
When ${ KMnO }_{ 4 }$ is reduced with oxalic acid in an acidic solution, the oxidation number of Mn changes from:
(A) +2 to +7
(B) +4 to +7
(C) +7 to +2
(D) +6 and +2
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Oxidation number is the residual charge which a molecule has or seems to have when different elements are taken out as ions by counting the number of shared electrons.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The reaction involved between potassium permanganate and oxalic acid is given below;
${ 2KMnO }_{ 4 }{ +5H }_{ 2 }{ C }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 4 }{ +3H }_{ 2 }{ SO }_{ 4 }{ \rightarrow K }_{ 2 }{ SO }_{ 4 }{ +2MnSO }_{ 4 }{ +10CO }_{ 2 }{ +8H }_{ 2 }{ O }$
Firstly, assign the oxidation number of Manganese:
Let, the oxidation number of Mn is ‘x’.
The oxidation number of ${ SO }_{ 4 }^{ 2- }$ = ${ x+4\times (-2)=-2 }$
x = ${ +6 }$
and K = ${ +1 }$
Now, for ${ KMnO }_{ 4 }$, we can calculate;
${ 1+ x + 4\times(-2) = 0 }$
${ x +1 - 8 = 0 }$
${ x -7 = 0 }$
x = ${ +7 }$
In ${ MnSO }_{ 4 }$, x + (-2) = 0
x = ${ +2 }$
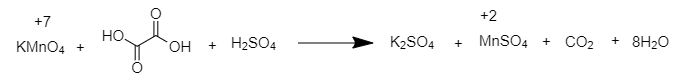
Therefore, When ${ KMnO }_{ 4 }$ is reduced with oxalic acid in acidic solution, the oxidation number of Mn changes from ${ +7 }$ to ${ +2 }$.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Additional Information:
(i) ${ KMnO }_{ 4 }$ is a deep purple crystalline solid which gives deep purple color to the solution when dissolved in water.
(ii) It is also a strong oxidizing agent, and hence widely used as an oxidizing agent in organic chemistry.
(iii) It is capable of destroying organic impurities and hence also used to purify impure water in well and ponds.
(iv) Oxalic acid: It is a colorless crystalline solid that dissolves in water to give colorless solutions. It is a weak acid and is used as a bleaching agent, cleanser rust remover, etc.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option D. But the oxidation state of S in ${ SO }_{ 4 }^{ 2- }$ is +6 while the oxidation state of Mn in ${ KMnO }_{ 4 }$ is ${ +7 }$, not ${ +6 }$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The reaction involved between potassium permanganate and oxalic acid is given below;
${ 2KMnO }_{ 4 }{ +5H }_{ 2 }{ C }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 4 }{ +3H }_{ 2 }{ SO }_{ 4 }{ \rightarrow K }_{ 2 }{ SO }_{ 4 }{ +2MnSO }_{ 4 }{ +10CO }_{ 2 }{ +8H }_{ 2 }{ O }$
Firstly, assign the oxidation number of Manganese:
Let, the oxidation number of Mn is ‘x’.
The oxidation number of ${ SO }_{ 4 }^{ 2- }$ = ${ x+4\times (-2)=-2 }$
x = ${ +6 }$
and K = ${ +1 }$
Now, for ${ KMnO }_{ 4 }$, we can calculate;
${ 1+ x + 4\times(-2) = 0 }$
${ x +1 - 8 = 0 }$
${ x -7 = 0 }$
x = ${ +7 }$
In ${ MnSO }_{ 4 }$, x + (-2) = 0
x = ${ +2 }$

Therefore, When ${ KMnO }_{ 4 }$ is reduced with oxalic acid in acidic solution, the oxidation number of Mn changes from ${ +7 }$ to ${ +2 }$.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Additional Information:
(i) ${ KMnO }_{ 4 }$ is a deep purple crystalline solid which gives deep purple color to the solution when dissolved in water.
(ii) It is also a strong oxidizing agent, and hence widely used as an oxidizing agent in organic chemistry.
(iii) It is capable of destroying organic impurities and hence also used to purify impure water in well and ponds.
(iv) Oxalic acid: It is a colorless crystalline solid that dissolves in water to give colorless solutions. It is a weak acid and is used as a bleaching agent, cleanser rust remover, etc.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option D. But the oxidation state of S in ${ SO }_{ 4 }^{ 2- }$ is +6 while the oxidation state of Mn in ${ KMnO }_{ 4 }$ is ${ +7 }$, not ${ +6 }$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




