
If Young’s double-slit experiment is performed underwater, how would the observed interference pattern be affected?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:Young’s double-slit experiment demonstrates that light exhibits the classical nature of both waves and particles. It requires the placement of two coherent sources of light that are placed a few distances apart.
Complete step by step solution:
Young’s double-slit experiment was introduced by an English physicist named Thomas Young. It demonstrates that light can exhibit both wave and particle nature when placed in two coherent sources of light that are a few distances apart. It shows that the wave and the particle nature of light are inseparable from each other and will exist simultaneously. Thomas Young placed a screen that had two-slit cuts in front of monochromatic light and shined the light through those slits.
If light only acted as a particle then, only the rays that were at the same position would pass through and the pattern visible on the screen would be in the form of two exact lines. Diagrammatically,
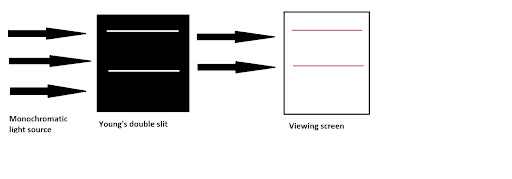
If light acted only as a wave, then, rays of light will diffract when they will pass through the screen. Diagrammatically,
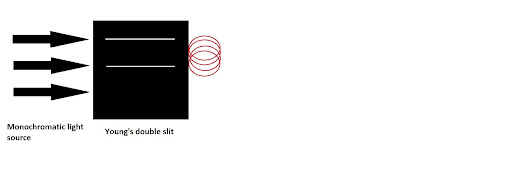
If the diffracted rays of light met from crest to crest, then there will be constructive interference that will result in a bright screen. If rays meet from crest to trough, then there will be destructive interference which will result in the occurrence of dark spots on the viewing screen. So, the pattern on the viewing screen will resemble the following which proves that light acts as a wave because of its diffracting nature.
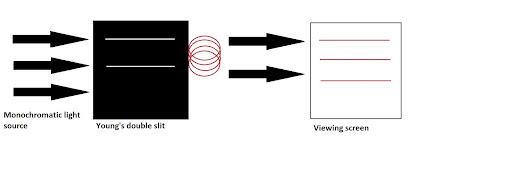
Important equations for Young’s double-slit experiment are as follows:
For constructive interference,
\[d\sin \theta = m\lambda \]
Where m is an integer which is known as spectral order.
For destructive interference,
\[d\sin \theta = (m + \dfrac{1}{2})\lambda \]
When \[m = 0\], \[\theta \] will also be equal to 0 for any value of \[\lambda \]. When \[m\] is equal to any other value, the maxima for different \[\lambda \] will occur at different \[\theta \].
Since the wavelength of light is smaller in water as compared to air, therefore, \[d\sin \theta = m\lambda \] indicates that the \[\theta \] will be decreased as well for \[m\]and \[d\]. Therefore, the pattern of the fringes will appear closer to each other on the viewing screen when the experiment is performed underwater. That means the wavelength of light would decrease since the position of light and dark fringes is directly proportional to the wavelength of light.
Note: Thomas young earlier used sunlight instead of monochromatic light for this experiment. But the results obtained were not proper since, in sunlight, each wavelength forms its own patterns and so the experiment was later performed with a monochromatic light source or a coherent light source.
Complete step by step solution:
Young’s double-slit experiment was introduced by an English physicist named Thomas Young. It demonstrates that light can exhibit both wave and particle nature when placed in two coherent sources of light that are a few distances apart. It shows that the wave and the particle nature of light are inseparable from each other and will exist simultaneously. Thomas Young placed a screen that had two-slit cuts in front of monochromatic light and shined the light through those slits.
If light only acted as a particle then, only the rays that were at the same position would pass through and the pattern visible on the screen would be in the form of two exact lines. Diagrammatically,

If light acted only as a wave, then, rays of light will diffract when they will pass through the screen. Diagrammatically,

If the diffracted rays of light met from crest to crest, then there will be constructive interference that will result in a bright screen. If rays meet from crest to trough, then there will be destructive interference which will result in the occurrence of dark spots on the viewing screen. So, the pattern on the viewing screen will resemble the following which proves that light acts as a wave because of its diffracting nature.

Important equations for Young’s double-slit experiment are as follows:
For constructive interference,
\[d\sin \theta = m\lambda \]
Where m is an integer which is known as spectral order.
For destructive interference,
\[d\sin \theta = (m + \dfrac{1}{2})\lambda \]
When \[m = 0\], \[\theta \] will also be equal to 0 for any value of \[\lambda \]. When \[m\] is equal to any other value, the maxima for different \[\lambda \] will occur at different \[\theta \].
Since the wavelength of light is smaller in water as compared to air, therefore, \[d\sin \theta = m\lambda \] indicates that the \[\theta \] will be decreased as well for \[m\]and \[d\]. Therefore, the pattern of the fringes will appear closer to each other on the viewing screen when the experiment is performed underwater. That means the wavelength of light would decrease since the position of light and dark fringes is directly proportional to the wavelength of light.
Note: Thomas young earlier used sunlight instead of monochromatic light for this experiment. But the results obtained were not proper since, in sunlight, each wavelength forms its own patterns and so the experiment was later performed with a monochromatic light source or a coherent light source.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




