
In order to convert aniline to chlorobenzene, the reagent(s) need is/are:
(A) ${\text{CuCl}}$
(B) ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl and C}}{{\text{u}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$
(C) ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/CC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}$
(D) ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/AlC}}{{\text{l}}_3}$
Answer
243.3k+ views
Hint: Initial process of this reaction is an in situ process which means a reagent has to be prepared inside the reaction mixture. This reaction takes place in two steps. This reaction is called the Sandmeyer reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
Aniline: Aniline is an organic compound which belongs to the group of amino benzene. Amino benzene is also called phenylamine. They are aromatic in nature. Aniline has the molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] where amine group is attached to the benzene ring.
Structure of aniline is:-
Aniline is freely soluble in chemicals such as alcohol and ether. It is slightly soluble in water. It is weakly basic in nature.
Chlorobenzene: Chlorobenzene is a haloarene. Chlorobenzene has the molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}$. Chlorobenzene is formed by chlorination of benzene in the presence of catalysts such as ferric chloride, sulphur chloride and anhydrous aluminium chloride. Chlorobenzene is soluble in water and it is volatile in nature.
The conversion of aniline to chlorobenzene takes place as follows:
a) Aniline is initially reacted with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at low temperature i.e $0 - 4^\circ C$. This gives diazonium ion or a diazonium salt. The nitrous acid is prepared in situ. After protonation, it loses one molecule of water thus providing nitronium ions. This ion acts as an electrophile in reaction with the aniline, thus forming diazonium salt.
b) The diazonium salt with some hydrochloric acid is further treated with copper chloride which finally gives Chlorobenzene.
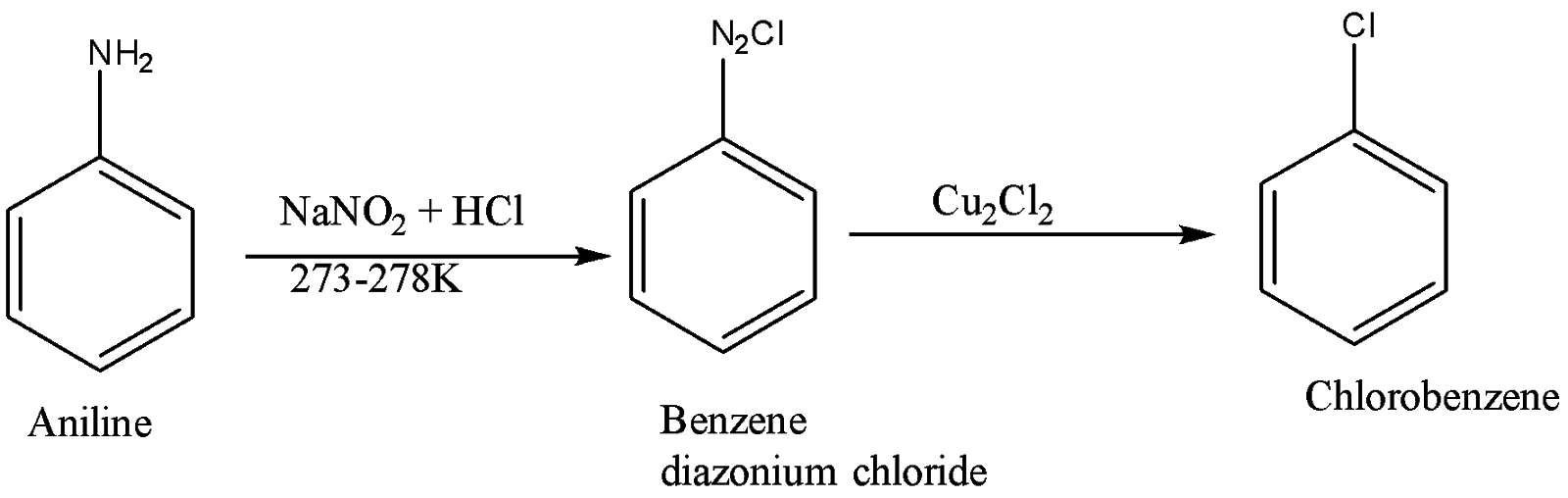
The second step in the reaction that is the conversion of Benzene diazonium chloride to chlorobenzene is known as the Sandmeyer reaction. In this particular reaction, aryl diazonium halides are converted to aryl halides. Here copper salts are used as reagents. Its reactant undergoes radical nucleophilic aromatic substitution. The substitution of the diazo group with the halogen is initiated by the one-electron transfer mechanism. There are some more transformations taking place such as cyanation, trifluoromethylation and hydroxylation.
So the correct option is (B).
Note: In the Sandmeyer reaction the solvent used for the preparation of aryl iodides is diiodomethane and for aryl bromides the solvent used is bromoform. The preparation of fluorobenzene is not obtained by the use of copper fluoride.
Complete step by step solution:
Aniline: Aniline is an organic compound which belongs to the group of amino benzene. Amino benzene is also called phenylamine. They are aromatic in nature. Aniline has the molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] where amine group is attached to the benzene ring.
Structure of aniline is:-

Aniline is freely soluble in chemicals such as alcohol and ether. It is slightly soluble in water. It is weakly basic in nature.
Chlorobenzene: Chlorobenzene is a haloarene. Chlorobenzene has the molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}$. Chlorobenzene is formed by chlorination of benzene in the presence of catalysts such as ferric chloride, sulphur chloride and anhydrous aluminium chloride. Chlorobenzene is soluble in water and it is volatile in nature.
The conversion of aniline to chlorobenzene takes place as follows:
a) Aniline is initially reacted with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at low temperature i.e $0 - 4^\circ C$. This gives diazonium ion or a diazonium salt. The nitrous acid is prepared in situ. After protonation, it loses one molecule of water thus providing nitronium ions. This ion acts as an electrophile in reaction with the aniline, thus forming diazonium salt.
b) The diazonium salt with some hydrochloric acid is further treated with copper chloride which finally gives Chlorobenzene.

The second step in the reaction that is the conversion of Benzene diazonium chloride to chlorobenzene is known as the Sandmeyer reaction. In this particular reaction, aryl diazonium halides are converted to aryl halides. Here copper salts are used as reagents. Its reactant undergoes radical nucleophilic aromatic substitution. The substitution of the diazo group with the halogen is initiated by the one-electron transfer mechanism. There are some more transformations taking place such as cyanation, trifluoromethylation and hydroxylation.
So the correct option is (B).
Note: In the Sandmeyer reaction the solvent used for the preparation of aryl iodides is diiodomethane and for aryl bromides the solvent used is bromoform. The preparation of fluorobenzene is not obtained by the use of copper fluoride.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




