
Pyrolysis of ethyl acetate gives:
A. \[C{H_3}COC{H_3}\]
B. \[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]
C. \[C{H_2} = C = O\]
D. \[C{H_3} - CHO\]
Answer
241.2k+ views
Hint: Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of a substance at a particular temperature in an inert atmosphere, it involves a change of chemical composition. On decomposition of ester carboxylic acid and ethylene are formed.
Complete step by step answer:
Pyrolysis of ethyl acetate \[\left( {C{H_3}COOC{H_2}C{H_3}} \right)\] gives ethane and acetic acid.
\[\mathop {\left( {C{H_3}COOC{H_2}C{H_3}} \right)}\limits_{\left( {ethyl{\text{ }}acetate} \right)} \xrightarrow[{Pyrolysis}]{\Delta }\mathop {C{H_3}COOH}\limits_{\left( {acetic{\text{ }}acid} \right)} + \mathop {C{H_2} = {\text{ }}C{H_2}}\limits_{\left( {ethylene} \right)} \]
Ethyl acetate is heated in the presence of liquid nitrogen and glass wool.
Pyrolysis reaction is converting esters containing a $\beta - $hydrogen atom into the corresponding carboxylic acid and alkene. The reaction is a unimolecular elimination and operates in a syn-elimination. The mechanism involves a unimolecular six – centered transition state producing equimolar ethylene and acetic acid.
Mechanism of pyrolysis of ethyl acetate
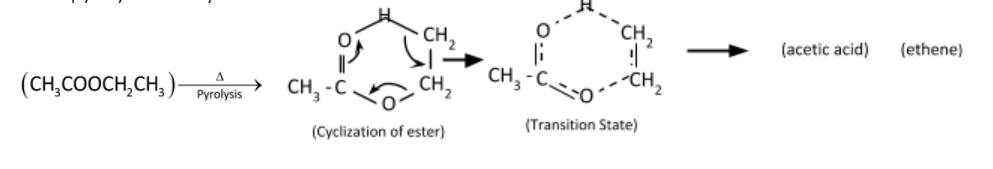
Therefore, the correct option is (D).
Note:
Ethyl acetate is a colorless liquid and is commonly known as ethyl ethanoate. Ethyl acetate is a polar aprotic solvent and it is a standard solvent. It is an important chemical compound. It is used especially for paints, varnishes, lacquers, cleaning and perfumes. The thermal decomposition of ethyl acetate follows a first order unimolecular reaction. The kinetic and thermodynamic parameters are obtained experimentally by applying the Arrhenius equation at a temperature range from $400^\circ $ to $600^\circ $C. The products from the pyrolysis of ethyl acetate were analyzed by gas chromatography.
Complete step by step answer:
Pyrolysis of ethyl acetate \[\left( {C{H_3}COOC{H_2}C{H_3}} \right)\] gives ethane and acetic acid.
\[\mathop {\left( {C{H_3}COOC{H_2}C{H_3}} \right)}\limits_{\left( {ethyl{\text{ }}acetate} \right)} \xrightarrow[{Pyrolysis}]{\Delta }\mathop {C{H_3}COOH}\limits_{\left( {acetic{\text{ }}acid} \right)} + \mathop {C{H_2} = {\text{ }}C{H_2}}\limits_{\left( {ethylene} \right)} \]
Ethyl acetate is heated in the presence of liquid nitrogen and glass wool.
Pyrolysis reaction is converting esters containing a $\beta - $hydrogen atom into the corresponding carboxylic acid and alkene. The reaction is a unimolecular elimination and operates in a syn-elimination. The mechanism involves a unimolecular six – centered transition state producing equimolar ethylene and acetic acid.
Mechanism of pyrolysis of ethyl acetate

Therefore, the correct option is (D).
Note:
Ethyl acetate is a colorless liquid and is commonly known as ethyl ethanoate. Ethyl acetate is a polar aprotic solvent and it is a standard solvent. It is an important chemical compound. It is used especially for paints, varnishes, lacquers, cleaning and perfumes. The thermal decomposition of ethyl acetate follows a first order unimolecular reaction. The kinetic and thermodynamic parameters are obtained experimentally by applying the Arrhenius equation at a temperature range from $400^\circ $ to $600^\circ $C. The products from the pyrolysis of ethyl acetate were analyzed by gas chromatography.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




