
Main Products formed during a reaction of 1-methoxy naphthalene with hydroiodic acid are:
A.
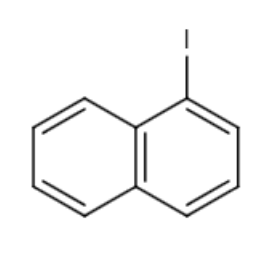 and CH3I
and CH3I
B.
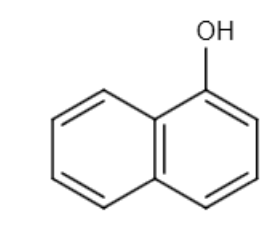 and CH3OH
and CH3OH
C.
 and CH3OH
and CH3OH
D.
 and CH3I
and CH3I
Answer
242.4k+ views
Hint: Here, in this question, 1-methoxy naphthalene is given. It reacts with hydroiodic acid. First of all, hydrogen ions react with 1-methoxy naphthalene followed by iodide ions.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The structure of 1-methoxy naphthalene is as follows:
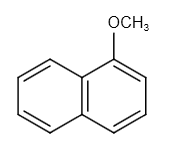
1-methoxy naphthalene reacts with hydrogen ion as follows:
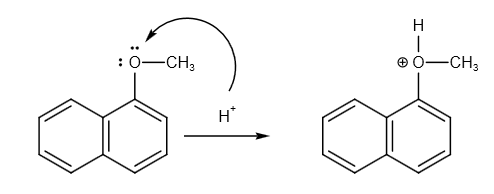
Hydrogen ions attack oxygen and bind with oxygen.
It will further react with iodine ion as follows:
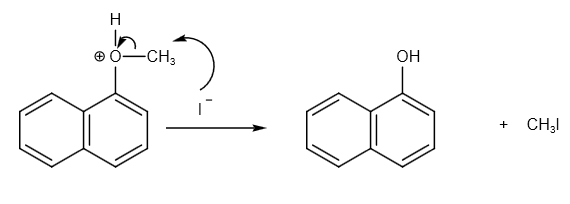
The carbon and oxygen bond breaks and iodine ions attack carbon to form methyl iodide.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Additional Information:
The odour of naphthalene, a white, crystalline volatile substance, is often compared to that of mothballs. The substance slowly sublimes (changes from a solid to a gas) at room temperature, producing a vapour that is extremely combustible. The structure of naphthalene can be used to predict how soluble it is in water. A polyatomic hydrocarbon is naphthene. It is a hydrophobic molecule since it contains a lot of carbon atoms. The hydrophobic nature of this naphthalene makes it insoluble in water. The liquid nature of naphthalene is not thoroughly covered in this article. In 1-methoxy naphthalene, there is one hydrogen of naphthalene substituted by the methyl group.
Note: We must keep in mind that hydrogen iodide is a halide of hydrogen and a diatomic molecule. Aqueous solutions of HI are also referred to as hydroiodic acid, a solid acid. Hydroiodic acid and hydrogen iodide, however, are different in that the former is a gas under normal circumstances while the latter is an aqueous gas solution.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The structure of 1-methoxy naphthalene is as follows:

1-methoxy naphthalene reacts with hydrogen ion as follows:

Hydrogen ions attack oxygen and bind with oxygen.
It will further react with iodine ion as follows:

The carbon and oxygen bond breaks and iodine ions attack carbon to form methyl iodide.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Additional Information:
The odour of naphthalene, a white, crystalline volatile substance, is often compared to that of mothballs. The substance slowly sublimes (changes from a solid to a gas) at room temperature, producing a vapour that is extremely combustible. The structure of naphthalene can be used to predict how soluble it is in water. A polyatomic hydrocarbon is naphthene. It is a hydrophobic molecule since it contains a lot of carbon atoms. The hydrophobic nature of this naphthalene makes it insoluble in water. The liquid nature of naphthalene is not thoroughly covered in this article. In 1-methoxy naphthalene, there is one hydrogen of naphthalene substituted by the methyl group.
Note: We must keep in mind that hydrogen iodide is a halide of hydrogen and a diatomic molecule. Aqueous solutions of HI are also referred to as hydroiodic acid, a solid acid. Hydroiodic acid and hydrogen iodide, however, are different in that the former is a gas under normal circumstances while the latter is an aqueous gas solution.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




