
In an experiment to measure the speed of sound by a resonating air column, a tuning fork of frequency 500Hz is used. The length of the air column is varied by changing the water level in the resonance tube. Two successive resonances are heard at the air column with lengths 50.7 cm and 83.9 cm. Which of the following statements are true?
(This question has multiple answers)
Option A: the speed of sound determined from this experiment is $332m{s^{ - 1}}$
Option B: the end correction in this experiment is$0.9cm$.
Option C: wavelength of the sound is 66.4 cm.
Option D: the resonance at 50.7 cm corresponds to the fundamental harmonic.
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: When two longitudinal waves of same frequency travel through a medium in the opposite directions standing waves are produced.
Complete solution:
In an organ pipe column the sound behaves as a standing wave. The waves resonate harmonically.
There are two types of organ pipes;
Closed organ pipe: One end of the pipe is closed.
Open organ pipe: Both the ends are open.
In an air column filled with water, the conditions are the same as a closed organ pipe.
Hence, we can treat the situation as a closed organ pipe.
Now for standing waves in closed pipe the condition is given by;
$l = (2n + 1)\dfrac{\lambda }{4}$ (equation: 1)
Here l=length of air column, n= 0, 1, 2… $\lambda $=wavelength of the wave.
The diagram below will help you understand the situation
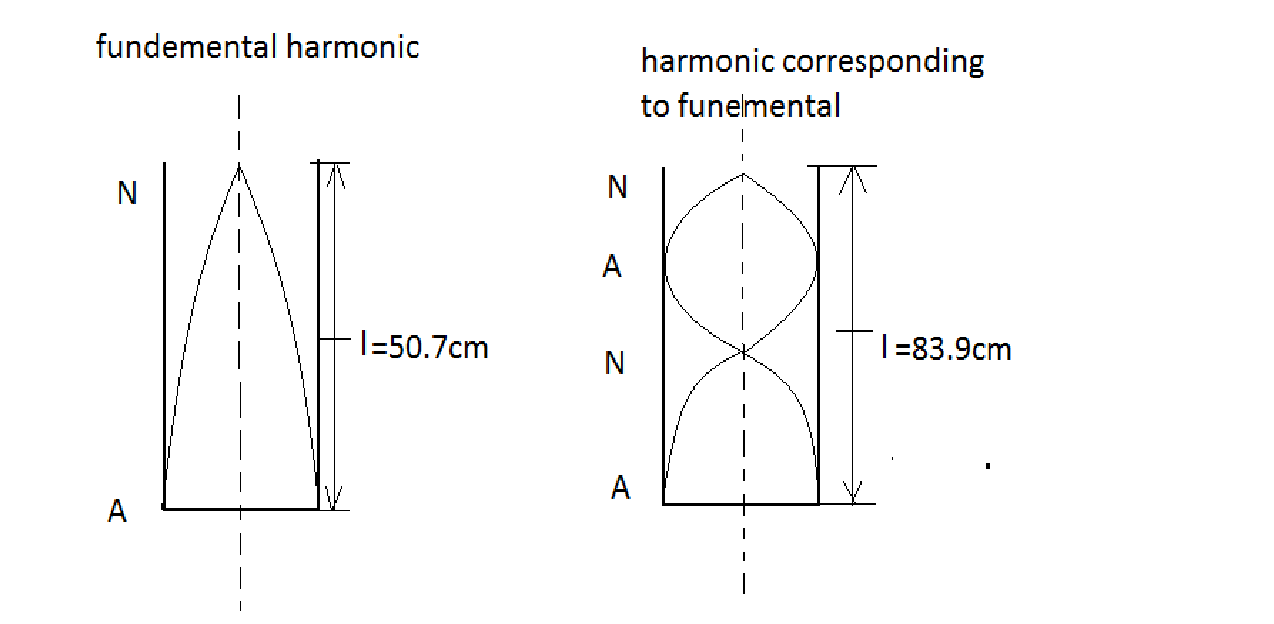
Now the above figure is just an example but not the actual case, as we do not know the number of harmonics.
Now, let us assume that the two successive harmonics at 50.7 and 83.9 cms be ${n_1}$ and ${n_2}$ respectively.
As the difference in length of two successive resonating air columns is half the wavelength of the wave,
$83.9 - 50.7 = \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
Thus,$\lambda = 2 \times 33.2 = 66.4$
Hence, wavelength of sound is 66.4cm
Now as $\dfrac{\lambda }{4} = 16.6cm$, 50.7 is not the fundamental harmonic.
Also, as $\dfrac{{3\lambda }}{4} = 49.8 = e + 50.7cm$ (here, e is the end correction)
50.7 is the third harmonic and so 83.9 will be the fifth harmonic.
Now, $e = 49.8 - 50.7 = - 0.9cm$.
Hence the end correction is 0.9cm.
Now for the speed of sound $v = \lambda \upsilon $ ($\lambda $is the wavelength, $\upsilon $ is the frequency)
$v = 66.4 \times 500 = 33200cm{s^{ - 1}} = 332m{s^{ - 1}}$
Thus option A, option B and option C are correct.
Note:
(1) In the case of air columns, always consider some end correction.
(2) For organ pipe end correction may not be considered.
Complete solution:
In an organ pipe column the sound behaves as a standing wave. The waves resonate harmonically.
There are two types of organ pipes;
Closed organ pipe: One end of the pipe is closed.
Open organ pipe: Both the ends are open.
In an air column filled with water, the conditions are the same as a closed organ pipe.
Hence, we can treat the situation as a closed organ pipe.
Now for standing waves in closed pipe the condition is given by;
$l = (2n + 1)\dfrac{\lambda }{4}$ (equation: 1)
Here l=length of air column, n= 0, 1, 2… $\lambda $=wavelength of the wave.
The diagram below will help you understand the situation

Now the above figure is just an example but not the actual case, as we do not know the number of harmonics.
Now, let us assume that the two successive harmonics at 50.7 and 83.9 cms be ${n_1}$ and ${n_2}$ respectively.
As the difference in length of two successive resonating air columns is half the wavelength of the wave,
$83.9 - 50.7 = \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
Thus,$\lambda = 2 \times 33.2 = 66.4$
Hence, wavelength of sound is 66.4cm
Now as $\dfrac{\lambda }{4} = 16.6cm$, 50.7 is not the fundamental harmonic.
Also, as $\dfrac{{3\lambda }}{4} = 49.8 = e + 50.7cm$ (here, e is the end correction)
50.7 is the third harmonic and so 83.9 will be the fifth harmonic.
Now, $e = 49.8 - 50.7 = - 0.9cm$.
Hence the end correction is 0.9cm.
Now for the speed of sound $v = \lambda \upsilon $ ($\lambda $is the wavelength, $\upsilon $ is the frequency)
$v = 66.4 \times 500 = 33200cm{s^{ - 1}} = 332m{s^{ - 1}}$
Thus option A, option B and option C are correct.
Note:
(1) In the case of air columns, always consider some end correction.
(2) For organ pipe end correction may not be considered.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




