
Inorganic benzene is:
(A) \[{B_3}{N_6}{H_3}\]
(B) \[{B_3}{N_3}{H_6}\]
(C) \[A{l_3}{N_3}{H_6}\]
(D) None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The chemical name of inorganic benzene is borazine. It is a cyclic structure involving two atoms of p-block elements. It has similar chemical reactivity as benzene.
Complete step by step solution:
Here is the structure of Borazine which is known as inorganic benzene.
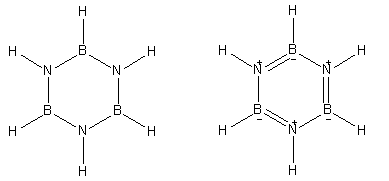
Both of the structures shown here are of borazine. It has boron, nitrogen and hydrogen atoms in its constitution.
- Borazine is known as inorganic benzene because it is made up of inorganic atoms and has similar reactivity as organic compound benzene. In its neutral structure, borazine has six hydrogen atoms directly bonded to the three nitrogen and three boron atoms.
- Borazine gives a secondary structure that involves three double bonds in the ring and positive and negative charges on nitrogen and boron atoms respectively.
- Borazine can give additional reactions as benzene can give. In fact some reactions like addition of bromine to the ring can be done without the requirement of a catalyst.
- Borazine also follows the Huckel rule, hence it is also aromatic, however it has some difference in comparison with benzene because it involves two atoms with different electronegativity.
- It does not involve Aluminium in its structure. It just has boron and nitrogen atoms arranges alternatively in the ring. So,its chemical formula is \[{{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}\].
Note: Do not consider that inorganic benzene has three hydrogen atoms as it will not fulfil the valency of the atoms. Make sure that the structure that you think of borazine should be able to give chemical reactions like benzene, the only structure possible is the answer.
Complete step by step solution:
Here is the structure of Borazine which is known as inorganic benzene.

Both of the structures shown here are of borazine. It has boron, nitrogen and hydrogen atoms in its constitution.
- Borazine is known as inorganic benzene because it is made up of inorganic atoms and has similar reactivity as organic compound benzene. In its neutral structure, borazine has six hydrogen atoms directly bonded to the three nitrogen and three boron atoms.
- Borazine gives a secondary structure that involves three double bonds in the ring and positive and negative charges on nitrogen and boron atoms respectively.
- Borazine can give additional reactions as benzene can give. In fact some reactions like addition of bromine to the ring can be done without the requirement of a catalyst.
- Borazine also follows the Huckel rule, hence it is also aromatic, however it has some difference in comparison with benzene because it involves two atoms with different electronegativity.
- It does not involve Aluminium in its structure. It just has boron and nitrogen atoms arranges alternatively in the ring. So,its chemical formula is \[{{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}\].
Note: Do not consider that inorganic benzene has three hydrogen atoms as it will not fulfil the valency of the atoms. Make sure that the structure that you think of borazine should be able to give chemical reactions like benzene, the only structure possible is the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




