
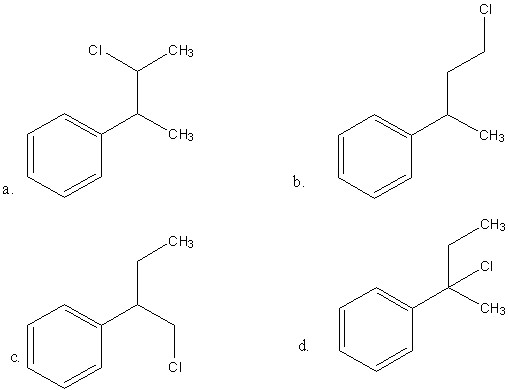
Reaction of Grignard reagent, C2H5MGBr with C8H8O followed by hydrolysis gives compound ‘A’ which reacts instantly with Lucas reagent to give compound B, C10H13Cl. The compound B us:
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: A Grignard reagent defines a chemical entity of the formula R-Mg-X, here, R indicates the alkyl or aryl group and X represents a halogen such as Chlorine, Bromine etc. It is one of the most useful reagents in chemistry due to its use in the manufacture of a variety of compounds.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The reaction of ketone with the Grignard reagent gives tertiary alcohol. And when tertiary alcohol undergoes reaction with Lucas reagent, it gives alkyl chloride. Therefore, \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{8}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{8}}}{\rm{O}}\]is a ketone.
The reaction of \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{8}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{8}}}{\rm{O}}\]and \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{MgBr}}\]are shown as below,
Image: Reaction with Grignard reagent
In the above reaction, the first step is the nucleophilic attack of the C-Mg bond to the Carbonyl Carbon takes place. And in the second step, protonation occurs. In this step, negatively charged Oxygen accepts a proton and results in the formation of alcohol.
The next reaction is the reaction of formed alcohol (A) with Lucas's reagent. Lucas' reagent defines a chemical entity composed of zinc chloride solution (anhydrous form) in hydrochloric acid (concentrated form).
So, the reaction is,
Image: Reaction with Lucas reagent
When tertiary alcohol undergoes reaction with Lucas reagent, it converts into alcohol. So, B is an alkyl chloride.
Hence,the correct option is B
Note: It is to be noted that Lucas reagent is useful in differentiating between primary, tertiary and secondary alcohols. The difference between them is measured by the time required by each to make the clear solution turbid.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The reaction of ketone with the Grignard reagent gives tertiary alcohol. And when tertiary alcohol undergoes reaction with Lucas reagent, it gives alkyl chloride. Therefore, \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{8}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{8}}}{\rm{O}}\]is a ketone.
The reaction of \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{8}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{8}}}{\rm{O}}\]and \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{MgBr}}\]are shown as below,
Image: Reaction with Grignard reagent
In the above reaction, the first step is the nucleophilic attack of the C-Mg bond to the Carbonyl Carbon takes place. And in the second step, protonation occurs. In this step, negatively charged Oxygen accepts a proton and results in the formation of alcohol.
The next reaction is the reaction of formed alcohol (A) with Lucas's reagent. Lucas' reagent defines a chemical entity composed of zinc chloride solution (anhydrous form) in hydrochloric acid (concentrated form).
So, the reaction is,
Image: Reaction with Lucas reagent
When tertiary alcohol undergoes reaction with Lucas reagent, it converts into alcohol. So, B is an alkyl chloride.
Hence,the correct option is B
Note: It is to be noted that Lucas reagent is useful in differentiating between primary, tertiary and secondary alcohols. The difference between them is measured by the time required by each to make the clear solution turbid.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




