
In the reaction ${C_6}{H_6}\xrightarrow{{C{H_3}Cl/AlC{l_3}}}A\xrightarrow{{KMn{O_4}}}B$, B is :
a.) benzoic acid
b.) benzoyl chloride
c.) benzaldehyde
d.) chlorobenzene
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The first reagent given is the methyl chloride in the presence of aluminium trichloride. It functions in alkylation of the compound while the second reagent functions in oxidation of the compound. The answer to this question is a carboxylic acid with molecular mass 122 g. This is because the ultimate product of oxidation of alkyl is the acid.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us move step by step in the reaction to get the correct product.
We have the initial reactant benzene. We know that benzene is electron rich in nature. It is even highly stable due to resonance and thus it does not let resonance chain break. So, it does not give addition reactions.
It can very easily give aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions.
The first reagent is the methyl chloride in the presence of aluminium trichloride. It is an alkylation reaction where benzene gets converted into toluene and HCl is released as a byproduct. The A product formed is toluene. This reaction is Friedel Crafts alkylation. The reaction can be written as -
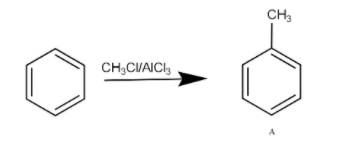
This reaction involves following mechanism-
The methyl chloride reacts with aluminium chloride to give $ \oplus C{H_3}$carbocation. This methyl carbocation is an electrophile and this gets attached to benzene.
$C{H_3}Cl + AlC{l_3} \to \oplus C{H_3}$

This carbocation is stabilised by resonance as-
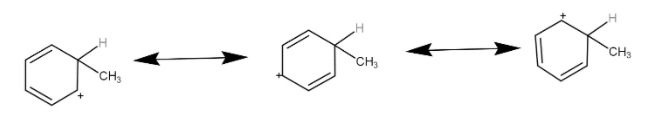
The hydrogen is eliminated restoring resonance.
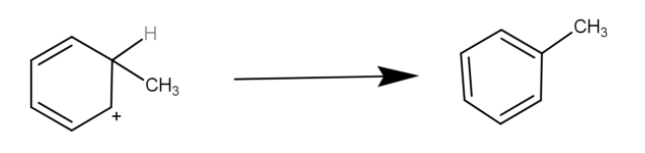
The second reagent that acts on toluene is potassium permanganate. The potassium permanganate is used for oxidation and here also, it does oxidation of the methyl group of toluene.
The oxidation is the addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen. Here, the oxygen will get bonded with carbon and result in the formation of Benzoic acid. The benzoic acid is the product B.
The answer can-not be benzaldehyde because the potassium permanganate is a very strong reagent and it converts the benzaldehyde formed into benzoic acid. Firstly, from toluene benzaldehyde is formed which later gets converted into benzoic acid.
The reaction for this is as -
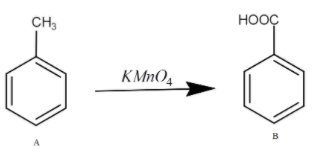
So, the answer is option a.)
Note: It must be noted that alkylation means the addition of alkyl groups. As here, the reagent was methyl chloride; this means the reagent had a methyl group. So, the methylation occurred. If it would have been ethyl chloride along with aluminium trichloride, the ethylation would have occurred.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us move step by step in the reaction to get the correct product.
We have the initial reactant benzene. We know that benzene is electron rich in nature. It is even highly stable due to resonance and thus it does not let resonance chain break. So, it does not give addition reactions.
It can very easily give aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions.
The first reagent is the methyl chloride in the presence of aluminium trichloride. It is an alkylation reaction where benzene gets converted into toluene and HCl is released as a byproduct. The A product formed is toluene. This reaction is Friedel Crafts alkylation. The reaction can be written as -

This reaction involves following mechanism-
The methyl chloride reacts with aluminium chloride to give $ \oplus C{H_3}$carbocation. This methyl carbocation is an electrophile and this gets attached to benzene.
$C{H_3}Cl + AlC{l_3} \to \oplus C{H_3}$

This carbocation is stabilised by resonance as-

The hydrogen is eliminated restoring resonance.

The second reagent that acts on toluene is potassium permanganate. The potassium permanganate is used for oxidation and here also, it does oxidation of the methyl group of toluene.
The oxidation is the addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen. Here, the oxygen will get bonded with carbon and result in the formation of Benzoic acid. The benzoic acid is the product B.
The answer can-not be benzaldehyde because the potassium permanganate is a very strong reagent and it converts the benzaldehyde formed into benzoic acid. Firstly, from toluene benzaldehyde is formed which later gets converted into benzoic acid.
The reaction for this is as -

So, the answer is option a.)
Note: It must be noted that alkylation means the addition of alkyl groups. As here, the reagent was methyl chloride; this means the reagent had a methyl group. So, the methylation occurred. If it would have been ethyl chloride along with aluminium trichloride, the ethylation would have occurred.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




