
Out of soft iron and steel which has more coercivity, less retentivity.
(A) Iron
(B) Steel
(C) Both are equal
(D) Can’t say
Answer
240k+ views
Hint: First of all define the terms retentivity and coercivity. Then use the hysteresis curve of both soft iron and steel.
Retentivity is the amount of magnetization left when an external magnetizing field is removed. Coercivity is the reverse external magnetizing field which is required to demagnetize the substance completely.
Complete solution:
Hysteresis curve shows the pattern of change in the value magnetising force (H) with magnetic flux density (B). The area under hysteresis loop represents the loss in energy in one complete cycle of magnetising and demagnetising of a magnetic material.
With increase in the value of the magnetic field, there is an increase in the value of magnetism. When the values of B and H are zero then substance retains some amount of magnetism known as residual magnetism. The force required to remove the residual magnetism is known as Coercive force.
Hysteresis curve of steel is shown in figure (a) and the hysteresis curve of soft iron is shown in figure (b).
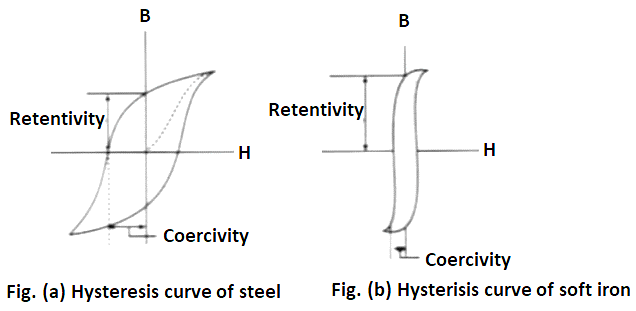
From the above figures it is clear that the steel has more coercivity and less retentivity as compared to the soft iron.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct choice.
Note: Retentivity of steel is more than the retentivity of soft iron. Soft iron is easily magnetized and demagnetized as compared to steel. The coercivity of soft iron is less than that of the coercivity of the steel. Energy loss in soft iron is less than energy loss in steel because of the small area of soft iron ( ${\text{B - H}}$ ) curve.
Retentivity is the amount of magnetization left when an external magnetizing field is removed. Coercivity is the reverse external magnetizing field which is required to demagnetize the substance completely.
Complete solution:
Hysteresis curve shows the pattern of change in the value magnetising force (H) with magnetic flux density (B). The area under hysteresis loop represents the loss in energy in one complete cycle of magnetising and demagnetising of a magnetic material.
With increase in the value of the magnetic field, there is an increase in the value of magnetism. When the values of B and H are zero then substance retains some amount of magnetism known as residual magnetism. The force required to remove the residual magnetism is known as Coercive force.
Hysteresis curve of steel is shown in figure (a) and the hysteresis curve of soft iron is shown in figure (b).

From the above figures it is clear that the steel has more coercivity and less retentivity as compared to the soft iron.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct choice.
Note: Retentivity of steel is more than the retentivity of soft iron. Soft iron is easily magnetized and demagnetized as compared to steel. The coercivity of soft iron is less than that of the coercivity of the steel. Energy loss in soft iron is less than energy loss in steel because of the small area of soft iron ( ${\text{B - H}}$ ) curve.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

The radius of two metallic sphere A and B are r1 and class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

If a wire of resistance R is stretched to double of class 12 physics JEE_Main

JEE Main Correction Window 2026 Session 1 Dates Announced - Edit Form Details, Dates and Link

Free Radical Substitution and Its Stepwise Mechanism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 1 (55/1/1) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Marking Scheme

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/5/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 2 (55/1/2) 2025 – PDF, Answer Key, & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions




