
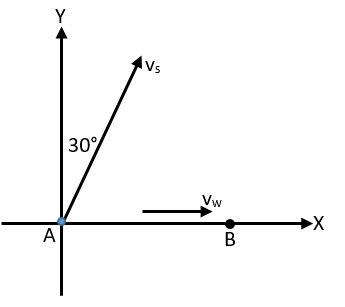
In the figure shown a source of sound of frequency 510 Hz moves with constant velocity \[{v_s} = 20m/s\] in the direction shown. The wind is blowing at a constant velocity of \[{v_w} = 20m/s\] towards an observer who is at rest at point B. The frequency detected by the observer corresponding to the sound emitted by the source at initial position A will be (speed of sound relative to air = 330 m/s)
A. 485 Hz
B. 500 Hz
C. 512 Hz
D. 525 Hz
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: As the source of sound is in motion with respect to the observer so there will be change in the frequency of the sound observed by the observer due to Doppler’s effect. To find the frequency detected by the observer we use the Doppler’s effect.
Formula used:
\[{f_{ap}} = {f_o}\left( {\dfrac{{v \pm {v_o}}}{{v \pm {v_s}}}} \right)\]
where \[{f_{ap}}\] is the apparent frequency heard by the listener moving with speed \[{v_o}\] with respect to the source which is moving with speed \[{v_s}\], \[{f_o}\] is the original frequency and v is the speed of sound in air
Complete step by step solution:
The original frequency of the sound emitted from the source is 510 Hz. It is given that the source is moving with constant velocity \[{v_s} = 20\,m/s\] in the direction making 60° with the line joining the source and the stationary observer. The wind is blowing at a constant velocity of \[{v_w} = 20\,m/s\] towards an observer.
The speed of sound in still air is given as 330 m/s. So, the effective speed of the sound in wind will be the resultant of the velocity of sound and the velocity of wind,
\[v = \left( {330 + 20} \right)\,m/s\]
The component of velocity of the source along the line joining the source and the object is \[{v_s}\sin 30^\circ \].
Using Doppler’s effect, the apparent frequency detected by the observer will be,
\[f' = {f_o}\left[ {\dfrac{{\left( {330 + 20} \right)}}{{\left( {330 + 20} \right) - {v_s}\sin 30^\circ }}} \right] \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow f' = {f_o}\left[ {\dfrac{{\left( {330 + 20} \right)}}{{\left( {330 + 20} \right) - {v_s}\sin 30^\circ }}} \right] \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow f' = \left( {510Hz} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{{\left( {330 + 20} \right)}}{{\left( {330 + 20} \right) - 20 \times \sin 30^\circ }}} \right] \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow f' = \left( {510Hz} \right) \times \left( {\dfrac{{350}}{{340}}} \right) \\ \]
\[\therefore f' = 525\,Hz\]
So, the frequency detected by the observer is 525 Hz.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: The velocity component along the line joining the source and the observer is used for the Doppler’s effect formula. The perpendicular component of the velocity doesn’t have an effect on the change in frequency due to Doppler’s effect.
Formula used:
\[{f_{ap}} = {f_o}\left( {\dfrac{{v \pm {v_o}}}{{v \pm {v_s}}}} \right)\]
where \[{f_{ap}}\] is the apparent frequency heard by the listener moving with speed \[{v_o}\] with respect to the source which is moving with speed \[{v_s}\], \[{f_o}\] is the original frequency and v is the speed of sound in air
Complete step by step solution:
The original frequency of the sound emitted from the source is 510 Hz. It is given that the source is moving with constant velocity \[{v_s} = 20\,m/s\] in the direction making 60° with the line joining the source and the stationary observer. The wind is blowing at a constant velocity of \[{v_w} = 20\,m/s\] towards an observer.
The speed of sound in still air is given as 330 m/s. So, the effective speed of the sound in wind will be the resultant of the velocity of sound and the velocity of wind,
\[v = \left( {330 + 20} \right)\,m/s\]
The component of velocity of the source along the line joining the source and the object is \[{v_s}\sin 30^\circ \].
Using Doppler’s effect, the apparent frequency detected by the observer will be,
\[f' = {f_o}\left[ {\dfrac{{\left( {330 + 20} \right)}}{{\left( {330 + 20} \right) - {v_s}\sin 30^\circ }}} \right] \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow f' = {f_o}\left[ {\dfrac{{\left( {330 + 20} \right)}}{{\left( {330 + 20} \right) - {v_s}\sin 30^\circ }}} \right] \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow f' = \left( {510Hz} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{{\left( {330 + 20} \right)}}{{\left( {330 + 20} \right) - 20 \times \sin 30^\circ }}} \right] \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow f' = \left( {510Hz} \right) \times \left( {\dfrac{{350}}{{340}}} \right) \\ \]
\[\therefore f' = 525\,Hz\]
So, the frequency detected by the observer is 525 Hz.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: The velocity component along the line joining the source and the observer is used for the Doppler’s effect formula. The perpendicular component of the velocity doesn’t have an effect on the change in frequency due to Doppler’s effect.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




