
What is Markovnikov’s rule? Explain with an example.
Answer
531.7k+ views
Hint: We should know that Markovnikov’s rule is an empirical rule which is used to predict regioselectivity of electrophilic addition reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Keeping the purpose in mind, we need to describe the mechanism of Markovnikov's rule.
Complete step by step solution:
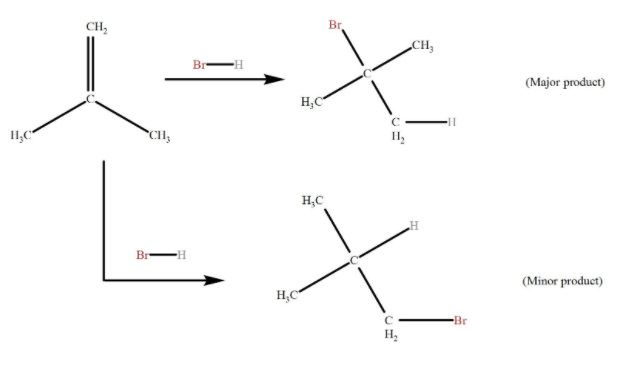
The Markovnikov’s rule states that with the addition of a protic acid HX to an asymmetric alkene, the acid hydrogen (H) gets attached to the carbon with more hydrogen substituents, and the halide (X) group gets attached to the carbon with more alkyl substituents.
Let us explain Markovnikov's rule with the help of a simple example.
When a protic acid HC (X = Cl, Br, I) is added to an asymmetrically substituted alkene, addition of acidic hydrogen takes place at the less substituted carbon atom of the double bond, while X is added to the more alkyl substituted carbon atom. In other words, hydrogen is added to the carbon atom with more number of hydrogen atoms attached to it and halide is added to the carbon with the least number of hydrogen atoms.
We should know that the driving force behind the reaction is the formation of carbocation in addition of H to the alkene, in the first step of the reaction. The most stable carbocation is formed when H is added to carbon having more number of hydrogen atoms already attached, due to factors like induction and hyperconjugation, which gives the major product with Br added to less hydrogen rich carbon.
Less stable carbocation (H added to less hydrogen rich carbon) is also present in small quantities, forming minor products in addition to Br to carbon having more hydrogen attached.
Note: There are various practical applications of Markovnikov’s rule. Some of them are Halohydrin formation (in alcohol and water), Oxymercurationand Demercuration and Acid catalysed hydration. These reactions are the laboratory usages of Markovnikov’s rule and are used in a variety of chemical processes.
Complete step by step solution:
The Markovnikov’s rule states that with the addition of a protic acid HX to an asymmetric alkene, the acid hydrogen (H) gets attached to the carbon with more hydrogen substituents, and the halide (X) group gets attached to the carbon with more alkyl substituents.
Let us explain Markovnikov's rule with the help of a simple example.
When a protic acid HC (X = Cl, Br, I) is added to an asymmetrically substituted alkene, addition of acidic hydrogen takes place at the less substituted carbon atom of the double bond, while X is added to the more alkyl substituted carbon atom. In other words, hydrogen is added to the carbon atom with more number of hydrogen atoms attached to it and halide is added to the carbon with the least number of hydrogen atoms.
We should know that the driving force behind the reaction is the formation of carbocation in addition of H to the alkene, in the first step of the reaction. The most stable carbocation is formed when H is added to carbon having more number of hydrogen atoms already attached, due to factors like induction and hyperconjugation, which gives the major product with Br added to less hydrogen rich carbon.
Less stable carbocation (H added to less hydrogen rich carbon) is also present in small quantities, forming minor products in addition to Br to carbon having more hydrogen attached.

Note: There are various practical applications of Markovnikov’s rule. Some of them are Halohydrin formation (in alcohol and water), Oxymercurationand Demercuration and Acid catalysed hydration. These reactions are the laboratory usages of Markovnikov’s rule and are used in a variety of chemical processes.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




