
pH of tomato juice is 4, that means is:
(A) Basic
(B) Acidic
(C) Neutral
(D) None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When there are more hydronium ions present in the solution than hydroxyl ions, the solution is said to be acidic. When there are more hydroxyl ions present in the solution than hydronium ions, then the solution is called a basic solution.
Step by step answer:
- Tomato contains more than more than 10 different types of acids. But out of them, tomatoes have two acids that occur in tomatoes at a very large percentage. These acids are citric acid and malic acid. Tomatoes also contain another essential acid like ascorbic acid, which is better known by its common name vitamin C. Structure of Citric acid and Malic acid is shown below.
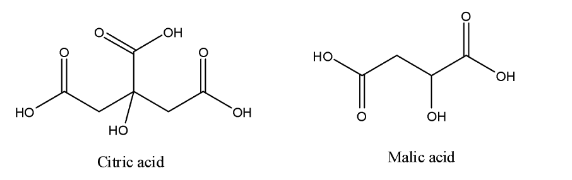
Citric Acid: The most abundant acid that is present in tomatoes is citric acid. Citric acid is slightly less acidic than vinegar.
Malic Acid: The amount of malic acid in a tomato juice is half that of citric acid. We use malic acid in energy production, where it's needed to complete a step in the chain reaction. We should understand that malic acid may help prevent calcium oxalate kidney stones.
- So, we are given that pH of the tomato juice is 4. Now, we know that there is a presence of various types of acid in this juice. So, we can say that the juice will be acidic in nature.
- In addition to that, we can also say that when the pH of any solution is between zero to 7 the solution is said to be an acidic solution. When the pH of the solution increases more than 7, then the solution is termed as a basic solution.
From the above discussion, we can say that tomato juice is acidic.
So, the correct answer is (B) acidic.
Note: Do not get confused between pH and pOH of the solution. Remember that when pH of the solution is between zero to 7, the solution is said to be acidic. When pOH of the solution is between 7 to 14, then the solution is said to be acidic.
Step by step answer:
- Tomato contains more than more than 10 different types of acids. But out of them, tomatoes have two acids that occur in tomatoes at a very large percentage. These acids are citric acid and malic acid. Tomatoes also contain another essential acid like ascorbic acid, which is better known by its common name vitamin C. Structure of Citric acid and Malic acid is shown below.

Citric Acid: The most abundant acid that is present in tomatoes is citric acid. Citric acid is slightly less acidic than vinegar.
Malic Acid: The amount of malic acid in a tomato juice is half that of citric acid. We use malic acid in energy production, where it's needed to complete a step in the chain reaction. We should understand that malic acid may help prevent calcium oxalate kidney stones.
- So, we are given that pH of the tomato juice is 4. Now, we know that there is a presence of various types of acid in this juice. So, we can say that the juice will be acidic in nature.
- In addition to that, we can also say that when the pH of any solution is between zero to 7 the solution is said to be an acidic solution. When the pH of the solution increases more than 7, then the solution is termed as a basic solution.
From the above discussion, we can say that tomato juice is acidic.
So, the correct answer is (B) acidic.
Note: Do not get confused between pH and pOH of the solution. Remember that when pH of the solution is between zero to 7, the solution is said to be acidic. When pOH of the solution is between 7 to 14, then the solution is said to be acidic.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




