
If the object lies beyond the center of curvature C, then the image formed between C and F in front of a concave mirror is:
A) Real and inverted
B) Virtual and inverted
C) Large in size
D) None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Rays emerging from a point meet at another point after reflection, and that point is called the image of the first point. The image is real if the rays converge to the point and it is virtual if the rays do not meet it but appear to diverge from a point when the rays are produced backward. During image formation we assume that the rays are paraxial, i.e., they are incident at points close to the pole P of the mirror and make small angles with the principal axis.
Complete solution:
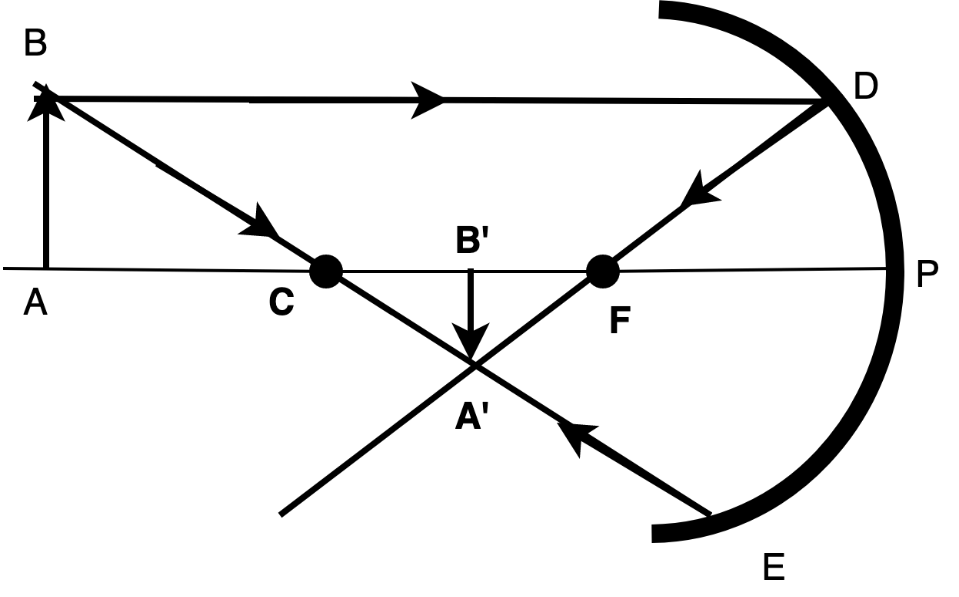
Now consider the following ray diagram. The object AB lies beyond the center of curvature. We consider two different rays emerging from the object. One parallel to the principal axis and the other directed towards the center of curvature of the mirror. The line parallel to the principal axis, after reflection at point D, will go through the focus F. A ray BE passing through the center of curvature will reflect in the same direction and path.
Now you can see clearly that the rays are converging to the point A’. Therefore the formed image will be A’B’. The image formed is real and inverted.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: When the object is kept at infinity the point-size image is formed at the focus of the concave mirror. When the object is kept at the center of curvature the formed image will be inverted and the same size. When the object lies between C and F the formed image will be always beyond the center of curvature.
Complete solution:

Now consider the following ray diagram. The object AB lies beyond the center of curvature. We consider two different rays emerging from the object. One parallel to the principal axis and the other directed towards the center of curvature of the mirror. The line parallel to the principal axis, after reflection at point D, will go through the focus F. A ray BE passing through the center of curvature will reflect in the same direction and path.
Now you can see clearly that the rays are converging to the point A’. Therefore the formed image will be A’B’. The image formed is real and inverted.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: When the object is kept at infinity the point-size image is formed at the focus of the concave mirror. When the object is kept at the center of curvature the formed image will be inverted and the same size. When the object lies between C and F the formed image will be always beyond the center of curvature.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




