
Ortho-hydrogen and para-hydrogen resembles in which of the following property
A. Thermal conductivity
B. Magnetic properties
C. Chemical properties
D. Heat capacity
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Ortho- hydrogen has parallel nuclear spins whereas para- hydrogen has Anti parallel spins. Due to having two parallel spins, ortho- hydrogen has an overall nuclear spin of $1$ and para-hydrogen has an overall nuclear spin-zero. Ortho-hydrogen and parahydrogen both have different physical properties.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The hydrogen (H) atoms have one proton inside the nucleus and one electron rotates around it. Proton also spins around its axis like an electron. If the protons of two H atoms of ${{H}_{2}}$ molecule rotate in the same direction then they are called ortho-hydrogen. When the protons of two hydrogens rotate in opposite directions then they are called para-hydrogen. Ortho and para-hydrogen are spin isomers of the molecular dihydrogen. At ${{0}^{{\mathrm O}}}K$hydrogen consists mainly of para-hydrogen and para-hydrogen is more stable than ortho-hydrogen. Ordinary hydrogen is an equilibrium mixture of both ortho and para hydrogen.
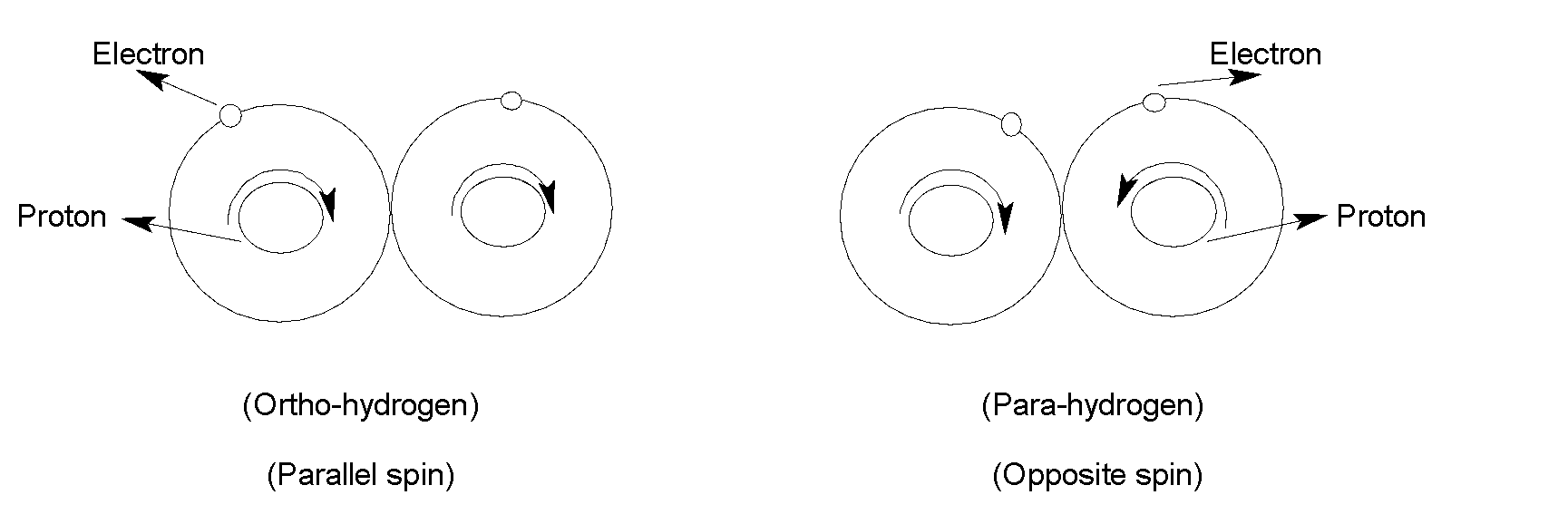
Ortho-hydrogen has an overall spin$=\left( +\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2} \right)=1$
And para-hydrogen has an overall spin $=\left( +\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2} \right)=0$
That is ortho hydrogen is in a triplet state as its overall nuclear spin is $1$ and para-hydrogen is in a singlet state as it has zero nuclear spins.
They have different nuclear energies due to differences in an overall nuclear spin. For this property, ortho-H and para-H have different physical properties such as thermal conductivity, heat capacity, boiling point, etc. But they have similar chemical properties because their electronic configuration is similar.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Para hydrogen can be converted into ortho-hydrogen in many different ways such as by passing an electric charge, by heating at a temperature greater than ${{800}^{{\mathrm O}}}C$, by treating with catalysis iron or platinum metal, by mixing with paramagnetic molecules such as NO, ${{O}_{2}}$ etc.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The hydrogen (H) atoms have one proton inside the nucleus and one electron rotates around it. Proton also spins around its axis like an electron. If the protons of two H atoms of ${{H}_{2}}$ molecule rotate in the same direction then they are called ortho-hydrogen. When the protons of two hydrogens rotate in opposite directions then they are called para-hydrogen. Ortho and para-hydrogen are spin isomers of the molecular dihydrogen. At ${{0}^{{\mathrm O}}}K$hydrogen consists mainly of para-hydrogen and para-hydrogen is more stable than ortho-hydrogen. Ordinary hydrogen is an equilibrium mixture of both ortho and para hydrogen.

Ortho-hydrogen has an overall spin$=\left( +\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2} \right)=1$
And para-hydrogen has an overall spin $=\left( +\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2} \right)=0$
That is ortho hydrogen is in a triplet state as its overall nuclear spin is $1$ and para-hydrogen is in a singlet state as it has zero nuclear spins.
They have different nuclear energies due to differences in an overall nuclear spin. For this property, ortho-H and para-H have different physical properties such as thermal conductivity, heat capacity, boiling point, etc. But they have similar chemical properties because their electronic configuration is similar.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Para hydrogen can be converted into ortho-hydrogen in many different ways such as by passing an electric charge, by heating at a temperature greater than ${{800}^{{\mathrm O}}}C$, by treating with catalysis iron or platinum metal, by mixing with paramagnetic molecules such as NO, ${{O}_{2}}$ etc.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




