
In the figure shown, after the switch $'S'$ is turned from the position $'A'$ to position $'B'$ , the energy dissipated in the circuit in terms of capacitance $'C'$ and total charge $'Q'$ is:
(A) $\dfrac{3}{8}\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{C}$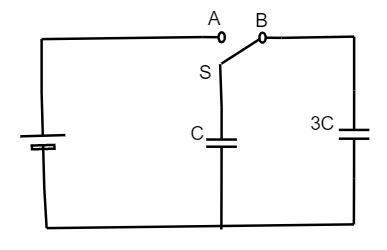
(B) $\dfrac{3}{4}\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{C}$
(C) $\dfrac{1}{8}\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{C}$
(D) $\dfrac{5}{8}\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{C}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Use the formula of the energy stored in the capacitor and find its answer. Use the formula of the energy liberated and substitute the value of the equivalent capacitance to find its answer. Subtract both the answer to find the value of the energy dissipated to the surrounding.
Formula used:
(1) The formula of the energy stored in the capacitor is given by
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$
Where $U$ is the energy stored in the capacitor, $C$ is the capacitance and $V$ is the voltage of the capacitor.
(2) The energy dissipated in the circuit is given by
$V = \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{{2{C_{eq}}}}$
Where $V$ is the energy dissipated to the surrounding and ${C_{eq}}$ is the equivalent capacitance of the circuit.
Complete step by step solution:
From the given circuit diagram, the capacitance of the $C$ and $3C$ are connected parallel to each other. $A$ and $B$ are two switch connections.
Using the formula of the energy stored we get
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$ ……………………….(1)
Substitute that $C = \dfrac{Q}{V}$ in the above step, we get
$U = \dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{{2C}}$ ……………………..(2)
Using the formula of the energy dissipated to the surrounding, we get
$V = \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{{2{C_{eq}}}}$ ……………………….(3)
From the circuit, the equivalent capacitance of the circuit is calculated as follows.
$\Rightarrow {C_{eq}} = 1 + 3 = 4$
Substitute this in the equation (2), we get
$\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{{2 \times 4}} = \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{8}$ …………….(4)
The change in the energy is obtained by subtracting the (4) and (1),
$\Rightarrow \Delta E = \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{2} - \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{8} = \dfrac{{3C{V^2}}}{8}$
Substituting the equation (2) in the above step, we get
$\Rightarrow \Delta E = \dfrac{3}{8}\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{C}$
Thus the option (A) is correct.
Note: The main work of the capacitance is to collect the energy and to store it. But there will be some loss of the energy and its mainly due to the voltage drop across the capacitor. If the voltage drop is high, then the power dissipation in the capacitor will also be high.
Formula used:
(1) The formula of the energy stored in the capacitor is given by
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$
Where $U$ is the energy stored in the capacitor, $C$ is the capacitance and $V$ is the voltage of the capacitor.
(2) The energy dissipated in the circuit is given by
$V = \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{{2{C_{eq}}}}$
Where $V$ is the energy dissipated to the surrounding and ${C_{eq}}$ is the equivalent capacitance of the circuit.
Complete step by step solution:
From the given circuit diagram, the capacitance of the $C$ and $3C$ are connected parallel to each other. $A$ and $B$ are two switch connections.
Using the formula of the energy stored we get
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$ ……………………….(1)
Substitute that $C = \dfrac{Q}{V}$ in the above step, we get
$U = \dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{{2C}}$ ……………………..(2)
Using the formula of the energy dissipated to the surrounding, we get
$V = \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{{2{C_{eq}}}}$ ……………………….(3)
From the circuit, the equivalent capacitance of the circuit is calculated as follows.
$\Rightarrow {C_{eq}} = 1 + 3 = 4$
Substitute this in the equation (2), we get
$\Rightarrow V = \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{{2 \times 4}} = \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{8}$ …………….(4)
The change in the energy is obtained by subtracting the (4) and (1),
$\Rightarrow \Delta E = \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{2} - \dfrac{{C{V^2}}}{8} = \dfrac{{3C{V^2}}}{8}$
Substituting the equation (2) in the above step, we get
$\Rightarrow \Delta E = \dfrac{3}{8}\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{C}$
Thus the option (A) is correct.
Note: The main work of the capacitance is to collect the energy and to store it. But there will be some loss of the energy and its mainly due to the voltage drop across the capacitor. If the voltage drop is high, then the power dissipation in the capacitor will also be high.
Recently Updated Pages
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Step-by-Step Guide to Young’s Double Slit Experiment Derivation

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Electric field due to uniformly charged sphere class 12 physics JEE_Main




