_3}$ proportional to tension T of the pulley:
So, we will find the tension T of the springs in each three cases by using the formula for tension of the connected system of motion.
$
\Rightarrow {T_1} = \dfrac{{2{m_1}{m_2}g}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {T_1} = \dfrac{{2 \times 2 \times 2g}}{{2 + 2}} \\
\Rightarrow {T_1} = 2g \\
$
We have substituted the value of masses in the formula given and calculated T1.
Now, we will calculate tension for second diagram
$
\Rightarrow {T_2} = \dfrac{{2 \times 3 \times 2g}}{{3 + 2}} \\
\Rightarrow {T_2} = \dfrac{{12g}}{5} = 2.4g \\
$ (Tension calculated for second diagram)
Now, we will move on to the third figure:
$
\Rightarrow {T_3} = \frac{{2 \times 1 \times 2g}}{{2 + 1}} \\
\Rightarrow {T_3} = \frac{{4g}}{3} = 1.66g \\
$(Tension in figure 3 is calculated)
By observation we got;
${T_2} > {T_1} > {T_3}$
As $T \propto x$
Therefore, we can write as:
${x_2} > {x_1} > {x_3}$
Option: (D) is correct.
Note: We have a number of daily life examples where we are observing Newton’s second law of motion such as, hitting the golf ball, cricket ball, football with a force the more we exert force the more we will observe the reaction. As in our question above force having higher magnitude was existing in the system.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

Important Questions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Units and Measurement - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 - Units And Measurements - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26




