
How is nitromethane prepared from
(i) $\alpha - $chloro sodium acetate
(ii) $\alpha - $nitro isobutylene?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Nitroalkanes can be obtained by treating alkyl halides with silver nitrate in alcoholic solution. Hydrolysis of $\alpha - $nitro alkene can produce nitromethane.
Complete step by step solution:
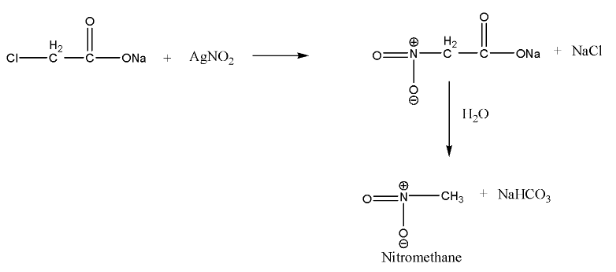
When $\alpha-$ chloro sodium acetate is treated with silver nitrate, the chlorine gets replaced by the nitro group and $\alpha - $nitro sodium acetate is formed, which undergoes hydrolysis to give nitro methane and sodium bicarbonate as a by-product.
This reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Since silver nitrite is predominantly covalent, only nitrogen pairs are available for bond formation. Hence, on adding $AgN{O_2}$, the attack of $NO_2^- $ takes place mainly through nitrogen and a nitroalkane is obtained as the major product.
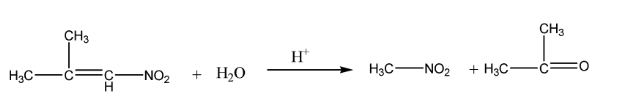
$\alpha - $nitro isobutylene undergoes hydrolysis in an acidic medium to give nitromethane and acetone.
Note: When $\alpha - $ chloro sodium acetate is treated with silver nitrate, some alkyl nitrate is also formed ($20-30\% $) in the reaction along with nitroalkane. This is because$NO_2^-$ ion is an ambident nucleophile and can attack the alkyl halide through nitrogen as well as through oxygen. If $\alpha -$ chloro sodium acetate is treated with $NaN{O_2}$ or $KN{O_2}$ in place of $AgN{O_2}$, the main product will be alkyl nitrite. Nitroalkenes do not undergo hydrolysis in the basic medium to form nitromethane.
Complete step by step solution:
When $\alpha-$ chloro sodium acetate is treated with silver nitrate, the chlorine gets replaced by the nitro group and $\alpha - $nitro sodium acetate is formed, which undergoes hydrolysis to give nitro methane and sodium bicarbonate as a by-product.
This reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Since silver nitrite is predominantly covalent, only nitrogen pairs are available for bond formation. Hence, on adding $AgN{O_2}$, the attack of $NO_2^- $ takes place mainly through nitrogen and a nitroalkane is obtained as the major product.

$\alpha - $nitro isobutylene undergoes hydrolysis in an acidic medium to give nitromethane and acetone.

Note: When $\alpha - $ chloro sodium acetate is treated with silver nitrate, some alkyl nitrate is also formed ($20-30\% $) in the reaction along with nitroalkane. This is because$NO_2^-$ ion is an ambident nucleophile and can attack the alkyl halide through nitrogen as well as through oxygen. If $\alpha -$ chloro sodium acetate is treated with $NaN{O_2}$ or $KN{O_2}$ in place of $AgN{O_2}$, the main product will be alkyl nitrite. Nitroalkenes do not undergo hydrolysis in the basic medium to form nitromethane.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




