
In HONO
No. of free lone pairs on one $O$ atom in the above-given compound are:
Answer
242.7k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you need to draw the Lewis dot structure of HONO. The Lewis dot structure follows the octet rule and it will provide you with a picture of bonding in the molecule and also the unshared pairs of electrons in the molecule which are called lone pairs.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us draw the Lewis dot structure of a HONO molecule step by step.
Step 1: Count the total number of valence electrons of the hydrogen atom, nitrogen atom and the oxygen atoms. The valence shell configuration and hence valence electrons of these atoms are:
$H(1{s^1})$= 1 electron
$N(2{s^2}2{p^3})$ = 5 electrons
$O(2{s^2}2{p^4})$ = $2 \times 6 = 12$ electrons (since, 2 oxygen atoms are there in HONO molecule)
Therefore, total valence electrons in HONO molecules = $1 + 5 + 12 = 18$ electrons.
Step 2: The skeletal structure of HONO is written as:
For skeletal structure, the central atom would be the one which shows maximum valency or has the ability to have greater valence. Thus, nitrogen would be the central atom because it can show maximum valence 5 which is greater than maximum valence 2 of oxygen and 1 of hydrogen. Therefore, the skeletal structure is: ${\text{H O N O}}$
Step 3: Draw a single bond (one shared electron pair) between H and O, O and N, N and O. Complete the octet on each atom. The remaining unshared valence electrons constitute the lone pairs. There will be double bond nitrogen and one oxygen atom to minimize lone pairs. Thus, the structure of HONO is:
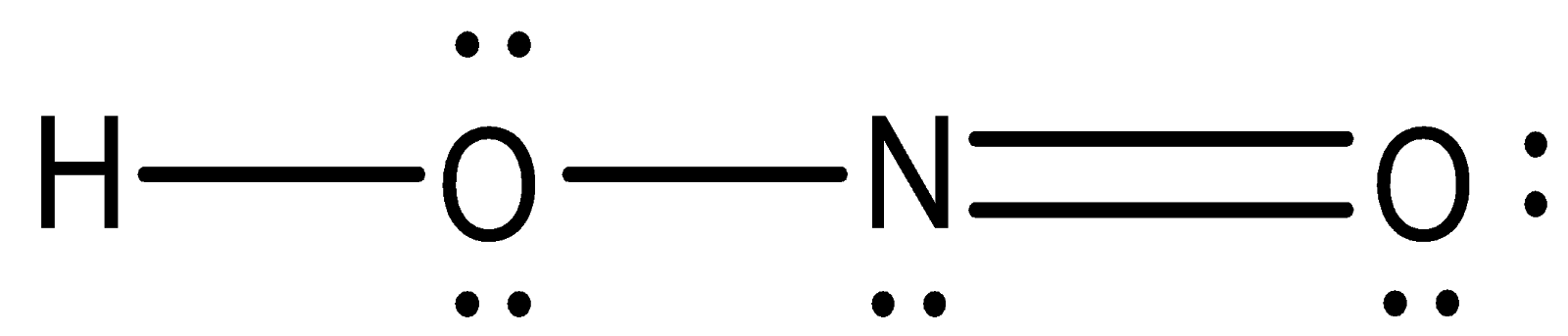
Hence, it is quite clear from the above structure of the HONO molecule that, on one oxygen atom, there are 2 free lone pairs.
Thus, the required answer is 2.
Note: It should be noted that after accounting the shared pairs of electron pairs for all the single bonds in a molecule, the remaining electron pairs are either utilized for multiple bonding or remain as the free lone pairs. The basic requirement is that each bonded atom in a molecule gets an octet of electrons.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us draw the Lewis dot structure of a HONO molecule step by step.
Step 1: Count the total number of valence electrons of the hydrogen atom, nitrogen atom and the oxygen atoms. The valence shell configuration and hence valence electrons of these atoms are:
$H(1{s^1})$= 1 electron
$N(2{s^2}2{p^3})$ = 5 electrons
$O(2{s^2}2{p^4})$ = $2 \times 6 = 12$ electrons (since, 2 oxygen atoms are there in HONO molecule)
Therefore, total valence electrons in HONO molecules = $1 + 5 + 12 = 18$ electrons.
Step 2: The skeletal structure of HONO is written as:
For skeletal structure, the central atom would be the one which shows maximum valency or has the ability to have greater valence. Thus, nitrogen would be the central atom because it can show maximum valence 5 which is greater than maximum valence 2 of oxygen and 1 of hydrogen. Therefore, the skeletal structure is: ${\text{H O N O}}$
Step 3: Draw a single bond (one shared electron pair) between H and O, O and N, N and O. Complete the octet on each atom. The remaining unshared valence electrons constitute the lone pairs. There will be double bond nitrogen and one oxygen atom to minimize lone pairs. Thus, the structure of HONO is:
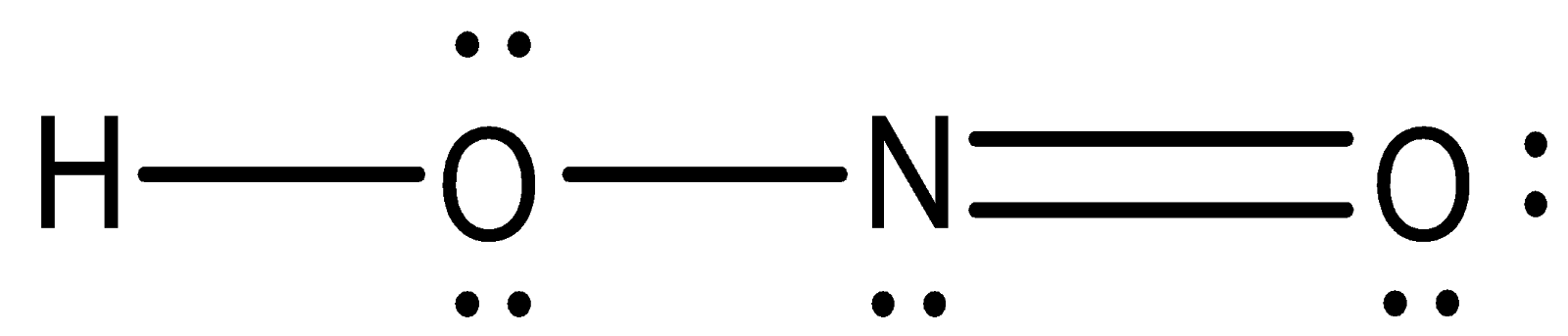
Hence, it is quite clear from the above structure of the HONO molecule that, on one oxygen atom, there are 2 free lone pairs.
Thus, the required answer is 2.
Note: It should be noted that after accounting the shared pairs of electron pairs for all the single bonds in a molecule, the remaining electron pairs are either utilized for multiple bonding or remain as the free lone pairs. The basic requirement is that each bonded atom in a molecule gets an octet of electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




