
In the reaction,
\[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{OH}} \overset{NaOH}{\rightarrow} (A) \overset{CO_{2}}{\rightarrow} (B)\overset{HCl}{\rightarrow} (C)\], the compound (C) is,
A. Benzoic acid
B. Salicylaldehyde
C. Chlorobenzene
D. Salicylic acid
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:/ Kolbe’s reaction is the reaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide in an acidic medium. Here, we must understand Kolbe's reaction in detail to identify the product obtained in the given reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will understand what Kolbe’s reaction is. Kolbe's reaction is the conversion of phenol into salicylic acid. In the first step, phenol is converted into phenoxide ion by reacting it with sodium hydroxide. In the second step, the reaction of phenoxide ions with carbon dioxide gives sodium salicylate. And the reaction of sodium salicylate with HCl gives salicylic acid.
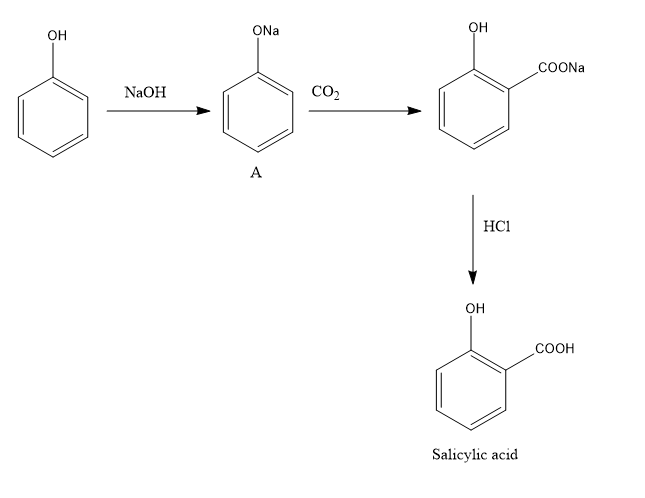
Fig: Kolbe’s reaction
Therefore, the product C obtained is salicylic acid. Hence, option D is right.
Additional Information: Let’s understand another important reaction of phenol, that is, the Riemer-Tiemann reaction. In this reaction, phenol to salicylaldehyde conversion takes place by reacting phenol with chloroform along with sodium hydroxide in the first step. In the second step, the formed intermediate again undergoes a reaction with sodium hydroxide in the acidic medium. The product formed in the reaction is salicylaldehyde.
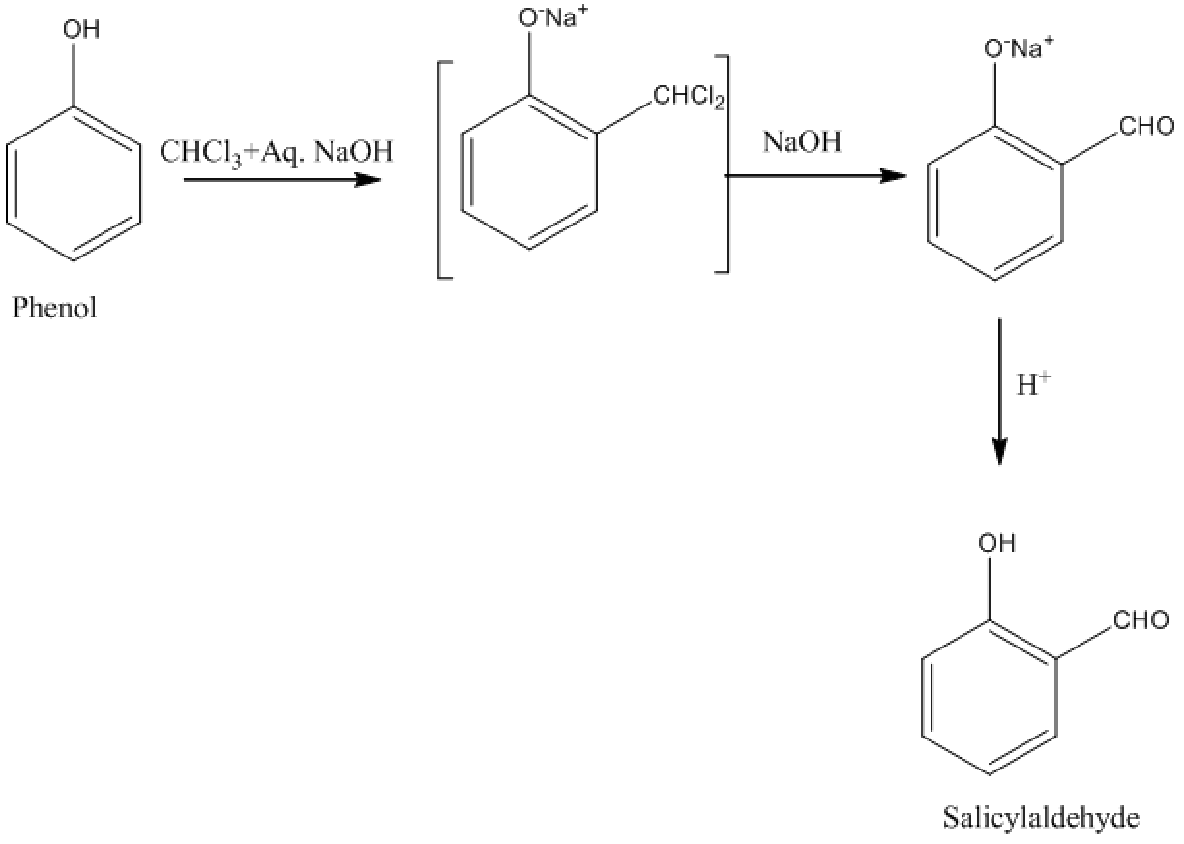
Fig: Riemer-Tiemann reaction
Note: Salicylic acid has some useful application in our everyday life. It treats acne by reducing redness and swelling. It blocked skin pores to shrink pimples. It is also useful for its application in loosening and softening dry, thickened skin. But frequent uses of salicylic acid may cause skin irritation.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will understand what Kolbe’s reaction is. Kolbe's reaction is the conversion of phenol into salicylic acid. In the first step, phenol is converted into phenoxide ion by reacting it with sodium hydroxide. In the second step, the reaction of phenoxide ions with carbon dioxide gives sodium salicylate. And the reaction of sodium salicylate with HCl gives salicylic acid.

Fig: Kolbe’s reaction
Therefore, the product C obtained is salicylic acid. Hence, option D is right.
Additional Information: Let’s understand another important reaction of phenol, that is, the Riemer-Tiemann reaction. In this reaction, phenol to salicylaldehyde conversion takes place by reacting phenol with chloroform along with sodium hydroxide in the first step. In the second step, the formed intermediate again undergoes a reaction with sodium hydroxide in the acidic medium. The product formed in the reaction is salicylaldehyde.

Fig: Riemer-Tiemann reaction
Note: Salicylic acid has some useful application in our everyday life. It treats acne by reducing redness and swelling. It blocked skin pores to shrink pimples. It is also useful for its application in loosening and softening dry, thickened skin. But frequent uses of salicylic acid may cause skin irritation.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




