
$(RCO)_2NH$ is
A. Primary Amine
B. Secondary Amine
C. Secondary Amide
D. Tertiary Amide
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Amides are organic compounds containing nitrogen atom. In amides nitrogen atom is attached to an acyl group (R-C=O). Basically, amide group is $R—CO—NH_2$ so when one hydrogen of ammonia is replaced by amide group, they can be called as derivative of ammonia $(NH_3)$.
Complete step by step solution: As we know the amide group is-
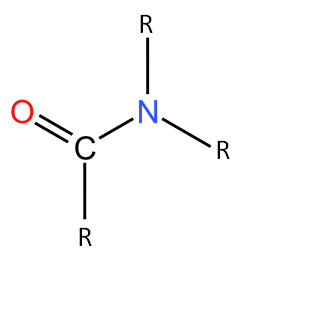
Here R can be any substituent like alkyl group, amide group, hydrogen, etc.
On the basis of the number of carbon groups attached to nitrogen, the amides are classified into three types.
1. Primary Amide
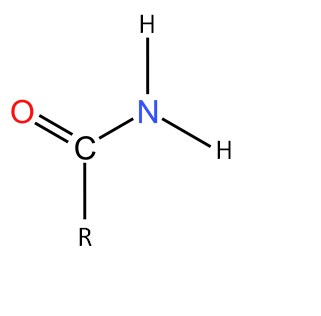
When only one hydrogen is replaced by the amide group it is called primary amide. The examples of primary amide are acetamide $(H_3C—CONH_2)$, benzamide $(C_6H_5—CONH_2)$
2. Secondary Amide

When the second hydrogen of attached to nitrogen is replaced by any alkyl, aryl, or amide group is called a secondary amide. The examples of secondary amides are acetamide $(C_2H_5—CONH—CH_3)$, N,N-dimethylformamide $(H—CON(CH_3)_2)$.
3. Tertiary Amide
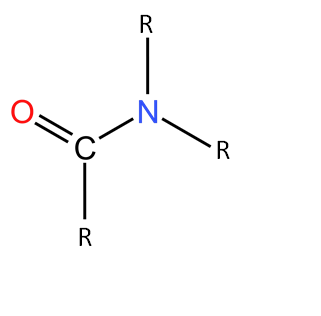
When all Hydrogens connected to Nitrogen are replaced by carbon-containing groups they are called tertiary amides. The examples of tertiary amides are N,N-dimethylacetamide $(CH_3—CON(CH_3)_2)$, N,N-dimethylbenzamide $(C_6H_5—CON(CH_3)_2)$.
In $(RCO)_2NH$ two amide groups and one hydrogen is attached to the nitrogen, the structure of $(RCO)_2NH$ is given as:
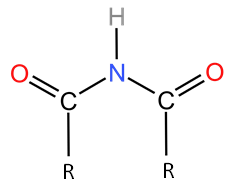
Hence, it is a secondary amide.
Thus, Option (C) is correct
Note: When amide is a part of a protein it is called a peptide bond. Amides are important parts of several compounds like proteins, plastics, nylons, polymers, etc. To prepare amide, coupling of carboxylic acid and amine can be done. They are also prepared by Beckmann rearrangement and Schmidt reaction.
Complete step by step solution: As we know the amide group is-

Here R can be any substituent like alkyl group, amide group, hydrogen, etc.
On the basis of the number of carbon groups attached to nitrogen, the amides are classified into three types.
1. Primary Amide

When only one hydrogen is replaced by the amide group it is called primary amide. The examples of primary amide are acetamide $(H_3C—CONH_2)$, benzamide $(C_6H_5—CONH_2)$
2. Secondary Amide

When the second hydrogen of attached to nitrogen is replaced by any alkyl, aryl, or amide group is called a secondary amide. The examples of secondary amides are acetamide $(C_2H_5—CONH—CH_3)$, N,N-dimethylformamide $(H—CON(CH_3)_2)$.
3. Tertiary Amide

When all Hydrogens connected to Nitrogen are replaced by carbon-containing groups they are called tertiary amides. The examples of tertiary amides are N,N-dimethylacetamide $(CH_3—CON(CH_3)_2)$, N,N-dimethylbenzamide $(C_6H_5—CON(CH_3)_2)$.
In $(RCO)_2NH$ two amide groups and one hydrogen is attached to the nitrogen, the structure of $(RCO)_2NH$ is given as:

Hence, it is a secondary amide.
Thus, Option (C) is correct
Note: When amide is a part of a protein it is called a peptide bond. Amides are important parts of several compounds like proteins, plastics, nylons, polymers, etc. To prepare amide, coupling of carboxylic acid and amine can be done. They are also prepared by Beckmann rearrangement and Schmidt reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




