
In the given figure, 0 is the centre of regular pentagon ABCDE. Five forces each of
magnitude $\mathrm{F}_{0}$ are acted as shown in figure. The resultant force is
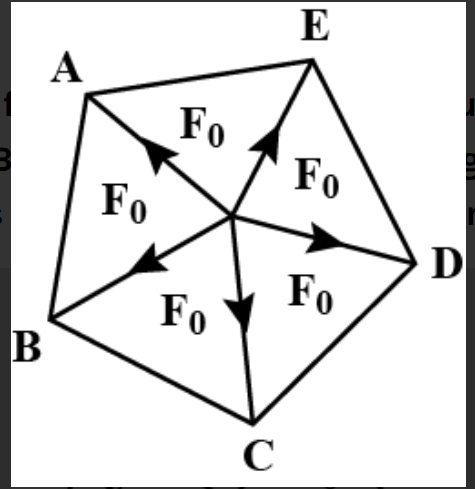
(A) $5 F_{0}$
(B) $5 F_{0} \cos 72^{\circ}$
(C) $5 F_{0} \sin 72^{\circ}$
(D) zero
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We know that the net force is the vector sum of all the forces acting on an object. When an object is in equilibrium (either at rest or moving with constant velocity), the net force acting on it is zero. A vector can only have zero magnitude if all of its components are zero. The action from a force can cause an object to move or speed up (accelerate), to slow down (decelerate), to stop, or to change direction. Since any change in velocity is considered acceleration, it can be said that a force on an object results in the acceleration of an object.
Complete step by step answer
When two or more forces act on an object, the resultant force can be found by adding up the individual forces. A resultant force is the single force and associated torque obtained by combining a system of forces and torques acting on a rigid body. The defining feature of a resultant force, or resultant force-torque, is that it has the same effect on the rigid body as the original system of forces.
According to Newton's First Law of motion, an object remains in the same state of motion unless a resultant force acts on it. If the resultant force on an object is zero, this means: a stationary object stays stationary. a moving object continues to move at the same velocity.
All forces are acting at an equal angle with each other and completing 360 degrees and are of the same magnitude so their resultant will be zero.
So, the correct answer is option D.
Note: We can conclude that the resultant is the vector sum of all the individual vectors. The resultant is the result of combining the individual vectors together. The resultant can be determined by adding the individual forces together using vector addition methods. Net force, also known as resultant force, is a vector quantity produced when two or more forces act upon one object. The concept of net force is the same as the mathematical concept of vector addition. When two forces acting on an object are equal in size but act in opposite directions, we say that they are balanced forces. A stationary object stays still. a moving object continues to move at the same speed and in the same direction.
Complete step by step answer
When two or more forces act on an object, the resultant force can be found by adding up the individual forces. A resultant force is the single force and associated torque obtained by combining a system of forces and torques acting on a rigid body. The defining feature of a resultant force, or resultant force-torque, is that it has the same effect on the rigid body as the original system of forces.
According to Newton's First Law of motion, an object remains in the same state of motion unless a resultant force acts on it. If the resultant force on an object is zero, this means: a stationary object stays stationary. a moving object continues to move at the same velocity.
All forces are acting at an equal angle with each other and completing 360 degrees and are of the same magnitude so their resultant will be zero.
So, the correct answer is option D.
Note: We can conclude that the resultant is the vector sum of all the individual vectors. The resultant is the result of combining the individual vectors together. The resultant can be determined by adding the individual forces together using vector addition methods. Net force, also known as resultant force, is a vector quantity produced when two or more forces act upon one object. The concept of net force is the same as the mathematical concept of vector addition. When two forces acting on an object are equal in size but act in opposite directions, we say that they are balanced forces. A stationary object stays still. a moving object continues to move at the same speed and in the same direction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




