
Ribose is an example of: -
(a) Aldopentose
(b) Ketopentose
(c) Aldohexose
(d) Ketohexose
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Ribose is a five-carbon membered ring. It contains aldehyde groups. It is a product obtained by the hydrolysis of DNA or RNA. It is found in the furanose form.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first study monosaccharides and the structure of pentose and hexose.
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed into smaller molecules. They contain 3 to 7 carbon atoms. There are twenty monosaccharides which occur in nature. These are of two types:
Aldose: monosaccharides containing an aldehyde (-CHO) group are called aldose. Since the aldehyde group is monovalent, therefore, it is always present at one end of the carbon chain, i.e., at\[{{C}_{1}}\].
Ketose: monosaccharides containing a keto ( >C=O) group are called ketose. Since the keto group is divalent, it can be present anywhere along the carbon chain. However, in all the naturally occurring ketose, the keto group is always present at a carbon atom next to the terminal carbon, i.e., at\[{{C}_{2}}\].
Aldoses and ketose are further classified as trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses, heptoses, etc. according to as they contain three, four, five, six, seven, etc.
Ribose is a sugar that is obtained by the hydrolysis of the RNA molecule.
It has five carbon atoms in the ring.
It contains aldehyde groups. Hence, it is aldopentose.
The structure of ribose is:
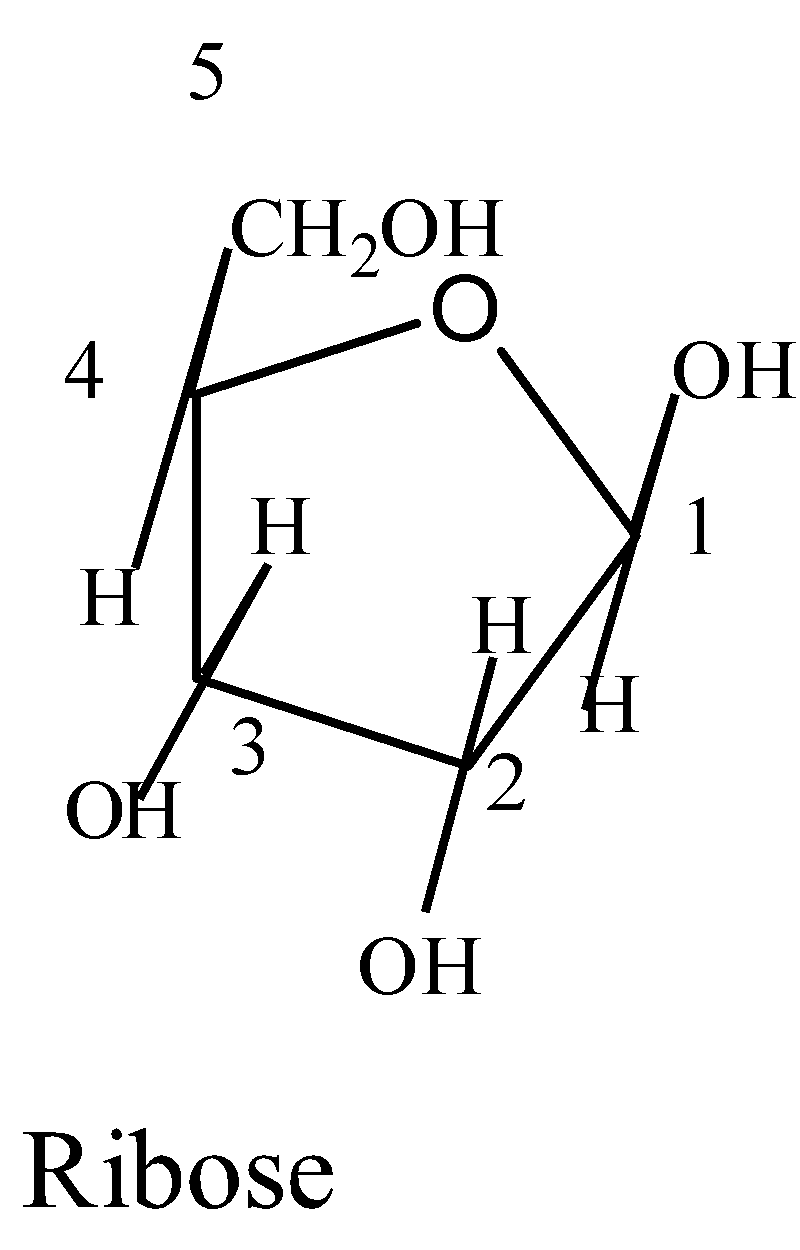
Cyclic hemiacetal of an aldopentose or a cyclic hemiketal of a ketohexose is called the Furanose ring.
There are four carbon and one oxygen atom with the anomeric carbon to the right of the oxygen in the furanose ring of ribose. The substituent on the highest numbered chiral carbon atom will point downwards out of the plane in L-configuration and will point upward in the D-configuration. The furanose structure of ribose is given below:
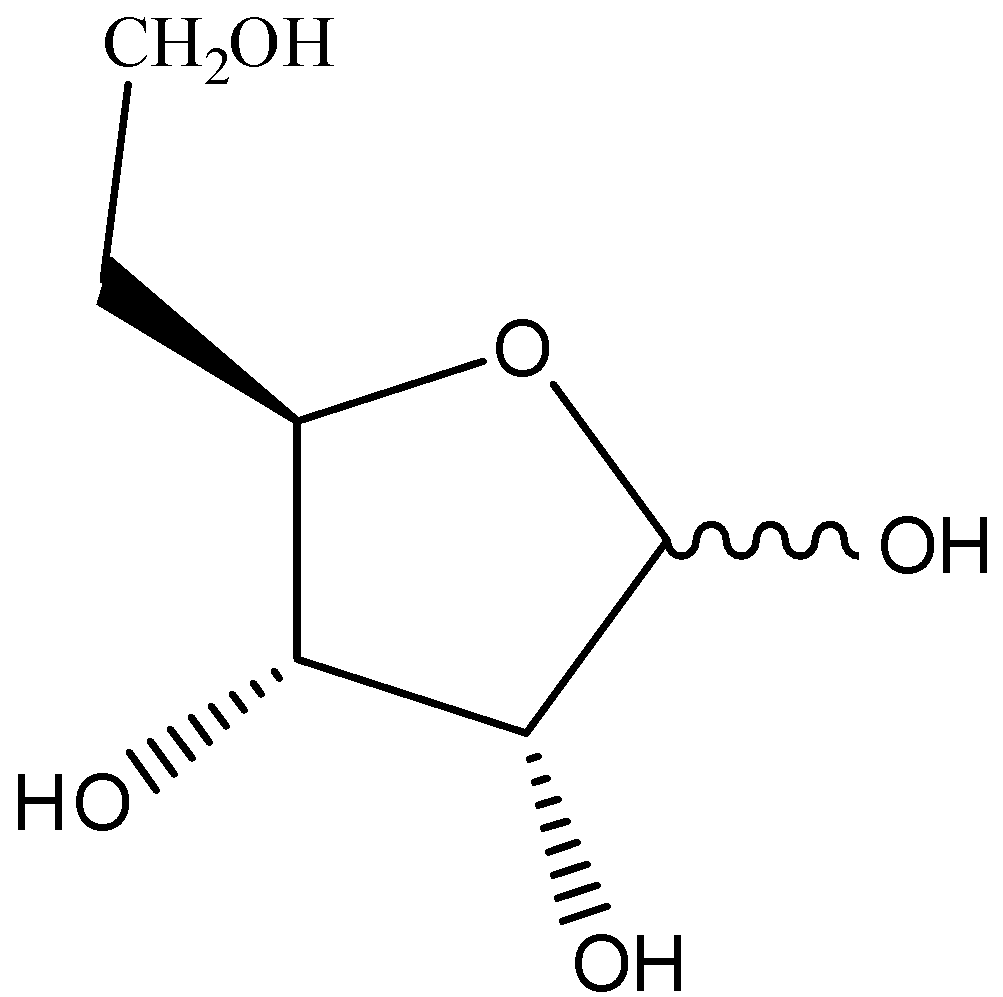
Note: Two sugars are obtained by hydrolysis of DNA and RNA, these are deoxyribose and ribose, both these sugars are found in the furanose form so don’t get confused between them. They just differ by only one alcohol group. Ribose has one extra alcohol group.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first study monosaccharides and the structure of pentose and hexose.
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed into smaller molecules. They contain 3 to 7 carbon atoms. There are twenty monosaccharides which occur in nature. These are of two types:
Aldose: monosaccharides containing an aldehyde (-CHO) group are called aldose. Since the aldehyde group is monovalent, therefore, it is always present at one end of the carbon chain, i.e., at\[{{C}_{1}}\].
Ketose: monosaccharides containing a keto ( >C=O) group are called ketose. Since the keto group is divalent, it can be present anywhere along the carbon chain. However, in all the naturally occurring ketose, the keto group is always present at a carbon atom next to the terminal carbon, i.e., at\[{{C}_{2}}\].
Aldoses and ketose are further classified as trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses, heptoses, etc. according to as they contain three, four, five, six, seven, etc.
Ribose is a sugar that is obtained by the hydrolysis of the RNA molecule.
It has five carbon atoms in the ring.
It contains aldehyde groups. Hence, it is aldopentose.
The structure of ribose is:

Cyclic hemiacetal of an aldopentose or a cyclic hemiketal of a ketohexose is called the Furanose ring.
There are four carbon and one oxygen atom with the anomeric carbon to the right of the oxygen in the furanose ring of ribose. The substituent on the highest numbered chiral carbon atom will point downwards out of the plane in L-configuration and will point upward in the D-configuration. The furanose structure of ribose is given below:

Note: Two sugars are obtained by hydrolysis of DNA and RNA, these are deoxyribose and ribose, both these sugars are found in the furanose form so don’t get confused between them. They just differ by only one alcohol group. Ribose has one extra alcohol group.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




