
What is produced in a rigid reflecting plane for displacement waves?
A) Beats
B) Node and antinode
C) Antinode
D) Node
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When waves are propagating in the medium with time, it produces displacement on both sides of their direction of propagation. The maximum displacement of waves is called the amplitude. A vibrating rope tied toward one side will create a standing wave, the wave train, subsequent to showing up at the fixed finish of the rope, will be pondered back and superimposed itself as another train of waves in a similar plane. Due to obstruction between the two waves, the resultant abundance of the two waves will be the total of their individual amplitudes.
Complete step by step solution:
We present a figure of displacement wave in which consistently there are positions (N) along the rope, called nodes, at which there is no development by any means. There the two wave trains are consistently in resistance. On either side of a node is a vibrating antinode (A). The antinodes substitute toward uprooting with the goal that the rope at any moment takes after a diagram of the numerical capacity called the sine function.
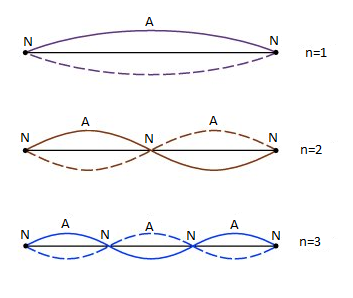
Hence it is clear that when a displacement wave incident at a rigid reflecting surface, makes Nodes and Antinodes. The mode of vibration in the waves depends on the number of nodes and antinodes formed.
Note: The best example of understanding of nodes and antinodes is open and closed organ pipes. Tied string is also an example of understanding nodes and antinodes. The expression of displacement/stationary wave in numeral form is –
\[y = 2a\cos( 2\pi x/\lambda) \sin (2\pi t/T)\]
Where \[x = \]displacement of wave in x-direction
\[\lambda = \] Wavelength of wave
\[t = \] Instant time
\[T = \] Time period of wave
Complete step by step solution:
We present a figure of displacement wave in which consistently there are positions (N) along the rope, called nodes, at which there is no development by any means. There the two wave trains are consistently in resistance. On either side of a node is a vibrating antinode (A). The antinodes substitute toward uprooting with the goal that the rope at any moment takes after a diagram of the numerical capacity called the sine function.

Hence it is clear that when a displacement wave incident at a rigid reflecting surface, makes Nodes and Antinodes. The mode of vibration in the waves depends on the number of nodes and antinodes formed.
Note: The best example of understanding of nodes and antinodes is open and closed organ pipes. Tied string is also an example of understanding nodes and antinodes. The expression of displacement/stationary wave in numeral form is –
\[y = 2a\cos( 2\pi x/\lambda) \sin (2\pi t/T)\]
Where \[x = \]displacement of wave in x-direction
\[\lambda = \] Wavelength of wave
\[t = \] Instant time
\[T = \] Time period of wave
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




