
o-xylene when oxidised in presence of \[{{\rm{V}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}\] the product is
A. Benzoic acid
B. Phenylacetic acid
C. Phthalic acid
D. Acetic acid
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Xylene or dimethyl benzene refers to the organic compounds with the formula \[{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}}\right)_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}\]. These originated from the replacement of two hydrogen atoms with methyl groups in a benzene ring.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Xylene has three structural isomers.
The position of hydrogen atoms that are replaced decides which of the three structural isomers is formed.
There is ortho-substituted xylene or xylene or 1,2-dimethylbenzene, para-substituted xylene or p-xylene or 1,3-dimethylbenzene and meta-substituted xylene or m-xylene or 1,4-dimethylbenzene.
Ortho-xylene structure is as follows:
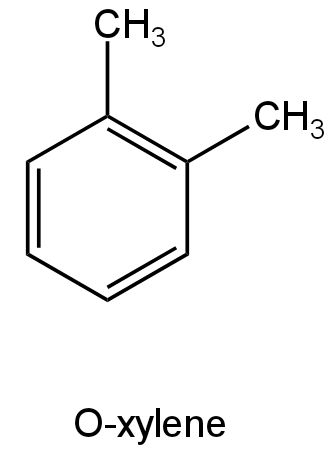
Image: Ortho-xylene
Vanadium(V) oxide or \[{{\rm{V}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}\]has a high oxidation state and behaves as an oxidizing agent.
When it is treated with xylene at 350-400 °C temperature, phthalic anhydride is formed as the product.
Then the phthalic anhydride on treatment with water forms phthalic acid.
The reaction occurs as follows:
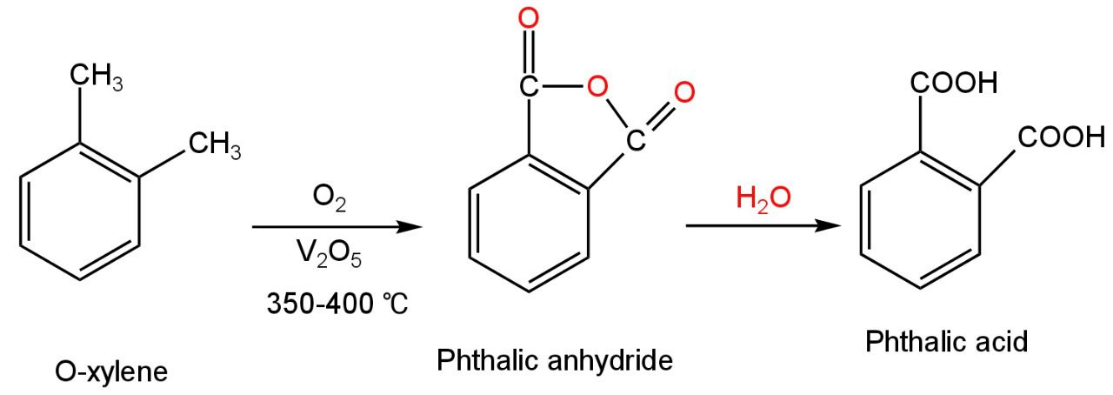
Image: Oxidation of o-xylene.
The oxidation of o-xylene in presence of vanadium(V) oxide does not produce benzoic acid or phenylacetic acid or acetic acid.
So, options A, B, and D are incorrect.
So, option C is correct.
Additional Information: Xylene is an uncoloured, explosive, little greasy liquid of tremendous industrial value.
Significant usage of vanadium(V) oxide is the manufacture of sulfuric acid.
Vanadium(V) oxide performs the important objective of catalysing the oxidation of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide by air in the contact process:\[{\rm{2S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ + }}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}} \to {\rm{2S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
Note: While attending to the question, one must have a clear idea about the structure of o-xylene. This compound of oxidation produces phthalic anhydride which on hydrolysis produces phthalic acid.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Xylene has three structural isomers.
The position of hydrogen atoms that are replaced decides which of the three structural isomers is formed.
There is ortho-substituted xylene or xylene or 1,2-dimethylbenzene, para-substituted xylene or p-xylene or 1,3-dimethylbenzene and meta-substituted xylene or m-xylene or 1,4-dimethylbenzene.
Ortho-xylene structure is as follows:

Image: Ortho-xylene
Vanadium(V) oxide or \[{{\rm{V}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}\]has a high oxidation state and behaves as an oxidizing agent.
When it is treated with xylene at 350-400 °C temperature, phthalic anhydride is formed as the product.
Then the phthalic anhydride on treatment with water forms phthalic acid.
The reaction occurs as follows:

Image: Oxidation of o-xylene.
The oxidation of o-xylene in presence of vanadium(V) oxide does not produce benzoic acid or phenylacetic acid or acetic acid.
So, options A, B, and D are incorrect.
So, option C is correct.
Additional Information: Xylene is an uncoloured, explosive, little greasy liquid of tremendous industrial value.
Significant usage of vanadium(V) oxide is the manufacture of sulfuric acid.
Vanadium(V) oxide performs the important objective of catalysing the oxidation of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide by air in the contact process:\[{\rm{2S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ + }}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}} \to {\rm{2S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
Note: While attending to the question, one must have a clear idea about the structure of o-xylene. This compound of oxidation produces phthalic anhydride which on hydrolysis produces phthalic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




