
\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CON}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} \overset{NaNO_{2/HCl}}{\rightarrow} {\rm{X}}\] ; X is ____
A.\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}}\]
B.\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CON}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}^ - }\]
C.\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
D.\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CHO}}\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint The general name of the compound ethanamide is acetamide. It is chemically represented as \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CON}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\] . It is prepared from ethanoic acid. In laboratory preparation, it is prepared from ammonium acetate via the process of dehydration. Here, we have to find the product of the reaction acetamide with sodium nitrate in an acidic medium.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s understand the reaction of acetamide with sodium nitrate in the acidic medium of HCl. Amide undergoes a reaction with nitrous acid (\[{\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\]) to give product of carboxylic acid.
But, the nature of nitrous is very unstable. Therefore, its preparation is done in situ by the reaction of sodium nitrite with dilute sulphuric acid (\[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\]) or hydrochloric acid (HCl) without the presence of heat. The chemical reaction is,
\[{\rm{NaN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\left( s \right) + {\rm{HCl}}\left( {aq} \right) \to {\rm{NaCl}}\left( {aq} \right) + \mathop {{\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}}\limits_{{\rm{Nitric}}\,{\rm{acid}}} \]
Now, the nitric acid undergoes a reaction with amide to give acetic acid. The reaction is,
\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CON}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} + {\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}} \to {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}} + {{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}} + {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}\]
Therefore, X is \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}}\]. Hence, option A is right.
Additional Information:
When aniline undergoes a reaction with nitrous acid at the temperature of 273K -278K, it results in the formation of benzenediazonium chloride. The production of nitrous acid is due to the reaction of sodium nitrile with hydrochloric acid.
Let’s understand the diazotization reaction in detail. In the diazotization reaction, the primary aromatic amine converts into diazonium salt.
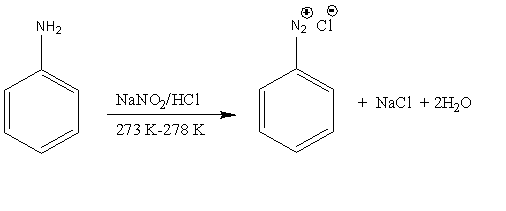
Image: Diazotization reaction
Note: The nature of nitrous acid is monoprotic and weak. Its use in the preparation of diazonium salts from amines is the most important one. In azo coupling reaction, diazonium salts acts as reagents to give azo dyes as a product. Its use as an oxidizer in liquid fuel rockets is also significant.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s understand the reaction of acetamide with sodium nitrate in the acidic medium of HCl. Amide undergoes a reaction with nitrous acid (\[{\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\]) to give product of carboxylic acid.
But, the nature of nitrous is very unstable. Therefore, its preparation is done in situ by the reaction of sodium nitrite with dilute sulphuric acid (\[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\]) or hydrochloric acid (HCl) without the presence of heat. The chemical reaction is,
\[{\rm{NaN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\left( s \right) + {\rm{HCl}}\left( {aq} \right) \to {\rm{NaCl}}\left( {aq} \right) + \mathop {{\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}}\limits_{{\rm{Nitric}}\,{\rm{acid}}} \]
Now, the nitric acid undergoes a reaction with amide to give acetic acid. The reaction is,
\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CON}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} + {\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}} \to {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}} + {{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}} + {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}\]
Therefore, X is \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}}\]. Hence, option A is right.
Additional Information:
When aniline undergoes a reaction with nitrous acid at the temperature of 273K -278K, it results in the formation of benzenediazonium chloride. The production of nitrous acid is due to the reaction of sodium nitrile with hydrochloric acid.
Let’s understand the diazotization reaction in detail. In the diazotization reaction, the primary aromatic amine converts into diazonium salt.

Image: Diazotization reaction
Note: The nature of nitrous acid is monoprotic and weak. Its use in the preparation of diazonium salts from amines is the most important one. In azo coupling reaction, diazonium salts acts as reagents to give azo dyes as a product. Its use as an oxidizer in liquid fuel rockets is also significant.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




